MCB Lecture 2 – Amino Acids and Proteins
... To form a peptide bond what happens? Hydrolysis – water is removed. What percentage of “likeness” do two polypeptide chains have to have to be considered structurally similar? 25% Orthologs – Same function, different species Paralogs – Same species, related sequence, different function. Size-Exclusi ...
... To form a peptide bond what happens? Hydrolysis – water is removed. What percentage of “likeness” do two polypeptide chains have to have to be considered structurally similar? 25% Orthologs – Same function, different species Paralogs – Same species, related sequence, different function. Size-Exclusi ...
4 Gene expression
... Lysis •Pellet is resuspended in the lysis buffer containing, and sonicated to further liberate the protein • Spin down the denaturing lysis buffer, cell wall and debris will pellet at the bottom and our protein is in the soluble supernatant. • Sonication. • Centrifuge. ...
... Lysis •Pellet is resuspended in the lysis buffer containing, and sonicated to further liberate the protein • Spin down the denaturing lysis buffer, cell wall and debris will pellet at the bottom and our protein is in the soluble supernatant. • Sonication. • Centrifuge. ...
Name: Ch 6 Take Home Quiz Due: 3/22/13 Multiple
... A) a peptide. B) a gene. C) a ribosome. D) an RNA. 8) Which of the following statements is NOT true of non-essential amino acids? A) They are synthesized by the body. B) They are not necessary for protein synthesis. C) There are 11 amino acids that belong to this group. D) They can be broken down to ...
... A) a peptide. B) a gene. C) a ribosome. D) an RNA. 8) Which of the following statements is NOT true of non-essential amino acids? A) They are synthesized by the body. B) They are not necessary for protein synthesis. C) There are 11 amino acids that belong to this group. D) They can be broken down to ...
Chapter 7 Reading Guide
... Use the information in Chapter 7 (p.125-139) as well as the Bozeman podcasts on the Cell Membrane and Transport Across Cell Membranes to complete the reading guide. Concept 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Draw and label a single phospholipid molecule. Explain why thes ...
... Use the information in Chapter 7 (p.125-139) as well as the Bozeman podcasts on the Cell Membrane and Transport Across Cell Membranes to complete the reading guide. Concept 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Draw and label a single phospholipid molecule. Explain why thes ...
Membrane Transport notes
... c. – carbohydrates for cell to cell recognition d. – cholesterols to keep membrane flexible ...
... c. – carbohydrates for cell to cell recognition d. – cholesterols to keep membrane flexible ...
Extend Your Understanding of the Bacterial
... bacterium. Transformation occurs in nature in certain types of bacteria and scientists have exploited and enhanced this property in the laboratory. Transformation allows scientists to move recombinant plasmids containing DNA from two or more species into bacterial cells to produce many copies of the ...
... bacterium. Transformation occurs in nature in certain types of bacteria and scientists have exploited and enhanced this property in the laboratory. Transformation allows scientists to move recombinant plasmids containing DNA from two or more species into bacterial cells to produce many copies of the ...
Protein Reading Questions Due Monday File
... 8. Explain the properties of the amino acid groups below, based on their R-group: a. Nonpolar side chains/Hydrophobic: b. Polar side chains/ Hydrophilic: c. Electrically charged side chains/Hydrophilic: 9. What are the bonds between amino acids in a polypeptide called AND what type of bond is it? ...
... 8. Explain the properties of the amino acid groups below, based on their R-group: a. Nonpolar side chains/Hydrophobic: b. Polar side chains/ Hydrophilic: c. Electrically charged side chains/Hydrophilic: 9. What are the bonds between amino acids in a polypeptide called AND what type of bond is it? ...
Loose Ends on Chapters 3,5,6
... from phosphoenolpyruvate to EII with the help of EI and HPr • The sugar molecule to be transported is phosphorylated as it goes across the membrane by EII • EII is specific for the sugar that it ...
... from phosphoenolpyruvate to EII with the help of EI and HPr • The sugar molecule to be transported is phosphorylated as it goes across the membrane by EII • EII is specific for the sugar that it ...
Check Your Knowledge Set 1(Download)
... 11. The transport method of low density lipoproteins (LDL) across the plasma membrane of human cells is: A) Exocytosis B) Active transport C) Passive transport D) Receptor-mediated endocytosis 12. Which series of terms is in the sequence of biological organization from the simplest to the most comp ...
... 11. The transport method of low density lipoproteins (LDL) across the plasma membrane of human cells is: A) Exocytosis B) Active transport C) Passive transport D) Receptor-mediated endocytosis 12. Which series of terms is in the sequence of biological organization from the simplest to the most comp ...
Protein Synthesis Is a Major Function of Cells
... 1. Transcription is the process of copying the DNA sequence of a gene into a mRNA transcript • Takes place in the nucleus 2. Translation is the process of copying the mRNA transcript into a sequence of amino acids which will eventually become a protein • The mRNA than moves to a ribosome, either at ...
... 1. Transcription is the process of copying the DNA sequence of a gene into a mRNA transcript • Takes place in the nucleus 2. Translation is the process of copying the mRNA transcript into a sequence of amino acids which will eventually become a protein • The mRNA than moves to a ribosome, either at ...
File - Mrs. LeCompte
... o Hydrophobic side chains orient themselves so that they are minimally exposed to water in the protein’s interior ...
... o Hydrophobic side chains orient themselves so that they are minimally exposed to water in the protein’s interior ...
plasmodium protein kinases: from database mining to the search for
... that no malarial PK clustered with the tyrosine kinase (TK) group; and (iv) that no members of the dualspecificity protein kinase (MAPKK) family (a subgroup of the STE group) are present in the P. falciparum genome. In addition, a novel, apparently Plasmodium-specific family of 18 genes encoding pro ...
... that no malarial PK clustered with the tyrosine kinase (TK) group; and (iv) that no members of the dualspecificity protein kinase (MAPKK) family (a subgroup of the STE group) are present in the P. falciparum genome. In addition, a novel, apparently Plasmodium-specific family of 18 genes encoding pro ...
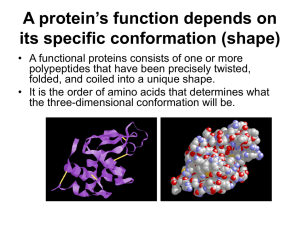
A protein’s function depends on its specific conformation
... • A functional proteins consists of one or more polypeptides that have been precisely twisted, folded, and coiled into a unique shape. • It is the order of amino acids that determines what the three-dimensional conformation will be. ...
... • A functional proteins consists of one or more polypeptides that have been precisely twisted, folded, and coiled into a unique shape. • It is the order of amino acids that determines what the three-dimensional conformation will be. ...
College 5
... bonding between two atoms in which both electrons shared in the bond come from the same atom. Once such a bond has been formed, its strength and description is no different from that of other polar covalent bonds. They may involve metal ions. In such complexes, a molecule "donates" its"free" pairs o ...
... bonding between two atoms in which both electrons shared in the bond come from the same atom. Once such a bond has been formed, its strength and description is no different from that of other polar covalent bonds. They may involve metal ions. In such complexes, a molecule "donates" its"free" pairs o ...
Molecular Mechanisms behind Cholesterol and Sugar Uptake
... Bjørn Panyella Pedersen [email protected], Sciencepark (3132) ...
... Bjørn Panyella Pedersen [email protected], Sciencepark (3132) ...
Chapter 6 Crossword Puzzle
... http://www.cdc.gov/nutrition/everyone/basics/protein.html. Do not close the window until you have answered all of the questions. On the website, click on Protein to answer questions 1 through 3. 1. Complementary proteins, when combined, do not include all of the essential amino acids. a. True b. Fal ...
... http://www.cdc.gov/nutrition/everyone/basics/protein.html. Do not close the window until you have answered all of the questions. On the website, click on Protein to answer questions 1 through 3. 1. Complementary proteins, when combined, do not include all of the essential amino acids. a. True b. Fal ...
Lecture 12/13 - Intracellular Transport + Cytoskeleton
... nuclear proteins get into the nucleus? 3.) Outline as many components of the nucleus as you can—think about nuclear import, export, anatomy of nucleus, nucleic acid synthesis. 4.) What structures serve as a passageway/gate into and out of the nucleus? 5.) What is the name of the amino acid sequence ...
... nuclear proteins get into the nucleus? 3.) Outline as many components of the nucleus as you can—think about nuclear import, export, anatomy of nucleus, nucleic acid synthesis. 4.) What structures serve as a passageway/gate into and out of the nucleus? 5.) What is the name of the amino acid sequence ...