* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemical Formulas and Chemical Compounds
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Bremsstrahlung wikipedia , lookup
Rigid rotor wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Host–guest chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Magnetorotational instability wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Ionic compound wikipedia , lookup
Debye–Hückel equation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
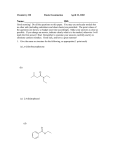
Chemical Formulas and Chemical Compounds A correctly written chemical formula must represent the known facts about the analytically determined composition of the compound Used to represent amounts of substance -H2O can represent: 1 mole of water molecules 1 molecule of water 1 molar mass of water molecules Monatomic Ions: Ions formed from a single atom -Followed by the name “ion” -Cation combined with anion Binary Compounds: Compounds composed of 2 different elements -Drop ending of element name and add “ide” Binary Ionic Compound: Compound composed of a metal and a non-metal 1. Write cation first 2. Subscripts represent number of atoms present a. If no subscript: One is understood b. Charges are not included in chemical 1. Compound is neutral c. Charges can be crossed over to get d. Find number of ions needed to equalize + and – charges Steps 1. Write symbols for ions side by side, positive ion first 2. Cross over charge values to give subscripts 3. Check subscripts and write formula Na + Cl Mg + Br Al + O Li2O formulas subscripts CaCl2 Different names are needed for positive ions of 2 different charges formed by the same metal (dblock) 2 Different naming systems 1. Old: Ion with lower charge - ous Ion with higher charge – ic Ex: Cu+ Cu2+ 2. New: Charge is indicated by Roman numeral (Stock system) Ex: Cu+ Cu+2 Nomenclature: Term that refers to methods of naming chemical compound Compounds Containing Polyatomic Ions -All but ammonium are – charged -Oxyanions: Polyatomic ions that contain O2 -In several cases 2 different oxyanions are formed from the same 2 elements -NO2and NO3(ite: less oxygen) (ate: more oxygen) -Ex: -EX: Sodium Carbonate -Ex: Aluminum Sulfate -Ex: Ammonium sulfate CaSO4 NaNO3 Ba -Ex: Copper (II) nitrate Fe(NO3)2 Cu2SO4 Binary Molecular Compounds -Compounds between nonmetals: Molecular -Old System (Greek prefixes) -Least electronegative element is given 1st -Oxygen and halogens are 2nd -Prefix Rules 1. Used with name of 1st element a. Only if more than one atom of that element is present 2. Second element a. Prefix if more than 1 compound can be formed by the 2 elements b. The root of the name of the second element c. Ending: “ide” (indicates compound containing 2 elements) EX: N2O5 P8Cl7 S3F9 Petacarbon hexachloride Tetranitrogen octaphosphide Trifluoride hexaiodide Acids: Molecular compound that contains one or more H Binary acid: H and a halogen (a more electronegative non-metal) -Occurs in a water solution -Ex: HCl Oxyacid: Acids containing H, O, and a 3rd element -Many polyatomic ions are produced by loss of H ions from oxyacids Ex: Sulfuric acid Phosphoric acid Nitric acid Salt: Ionic compound composed of cation and anion of an acid Ex: CaSO4 Hydrates: Compounds that attract and hold water molecules in their crystal structure Water of Hydration: Water locked in compound, can be removed by heating Anhydrous: Solid residue remaining after water has been removed Formula of hydrated compound: Place raised dot after anhydrous formula followed by the number of water molecules per formula unit of compound Ex: Copper II sulfate pentahydrate (hydrate: water) Sodium carbonate hepta hydrate Oxidation Numbers or oxidation states: Assigned to atoms in molecules, including molecular ions, to show general distribution of electrons among bonded atoms -Ownership is given to the more electronegative atom in bond Rules for assigning oxidation Numbers 1. Uncombined elements: 0 2. Monatomic ion = to charge 3. Fluorine = -1 4. Oxygen = -2 -Except in: Peroxides H2O2: O = -1 Superoxides KO2: O = -1/2 Compounds with Fluorine O = +2 + 5. H = 1 -Except in compounds with metals (NaH) –1 6. The more electronegative element in a binary compound -Oxidation # = to charge of ion 7. Algebraic sum of oxidation #s in neutral compound = 0 8. Algebraic sum of oxidation #s in polyatomic ions = the charge Practice: Assign the oxidation # for the purple element 1. CF4 ____ 2. PCl3 _____ 3. SO2 ______ 4. HNO3 _____ 5. SiO2 _______ 6. KH ________ 7. P2O5 _______ 8. HClO2 _______ 9. PCl3 _______ 10. PCl5 _______ 11. POCl3 _______ 12. SO3 2-_________ Empirical Formula: Simplest ratio of atoms in a compound Ex: B2H6 : Empirical Formula BH3 Steps: 1. Convert each amount to moles 2. Divide each mole amount by the smallest mole amount a. Results in your subscripts b. Must be close to a whole number; if not multiply by 2 3. Percents can be interchanged for grams Ex: If you have 2.128 g Cl and 1.203 g Ca what is the empirical formula? If you have 3.50% Fe and 1.50% O what is the empirical formula? Molecular Formula: Gives the actual # of atoms of each element in a molecular compound (empirical formula)X = molecular formula -X is the integral factor -Multiply subscripts in empirical formula by the integral factor X = Molecular formula mass/empirical formula mass Ex: If the molecular formula mass is 283.889g and the empirical formula is P2O5 what is the molecular formula?