Manipulating DNA - Lemon Bay High School
... • A Transgenic Tobacco Plant Genetic engineering has changed the way we interact with living things. This transgenic tobacco plant, which glows in the dark, was grown from a tobacco cell transformed with the firefly luciferase gene. The plant illustrates how DNA from one organism contains informat ...
... • A Transgenic Tobacco Plant Genetic engineering has changed the way we interact with living things. This transgenic tobacco plant, which glows in the dark, was grown from a tobacco cell transformed with the firefly luciferase gene. The plant illustrates how DNA from one organism contains informat ...
Sc9 - a 3.1(student notes)
... To be able to fit it all in cells, they are rolled up together in what we call : o Chromosomes. ...
... To be able to fit it all in cells, they are rolled up together in what we call : o Chromosomes. ...
DNA Glossary - FutureLearn
... DNA is located in the chromosomes present in the nucleus of the cell. The DNA of an individual is the same in every one of his or her cells (but is not present in red blood cells because these cells have no nuclei) and different from everyone else’s other than identical twins. The DNA molecule resem ...
... DNA is located in the chromosomes present in the nucleus of the cell. The DNA of an individual is the same in every one of his or her cells (but is not present in red blood cells because these cells have no nuclei) and different from everyone else’s other than identical twins. The DNA molecule resem ...
No Slide Title
... Agrobacterium tumefaciens (soil bacterium) causes crown gall disease in infected plants. ...
... Agrobacterium tumefaciens (soil bacterium) causes crown gall disease in infected plants. ...
Human Genome - BEHS Science
... Genetic Disorders • Some are use of the gene therapy and development of new methods of crime detection are current areas of research. They have to locate where the gene is located and know it’s DNA sequence, The diagnosis may be made before birth. The DNA of people with the disorder is analyzed for ...
... Genetic Disorders • Some are use of the gene therapy and development of new methods of crime detection are current areas of research. They have to locate where the gene is located and know it’s DNA sequence, The diagnosis may be made before birth. The DNA of people with the disorder is analyzed for ...
Seeking an Increasingly Explicit Definition of Heredity
... Cracked genetic code- triplet mRNA codons specify each of the twenty amino acids. ...
... Cracked genetic code- triplet mRNA codons specify each of the twenty amino acids. ...
Genetic Engineering
... • Manipulation of __________________________ of an organism to improve or create specific traits in offspring – e.g., selective breeding, hybridization ...
... • Manipulation of __________________________ of an organism to improve or create specific traits in offspring – e.g., selective breeding, hybridization ...
Mutations & Genetic Engineering
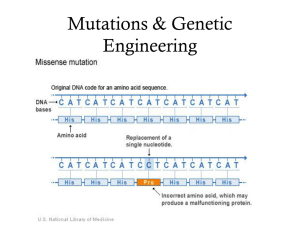
... –Huntington’s disease • Inversion – orientation is in the reverse direction • Translocation – two non homologous chromosomes exchange segments ...
... –Huntington’s disease • Inversion – orientation is in the reverse direction • Translocation – two non homologous chromosomes exchange segments ...
Unit 10 Biotechnology review guide 2014
... called ____________________________________. 13. What is the name used to describe the offspring from a cross between two varieties of plants in an attempt to create a new plant variety with traits from both parents? _______________ 14. The method whereby developing pure lines, breeders preserve des ...
... called ____________________________________. 13. What is the name used to describe the offspring from a cross between two varieties of plants in an attempt to create a new plant variety with traits from both parents? _______________ 14. The method whereby developing pure lines, breeders preserve des ...
genetic modification
... • Stage 2: Prepare a vector for the transferred gene by using plasmids (DNA molecules found in bacteria). Plasmids are cut by the same restriction enzyme which leaves on them the same sticky ends as the ones on the gene. ...
... • Stage 2: Prepare a vector for the transferred gene by using plasmids (DNA molecules found in bacteria). Plasmids are cut by the same restriction enzyme which leaves on them the same sticky ends as the ones on the gene. ...
Zoo/Bot 3333
... Samples of DNA obtained from a fetus (F) and her parents (M and P) were cut by restriction enzyme R, then analyzed by gel electrophoresis followed by the Southern blot technique and hybridization with the radioactively labeled DNA probe designated “CF probe” in the above figure. Enzyme R has a six b ...
... Samples of DNA obtained from a fetus (F) and her parents (M and P) were cut by restriction enzyme R, then analyzed by gel electrophoresis followed by the Southern blot technique and hybridization with the radioactively labeled DNA probe designated “CF probe” in the above figure. Enzyme R has a six b ...
Genetic Engineering
... Positive mutations desirable characteristics; can be increased by ____________, ____________, etc. (ex: seedless oranges) ...
... Positive mutations desirable characteristics; can be increased by ____________, ____________, etc. (ex: seedless oranges) ...
Resource - Chromosome Viewer (www
... Inside every one of our cells (except red blood cells) is a nucleus containing 23 pairs of chromosomes. These chromosomes are built from long strands of a ladder-shaped molecule called deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). The DNA molecule, in turn, is made up of many smaller components. These nucleotides, o ...
... Inside every one of our cells (except red blood cells) is a nucleus containing 23 pairs of chromosomes. These chromosomes are built from long strands of a ladder-shaped molecule called deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). The DNA molecule, in turn, is made up of many smaller components. These nucleotides, o ...
Principles of genetic engineering
... • Genetic engineering, also known as recombinant DNA technology, means altering the genes in a living organism to produce a Genetically Modified Organism (GMO) with a new genotype. • Various kinds of genetic modification are possible: inserting a foreign gene from one species into another, forming a ...
... • Genetic engineering, also known as recombinant DNA technology, means altering the genes in a living organism to produce a Genetically Modified Organism (GMO) with a new genotype. • Various kinds of genetic modification are possible: inserting a foreign gene from one species into another, forming a ...
Genetically Modified Organisms and Food All modern agricultural
... modification, and introduction of DNA into a target organism; when the target organism is a crop plant or domesticated animal used for food, the purpose is usually to impart to the target organism a desired trait that is unknown or very difficult to obtain by traditional methods (those in use befo ...
... modification, and introduction of DNA into a target organism; when the target organism is a crop plant or domesticated animal used for food, the purpose is usually to impart to the target organism a desired trait that is unknown or very difficult to obtain by traditional methods (those in use befo ...
Biotech unit Objectives
... Be able to explain the methods of the cell repairing mutations. Be able to explain the key genes and processes in cancer cell formation. Chapter 20 Key Terms Plasmid Thermocycler Streak plate DNA fingerprinting Blunt ends Gene library Lambda DNA Ti plasmid ...
... Be able to explain the methods of the cell repairing mutations. Be able to explain the key genes and processes in cancer cell formation. Chapter 20 Key Terms Plasmid Thermocycler Streak plate DNA fingerprinting Blunt ends Gene library Lambda DNA Ti plasmid ...
Human Genome Video Guide
... 1. We now know that the graceful human machine is in many ways the product of the ________________ within us. 2. The human genome is basically all of our __________________. 3. We are made up of over 110 ________________ cells. 4. DNA has a hidden structure that makes it ideal for ________________. ...
... 1. We now know that the graceful human machine is in many ways the product of the ________________ within us. 2. The human genome is basically all of our __________________. 3. We are made up of over 110 ________________ cells. 4. DNA has a hidden structure that makes it ideal for ________________. ...
Genomic library

A genomic library is a collection of the total genomic DNA from a single organism. The DNA is stored in a population of identical vectors, each containing a different insert of DNA. In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested with a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase. Next, the vector DNA can be taken up by a host organism - commonly a population of Escherichia coli or yeast - with each cell containing only one vector molecule. Using a host cell to carry the vector allows for easy amplification and retrieval of specific clones from the library for analysis.There are several kinds of vectors available with various insert capacities. Generally, libraries made from organisms with larger genomes require vectors featuring larger inserts, thereby fewer vector molecules are needed to make the library. Researchers can choose a vector also considering the ideal insert size to find a desired number of clones necessary for full genome coverage.Genomic libraries are commonly used for sequencing applications. They have played an important role in the whole genome sequencing of several organisms, including the human genome and several model organisms.