doc BIOL200 quiz 4 afternoon
... Question options: The only way to detect the presence of a plasmid in bacteria is to screen by ...
... Question options: The only way to detect the presence of a plasmid in bacteria is to screen by ...
Chapter 18-20 review
... skull with a small dried fragment of the scalp still attached. They extracted a tiny amount of DNA from the scalp tissue. How could they obtain sufficient DNA for an analysis of the ancient human's genes? a. subject the DNA to electrophoresis b. use a nucleic acid probe c. subject the specimen to am ...
... skull with a small dried fragment of the scalp still attached. They extracted a tiny amount of DNA from the scalp tissue. How could they obtain sufficient DNA for an analysis of the ancient human's genes? a. subject the DNA to electrophoresis b. use a nucleic acid probe c. subject the specimen to am ...
genome that an organism carries in its DNA. analysis of chromosomes.
... • XXY (extra copy of an X chromosome) • SYMPTOMS ...
... • XXY (extra copy of an X chromosome) • SYMPTOMS ...
Simon Rasmussen Assistant professor CBS
... Information never goes the other way (except for some virus) ...
... Information never goes the other way (except for some virus) ...
Insects and genetics
... 5. Mendel's law of segregation states that alternative forms of a particular factor (gene) remain discrete during the reproductive process; his second law, the law of independent_ assortment, states that different factors are inherited independently of one another. 6. Who was Thomas Hunt Morgan? Use ...
... 5. Mendel's law of segregation states that alternative forms of a particular factor (gene) remain discrete during the reproductive process; his second law, the law of independent_ assortment, states that different factors are inherited independently of one another. 6. Who was Thomas Hunt Morgan? Use ...
... replication in a similar fashion to what has been observed in prokaryotes. This led to attempts for generalizing the replicon model to eukaryotes. Several key factors involved in replication and conserved from yeast to man have been described to date. However, as yet, it is not understood how are de ...
Genes have fixed positions on chromosomes.
... function, and produce a white kernel. When the element moves, the pigment gene function is restored, producing a reddish splotch of color on the skin of the kernel. ...
... function, and produce a white kernel. When the element moves, the pigment gene function is restored, producing a reddish splotch of color on the skin of the kernel. ...
Transposable Elements
... function, and produce a white kernel. When the element moves, the pigment gene function is restored, producing a reddish splotch of color on the skin of the kernel. ...
... function, and produce a white kernel. When the element moves, the pigment gene function is restored, producing a reddish splotch of color on the skin of the kernel. ...
Genomics and Forensics - MCCC Faculty & Staff Web Pages
... Use the 1% to 0.1% that is different in DNA identification methods This small percentage leads to a unique DNA fingerprint; also called DNA typing or profiling ...
... Use the 1% to 0.1% that is different in DNA identification methods This small percentage leads to a unique DNA fingerprint; also called DNA typing or profiling ...
Advances in Genetics - Madison County Schools
... Ex. Crossing 2 turkeys that are both plump and grow quickly- offspring are likely to have both those desirable qualities Inbred organisms have alleles that are very similar to parents Inbred organisms are genetically very similar so they may inherit alleles that lead to genetic ...
... Ex. Crossing 2 turkeys that are both plump and grow quickly- offspring are likely to have both those desirable qualities Inbred organisms have alleles that are very similar to parents Inbred organisms are genetically very similar so they may inherit alleles that lead to genetic ...
Timeline
... DNA is made in a test tube for the first time. Messenger RNA is discovered. USDA registers the first biopesticide: Bacillus thuringiensis, or Bt. Green fluorescent protein (GFP) is isolated by Osamu Shimomura. New wheat varieties developed by American agricultural scientist, Norman Borlaug, increase ...
... DNA is made in a test tube for the first time. Messenger RNA is discovered. USDA registers the first biopesticide: Bacillus thuringiensis, or Bt. Green fluorescent protein (GFP) is isolated by Osamu Shimomura. New wheat varieties developed by American agricultural scientist, Norman Borlaug, increase ...
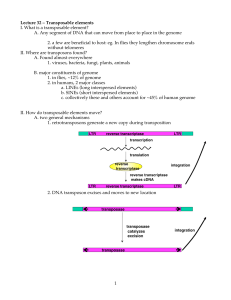
Transposable elements I. What is a transposable element?
... Lecture 32 – Transposable elements I. What is a transposable element? A. Any segment of DNA that can move from place to place in the genome 2. a few are beneficial to host: eg. In flies they lengthen chromosome ends without telomeres II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. vir ...
... Lecture 32 – Transposable elements I. What is a transposable element? A. Any segment of DNA that can move from place to place in the genome 2. a few are beneficial to host: eg. In flies they lengthen chromosome ends without telomeres II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. vir ...
Lab Quiz 4 Key
... Investigator lab (e.g., what does it tell you about your data)? (0.5 pt) {To determine whether or not you got DNA] ...
... Investigator lab (e.g., what does it tell you about your data)? (0.5 pt) {To determine whether or not you got DNA] ...
Genomic library

A genomic library is a collection of the total genomic DNA from a single organism. The DNA is stored in a population of identical vectors, each containing a different insert of DNA. In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested with a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase. Next, the vector DNA can be taken up by a host organism - commonly a population of Escherichia coli or yeast - with each cell containing only one vector molecule. Using a host cell to carry the vector allows for easy amplification and retrieval of specific clones from the library for analysis.There are several kinds of vectors available with various insert capacities. Generally, libraries made from organisms with larger genomes require vectors featuring larger inserts, thereby fewer vector molecules are needed to make the library. Researchers can choose a vector also considering the ideal insert size to find a desired number of clones necessary for full genome coverage.Genomic libraries are commonly used for sequencing applications. They have played an important role in the whole genome sequencing of several organisms, including the human genome and several model organisms.