Feb 1
... •Attach probes that detect genes to solid support •cDNA or oligonucleotides •Tiling path = probes for entire genome •Hybridize with labeled targets ...
... •Attach probes that detect genes to solid support •cDNA or oligonucleotides •Tiling path = probes for entire genome •Hybridize with labeled targets ...
Chapters 13-20 "Fill in the Blank"
... Now let’s move on to transcription & translation & how they are regulated. Translation is the conversion of 37._______ ____ _____________ while transcription is the conversion of 38._____________ _____ ________________. Transcription takes place in the 39._______________ when transcription factors b ...
... Now let’s move on to transcription & translation & how they are regulated. Translation is the conversion of 37._______ ____ _____________ while transcription is the conversion of 38._____________ _____ ________________. Transcription takes place in the 39._______________ when transcription factors b ...
DNA Test Review
... 3. If a DNA molecule has the sequence TACGAACCC, what would be the complimentary mRNA sequence? 4. The process by which a DNA molecule is copied is called _____. 5. What is a codon? 6. What are the types of RNA? 7. Messenger RNA is formed in the process of _____. 8. What happens during translation a ...
... 3. If a DNA molecule has the sequence TACGAACCC, what would be the complimentary mRNA sequence? 4. The process by which a DNA molecule is copied is called _____. 5. What is a codon? 6. What are the types of RNA? 7. Messenger RNA is formed in the process of _____. 8. What happens during translation a ...
Eötvös Loránd Science University Faculty of Sciences Department of
... 2. Replication, transcription, translation. DNA repair. 3. Terminology and landmarks in gene technology. Basics of molecular cloning:, vectors, inserts, ligation, amplification, selection. 4. DNA modifying enzymes and their application. Design of recombinant DNA constructs. 5. DNA introduction into ...
... 2. Replication, transcription, translation. DNA repair. 3. Terminology and landmarks in gene technology. Basics of molecular cloning:, vectors, inserts, ligation, amplification, selection. 4. DNA modifying enzymes and their application. Design of recombinant DNA constructs. 5. DNA introduction into ...
II. Transposable Elements in Bacteria Transposable Elements are
... In bacteria, transposable elements can generally be assigned to one of two major types, "Insertion Sequences (IS)" and "Composite Transposons". In practice, composite transposons are typically referred to simply as "transposons". Insertion sequences (IS's) are transposable elements whose only genes ...
... In bacteria, transposable elements can generally be assigned to one of two major types, "Insertion Sequences (IS)" and "Composite Transposons". In practice, composite transposons are typically referred to simply as "transposons". Insertion sequences (IS's) are transposable elements whose only genes ...
GENETIC TRANSFER AND RECOMBINATION (Chapter 8):
... 1. Requires cell to cell contact 2. Conjugation cells must be of opposite mating types (Donor cell carries plasmid) In Gram negative bacteria use a sex pili (projection of donor cell surface that contacts recipient and brings into contact) F factor (fertility factor): F+ cells have F plasmid/F- lack ...
... 1. Requires cell to cell contact 2. Conjugation cells must be of opposite mating types (Donor cell carries plasmid) In Gram negative bacteria use a sex pili (projection of donor cell surface that contacts recipient and brings into contact) F factor (fertility factor): F+ cells have F plasmid/F- lack ...
Prescott`s Microbiology, 9th Edition Chapter 18 – Microbial
... Figure 18.1 What is the function of the 3’-OH during DNA synthesis? This is where the 5’ phosphate of the next nucleotide is covalently attached during elongation. Figure 18.4 Why is it important that the DNA to be sequenced is immobilized in all three of these techniques? With a flow cell, unless t ...
... Figure 18.1 What is the function of the 3’-OH during DNA synthesis? This is where the 5’ phosphate of the next nucleotide is covalently attached during elongation. Figure 18.4 Why is it important that the DNA to be sequenced is immobilized in all three of these techniques? With a flow cell, unless t ...
from genome research to translational medicine
... Impairment of growth and development of the brain or CNS Disorder of brain function that affects emotion, learning ability and memory and that unfolds as the individual grows ...
... Impairment of growth and development of the brain or CNS Disorder of brain function that affects emotion, learning ability and memory and that unfolds as the individual grows ...
Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning
... To be useful, the recombinant molecule must be replicated many times to provide material for analysis, sequencing, etc. Producing many identical copies of the same recombinant molecule is called cloning. Cloning can be done in vitro, by a process called the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Here, how ...
... To be useful, the recombinant molecule must be replicated many times to provide material for analysis, sequencing, etc. Producing many identical copies of the same recombinant molecule is called cloning. Cloning can be done in vitro, by a process called the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Here, how ...
16.1 * Producing DNA Fragments
... then transferring it into microorganisms. • The microorganisms then act as ‘factories’ where the gene product (the desired protein) is continuously manufactured. An example: The production of Insulin ...
... then transferring it into microorganisms. • The microorganisms then act as ‘factories’ where the gene product (the desired protein) is continuously manufactured. An example: The production of Insulin ...
Methods Used in Medical and Population Genetics
... that underlie common diseases because the impact of each DNA variant is often quite small. To bring these subtle disease risk factors to light, scientists conduct “association studies” on a great number of people, to identify variants that are found more often in people with a trait or disease than ...
... that underlie common diseases because the impact of each DNA variant is often quite small. To bring these subtle disease risk factors to light, scientists conduct “association studies” on a great number of people, to identify variants that are found more often in people with a trait or disease than ...
Glossary AV 121017
... One of several alternative forms of a DNA sequence at a specific chromosomal location (locus). At each autosomal chromosomal locus in a cell two alleles are present, one inherited from the mother, the other from the father DeoxyriboNucleic Acid - doublestrand A polymorphic DNA segment at a known chr ...
... One of several alternative forms of a DNA sequence at a specific chromosomal location (locus). At each autosomal chromosomal locus in a cell two alleles are present, one inherited from the mother, the other from the father DeoxyriboNucleic Acid - doublestrand A polymorphic DNA segment at a known chr ...
Chapter 5-3 - Mahtomedi Middle School
... Will other genetic disorders be caused by correcting one genetic disorder? ...
... Will other genetic disorders be caused by correcting one genetic disorder? ...
Course description
... identifying functional regions in genomes and to encourage them to use web-based bioinformatics tools for exploring the databases of genomic and epigenetic data. Students will be expected to develop creative projects that address issues in functional genomics of high interest to them. The objective ...
... identifying functional regions in genomes and to encourage them to use web-based bioinformatics tools for exploring the databases of genomic and epigenetic data. Students will be expected to develop creative projects that address issues in functional genomics of high interest to them. The objective ...
vaccinology 14 - Lectures For UG-5
... 1. the virus is dependent on the co-infection and helper functions of other viruses such as adenovirus and herpesvirus for efficient replication. 2. No human disease has been associated with AAV; instead, it was shown to have beneficial effects for the host as it inhibits the activity of oncogenic v ...
... 1. the virus is dependent on the co-infection and helper functions of other viruses such as adenovirus and herpesvirus for efficient replication. 2. No human disease has been associated with AAV; instead, it was shown to have beneficial effects for the host as it inhibits the activity of oncogenic v ...
Recombinant DNA Libraries
... library made from only that chromosome. Human, for example, have 24 different chromosome libraries (22 autosomes, X and Y). 2. Separating chromosome so they may be individually cloned is accomplished with techniques such as flow cytometry. ...
... library made from only that chromosome. Human, for example, have 24 different chromosome libraries (22 autosomes, X and Y). 2. Separating chromosome so they may be individually cloned is accomplished with techniques such as flow cytometry. ...
DNA sequencing
... variation in which each possible sequence is present in at least 1% of people. For example, a place in the genome where 93 percent of people have a T and the remaining 7 percent have an A is a polymorphism. If one of the possible sequences is present in less than 1 percent of people (99.9 percent of ...
... variation in which each possible sequence is present in at least 1% of people. For example, a place in the genome where 93 percent of people have a T and the remaining 7 percent have an A is a polymorphism. If one of the possible sequences is present in less than 1 percent of people (99.9 percent of ...
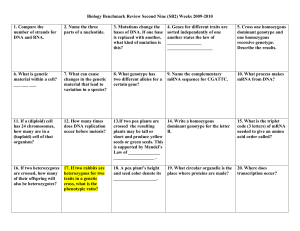
Biology Benchmark Review Second Nine (SB2) Weeks 2009-2010
... 13.If two pea plants are 14. Write a homozygous crossed the resulting dominant genotype for the letter plants may be tall or ...
... 13.If two pea plants are 14. Write a homozygous crossed the resulting dominant genotype for the letter plants may be tall or ...
amino acids
... beginning with codon Start and ending with Stop, longer than implied by the case. Potentially coding sequence. Similar issue: finding of regulatory sequences and other functional motifs. ...
... beginning with codon Start and ending with Stop, longer than implied by the case. Potentially coding sequence. Similar issue: finding of regulatory sequences and other functional motifs. ...
Introduction to your genome
... • If you want to do that, order ASAP, it takes several weeks to get the data back. • Your grade does not depend in any way on whether you analyze your own genome. • You do not need to tell me if you analyze your own genome. • We cannot offer to pay for the test, or provide any counseling ...
... • If you want to do that, order ASAP, it takes several weeks to get the data back. • Your grade does not depend in any way on whether you analyze your own genome. • You do not need to tell me if you analyze your own genome. • We cannot offer to pay for the test, or provide any counseling ...
Genomic library

A genomic library is a collection of the total genomic DNA from a single organism. The DNA is stored in a population of identical vectors, each containing a different insert of DNA. In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested with a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase. Next, the vector DNA can be taken up by a host organism - commonly a population of Escherichia coli or yeast - with each cell containing only one vector molecule. Using a host cell to carry the vector allows for easy amplification and retrieval of specific clones from the library for analysis.There are several kinds of vectors available with various insert capacities. Generally, libraries made from organisms with larger genomes require vectors featuring larger inserts, thereby fewer vector molecules are needed to make the library. Researchers can choose a vector also considering the ideal insert size to find a desired number of clones necessary for full genome coverage.Genomic libraries are commonly used for sequencing applications. They have played an important role in the whole genome sequencing of several organisms, including the human genome and several model organisms.