Chapter 20 Notes: DNA Technology
... 1. Main techniques for manipulating DNA 2. How genomes are analyzed & compared at the DNA level 3. Practical applications of DNA technology (including social & ethical issues) ...
... 1. Main techniques for manipulating DNA 2. How genomes are analyzed & compared at the DNA level 3. Practical applications of DNA technology (including social & ethical issues) ...
Genetic Engineering
... a. mechanical vectors = Carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid (____small rings of DNA_____) 3. If host and foreign DNA have been cleaved by the same restriction enzyme, the ends can ___join the ends ____ together. 4. Gene cloning occur ...
... a. mechanical vectors = Carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid (____small rings of DNA_____) 3. If host and foreign DNA have been cleaved by the same restriction enzyme, the ends can ___join the ends ____ together. 4. Gene cloning occur ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... Foreign genes have been introduced into plant cells. Foreign genes transferred to cotton, corn, and potato strains have made these plants resistant to pests. Transgenic Animals Techniques have been developed to insert genes into the eggs of animals. Gene pharming is the use of transgenic farm animal ...
... Foreign genes have been introduced into plant cells. Foreign genes transferred to cotton, corn, and potato strains have made these plants resistant to pests. Transgenic Animals Techniques have been developed to insert genes into the eggs of animals. Gene pharming is the use of transgenic farm animal ...
Who am I?
... What is cloning? Clones are identical copies of living things. Humans have cloned a lot of things already. ...
... What is cloning? Clones are identical copies of living things. Humans have cloned a lot of things already. ...
Genetic Engineering Guied Notes
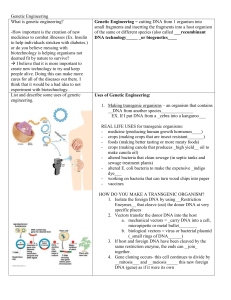
... 1. Isolate the foreign DNA by using __Restriction Enzymes__ that cleave (cut) the donor DNA at very specific places 2. Vectors transfer the donor DNA into the host a. mechanical vectors = _carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet________ b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid ...
... 1. Isolate the foreign DNA by using __Restriction Enzymes__ that cleave (cut) the donor DNA at very specific places 2. Vectors transfer the donor DNA into the host a. mechanical vectors = _carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet________ b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid ...
Genome Sequencing Machine Learning for Big Data Seminar by Guided by
... a gene-altering the protein made by that gene. The disease arises because the protein does not work as it should do. Some genomic conditions also affect coding regions. A translocation, for example, can end up fusing genes together, creating an entirely new protein. More often, genes are lost enti ...
... a gene-altering the protein made by that gene. The disease arises because the protein does not work as it should do. Some genomic conditions also affect coding regions. A translocation, for example, can end up fusing genes together, creating an entirely new protein. More often, genes are lost enti ...
13-2 Manipulating DNA
... 5) Used to locate and identify a particular genes or used to compare individuals. Knowing the sequence of an organism’s DNA allows researchers to study specific genes, to compare them with the genes of other organisms, and to try to discover the functions of different genes and gene combinations. ...
... 5) Used to locate and identify a particular genes or used to compare individuals. Knowing the sequence of an organism’s DNA allows researchers to study specific genes, to compare them with the genes of other organisms, and to try to discover the functions of different genes and gene combinations. ...
Unit 4: Genetics
... 4.4.2 State that gel electrophoresis involves the separation of fragmented pieces of DNA according to their charge and size. • The wells are at the top of the picture. The smallest fragments move the greatest distance from the well, and are found closer to the bottom of the picture. ...
... 4.4.2 State that gel electrophoresis involves the separation of fragmented pieces of DNA according to their charge and size. • The wells are at the top of the picture. The smallest fragments move the greatest distance from the well, and are found closer to the bottom of the picture. ...
Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... 3. What are the stages of the lytic cycle? The lysogenic cycle? 4. What does a retrovirus need to do in order to incorporate into the host cell’s genome? 5. What is a viroid? A prion? What are some examples of prion diseases? 6. Of what is the envelope of a virus composed? 7. How do vaccines work? 8 ...
... 3. What are the stages of the lytic cycle? The lysogenic cycle? 4. What does a retrovirus need to do in order to incorporate into the host cell’s genome? 5. What is a viroid? A prion? What are some examples of prion diseases? 6. Of what is the envelope of a virus composed? 7. How do vaccines work? 8 ...
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Det matematisk
... The written exam gives a maximum score of 100 points. Each of the 20 questions gives 5 points each. Give short answers to all questions! Use drawings or figures to illustrate your answer if you like. Make sure that your copy of this examination paper is complete before answering. ------------------- ...
... The written exam gives a maximum score of 100 points. Each of the 20 questions gives 5 points each. Give short answers to all questions! Use drawings or figures to illustrate your answer if you like. Make sure that your copy of this examination paper is complete before answering. ------------------- ...
GE Nova Video Questions
... Plasmids are present in larger numbers than the chromosomes in cells The size of plasmids make them easier to handle than chromosomal DNA. 3. To cut DNA. 4. (i) cut (ii) enzyme, gene (iii) mixed (iv) transferred ...
... Plasmids are present in larger numbers than the chromosomes in cells The size of plasmids make them easier to handle than chromosomal DNA. 3. To cut DNA. 4. (i) cut (ii) enzyme, gene (iii) mixed (iv) transferred ...
No Slide Title
... •Genes which are close to one another on a chromosome are typically linked together and inherited as a set •The further away two genes lie from one another, the less likely they will be inherited together •Recombination occurs with increasing frequency as the distance between two genes increases •Us ...
... •Genes which are close to one another on a chromosome are typically linked together and inherited as a set •The further away two genes lie from one another, the less likely they will be inherited together •Recombination occurs with increasing frequency as the distance between two genes increases •Us ...
Genetic Technology 13.1 and 13.2 notes
... In the transgenic tobacco plant, the light producing firefly DNA was inserted into bacterial DNA before being placed inside the plant. ...
... In the transgenic tobacco plant, the light producing firefly DNA was inserted into bacterial DNA before being placed inside the plant. ...
Genome Sequencing Using a Mapping Approach
... Shotgun Approach 1. The shotgun approach obtains a genomic sequence by breaking the genome into overlapping fragments for cloning and sequencing. 2. A computer is then used to assemble the genomic sequence. 3. Advances that have made this approach practical for large genomes include: a. Better compu ...
... Shotgun Approach 1. The shotgun approach obtains a genomic sequence by breaking the genome into overlapping fragments for cloning and sequencing. 2. A computer is then used to assemble the genomic sequence. 3. Advances that have made this approach practical for large genomes include: a. Better compu ...
Gen.1303 Genome: The total genetic content contained in a haploid
... A complex of nucleic acids and proteins, primary histones, in the cell nucleus that stains readily with basic dyes and condenses to form chromosomes during cell division. Genetics: The branch of biology that deals with heredity, especially the mechanism of hereditary transmission and the variation o ...
... A complex of nucleic acids and proteins, primary histones, in the cell nucleus that stains readily with basic dyes and condenses to form chromosomes during cell division. Genetics: The branch of biology that deals with heredity, especially the mechanism of hereditary transmission and the variation o ...
Biotechnology Genetic Engineering and Recombinant DNA
... organism based on its genetic make up. understand the general pathway by which ribosomes make proteins. understand how altering an organisms genetic make-up changes the proteins the organism ...
... organism based on its genetic make up. understand the general pathway by which ribosomes make proteins. understand how altering an organisms genetic make-up changes the proteins the organism ...
Biotechnology
... organism based on its genetic make up. understand the general pathway by which ribosomes make proteins. understand how altering an organisms genetic make-up changes the proteins the organism ...
... organism based on its genetic make up. understand the general pathway by which ribosomes make proteins. understand how altering an organisms genetic make-up changes the proteins the organism ...
Term: SPRING 2000 - Washington University in St. Louis
... The newly emergent disciplines of genomics and bioinformatics deal with studying the structure of the genome, including the identification and analysis of gene structure. In addition, genomic sequence information can be used to explore phylogenetic relationships between organisms. The focus of the t ...
... The newly emergent disciplines of genomics and bioinformatics deal with studying the structure of the genome, including the identification and analysis of gene structure. In addition, genomic sequence information can be used to explore phylogenetic relationships between organisms. The focus of the t ...
EXAM 2
... 22. ___T___ For most diploid eukaryotic organisms, sexual reproduction is the only mechanism resulting in new members of a species. 23. ___T___ In C. elegans, the male phenotype is determined by the presence of one X chromosome. 24. ___T___ If a human is monosomic X, the individual will be female. 2 ...
... 22. ___T___ For most diploid eukaryotic organisms, sexual reproduction is the only mechanism resulting in new members of a species. 23. ___T___ In C. elegans, the male phenotype is determined by the presence of one X chromosome. 24. ___T___ If a human is monosomic X, the individual will be female. 2 ...
geneticengineering fall 2012 genetics unit
... engineered foods are worried about the adverse effects that the foods might have on them. Since this is a new technology, there hasn’t been a lot of time to examine the long term effects of these new foods. Some consider it inorganic. ...
... engineered foods are worried about the adverse effects that the foods might have on them. Since this is a new technology, there hasn’t been a lot of time to examine the long term effects of these new foods. Some consider it inorganic. ...
Apple Molecular Biology: Animation 2
... 1. Go to the Apple Genomics website at www.four-h.purdue.edu/apple_genomics 2. Click on the link Apple Molecular Biology. 3. Click on the link Cloning. 4. After reading the introduction click on the third and fourth animation to learn more about cloning. 5. Then complete the review questions on this ...
... 1. Go to the Apple Genomics website at www.four-h.purdue.edu/apple_genomics 2. Click on the link Apple Molecular Biology. 3. Click on the link Cloning. 4. After reading the introduction click on the third and fourth animation to learn more about cloning. 5. Then complete the review questions on this ...
Genomic library

A genomic library is a collection of the total genomic DNA from a single organism. The DNA is stored in a population of identical vectors, each containing a different insert of DNA. In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested with a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase. Next, the vector DNA can be taken up by a host organism - commonly a population of Escherichia coli or yeast - with each cell containing only one vector molecule. Using a host cell to carry the vector allows for easy amplification and retrieval of specific clones from the library for analysis.There are several kinds of vectors available with various insert capacities. Generally, libraries made from organisms with larger genomes require vectors featuring larger inserts, thereby fewer vector molecules are needed to make the library. Researchers can choose a vector also considering the ideal insert size to find a desired number of clones necessary for full genome coverage.Genomic libraries are commonly used for sequencing applications. They have played an important role in the whole genome sequencing of several organisms, including the human genome and several model organisms.