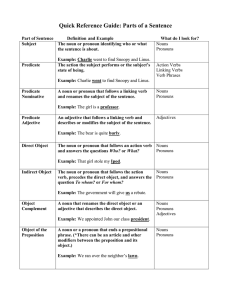
Parts of Speech - Writing Center
... Article, adjective, noun, verb, adverb, conjunction, verb, pronoun ...
... Article, adjective, noun, verb, adverb, conjunction, verb, pronoun ...
16 Mar 09 - Pegasus @ UCF
... few/little? Why can’t I say much persons (In Spanish it’s "muchas personas")? Why do I say many cars but much/a lot of traffic (not many traffics)? singular and plural nouns – Do all languages have plural suffixes (like our -s)? In English, what is the regular plural? Irregular? What about the pronu ...
... few/little? Why can’t I say much persons (In Spanish it’s "muchas personas")? Why do I say many cars but much/a lot of traffic (not many traffics)? singular and plural nouns – Do all languages have plural suffixes (like our -s)? In English, what is the regular plural? Irregular? What about the pronu ...
subject(ed) verb(ing) agreement(s)
... 10) Collective nouns are words that imply more than one person but that are considered singular and take a singular verb, such as: group, team, committee, class, and family. In very few cases, the plural verb is used if the individuals in the group are thought of and specifically referred to: - The ...
... 10) Collective nouns are words that imply more than one person but that are considered singular and take a singular verb, such as: group, team, committee, class, and family. In very few cases, the plural verb is used if the individuals in the group are thought of and specifically referred to: - The ...
Adult Education Dictionary: Grammar
... A predicate nominative follows a linking verb and tells about the subject. Examples: John Smith is the administrative assistant to the director of personnel... ...
... A predicate nominative follows a linking verb and tells about the subject. Examples: John Smith is the administrative assistant to the director of personnel... ...
Christian`s Parts of Speech Notes
... So. . . .Anything you can see, hear, taste, touch (feel) or smell is a NOUN! Can you put “a,” “an” or “the” in front of the word? ...
... So. . . .Anything you can see, hear, taste, touch (feel) or smell is a NOUN! Can you put “a,” “an” or “the” in front of the word? ...
Verb
... The rain began with gusty showers…And at first the dry earth sucked the moisture down and blackened. For two days the earth drank the rain, until the earth was full. Then puddles formed…. ...
... The rain began with gusty showers…And at first the dry earth sucked the moisture down and blackened. For two days the earth drank the rain, until the earth was full. Then puddles formed…. ...
Linking or Action Verb? (Sense words) Definition: Linking verb: A
... Action verb: A verb that shows action. It may or may not have a noun or pronoun following it that receives the action of the verb (direct object). There are some words (sense words) that will be linking or action verbs depending on how they are used in a sentence. Examples: Mary seems to like the ho ...
... Action verb: A verb that shows action. It may or may not have a noun or pronoun following it that receives the action of the verb (direct object). There are some words (sense words) that will be linking or action verbs depending on how they are used in a sentence. Examples: Mary seems to like the ho ...
HELPING VERBS
... What was delivered this afternoon? The children were beginning to fall asleep when the phone rang. I will be finished in about an hour. They have been gone a long time. ...
... What was delivered this afternoon? The children were beginning to fall asleep when the phone rang. I will be finished in about an hour. They have been gone a long time. ...
Old English Grammar, Basically. GENERALIZATIONS Remember
... o When we want to say ‘kings,’ however, we say ‘cyningas.’ o Because Old English uses many different endings to signify these grammatical functions, Old English affords greater variety in word order than ...
... o When we want to say ‘kings,’ however, we say ‘cyningas.’ o Because Old English uses many different endings to signify these grammatical functions, Old English affords greater variety in word order than ...
File
... – Yesterday was a good day. – The teacher reviewed what had been covered yesterday. – When identifying POS, identify adverb words that modify verbs, adjectives and adverbs. ...
... – Yesterday was a good day. – The teacher reviewed what had been covered yesterday. – When identifying POS, identify adverb words that modify verbs, adjectives and adverbs. ...
INFINITIVES vs. GERUNDS
... o Verbs followed by a noun or pronoun + INFINITIVE: Advise, allow, ask, cause, convince, expect, forbid, force, get, invite, need, order, permit, persuade, remind, teach, tell, urge, want, warn, would like Example: I would like you to teach me how to cook tamales. ...
... o Verbs followed by a noun or pronoun + INFINITIVE: Advise, allow, ask, cause, convince, expect, forbid, force, get, invite, need, order, permit, persuade, remind, teach, tell, urge, want, warn, would like Example: I would like you to teach me how to cook tamales. ...
Direct Object & Direct Object Pronouns
... They have different forms depending on how they are being used in a sentence. Modelo: Ana es mi amgia. Replace Ana with ____________. ____________ es muy simpática. ...
... They have different forms depending on how they are being used in a sentence. Modelo: Ana es mi amgia. Replace Ana with ____________. ____________ es muy simpática. ...
Latin II Final Exam Review Vocabulary: The exam will start with a
... tenses applies to subordinate clauses. Verb ID’s: You’ll need to parse any tense of indicative, imperative or subjunctive verb (See forms tables, pages 331-333). Numbers: Ordinals, numerals and cardinals (see page 111) Translation: There will be three short paragraphs here with a few questions on ea ...
... tenses applies to subordinate clauses. Verb ID’s: You’ll need to parse any tense of indicative, imperative or subjunctive verb (See forms tables, pages 331-333). Numbers: Ordinals, numerals and cardinals (see page 111) Translation: There will be three short paragraphs here with a few questions on ea ...
II final guia de estudio 2011
... Past participles as adjectives: (p.144) o Verbs have a form called the past participle, which can be used as an adjective. You can use it to describe a condition or an injury to a part of the body. o When used as adjectives, participles must agree with nouns in number and gender. o Some participles ...
... Past participles as adjectives: (p.144) o Verbs have a form called the past participle, which can be used as an adjective. You can use it to describe a condition or an injury to a part of the body. o When used as adjectives, participles must agree with nouns in number and gender. o Some participles ...
Parts of Speech - Dallas Baptist University
... Example: I always read before I go to bed. Linking verbs link the subject with another word in the sentence. The other word either renames or describes the subject. The most common linking verbs are forms of the verb “be”: be, is, am, are, was, were. Example: Greg is my new friend. Adjectives – a wo ...
... Example: I always read before I go to bed. Linking verbs link the subject with another word in the sentence. The other word either renames or describes the subject. The most common linking verbs are forms of the verb “be”: be, is, am, are, was, were. Example: Greg is my new friend. Adjectives – a wo ...
Sentence Structure - Regent University
... concept doing an action or being described. Every single sentence must have at least one subject. There are three mains types of verbs: active verbs, passive verbs, and linking verbs. ...
... concept doing an action or being described. Every single sentence must have at least one subject. There are three mains types of verbs: active verbs, passive verbs, and linking verbs. ...
Film Strip
... • A action verb tells what the subject does, did, or will do. • What does the dog do? • The dog barks. ...
... • A action verb tells what the subject does, did, or will do. • What does the dog do? • The dog barks. ...
Words
... Each type of word has a different role in a sentence. Look at the following sentence: The young child quickly followed his parents into the room and then he sat down. The nouns are child, parents, room. Nouns are names for things. Child is the subject of the sentence and tells us who carried out the ...
... Each type of word has a different role in a sentence. Look at the following sentence: The young child quickly followed his parents into the room and then he sat down. The nouns are child, parents, room. Nouns are names for things. Child is the subject of the sentence and tells us who carried out the ...
Eight parts of speech
... together and shows the relation between them. "My hand is on the table" shows relation between hand and table. Prepositions are so called because they are generally placed before the words whose connection or relation with other words they point out. Examples of common English Prepositions: above, a ...
... together and shows the relation between them. "My hand is on the table" shows relation between hand and table. Prepositions are so called because they are generally placed before the words whose connection or relation with other words they point out. Examples of common English Prepositions: above, a ...
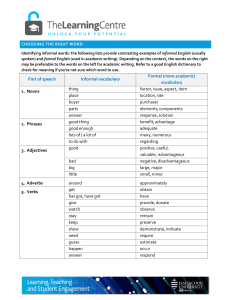
Part of speech Informal vocabulary Formal (more academic
... Identifying informal words: the following lists provide contrasting examples of informal English (usually spoken) and formal English (used in academic writing). Depending on the context, the words on the right may be preferable to the words on the left for academic writing. Refer to a good English d ...
... Identifying informal words: the following lists provide contrasting examples of informal English (usually spoken) and formal English (used in academic writing). Depending on the context, the words on the right may be preferable to the words on the left for academic writing. Refer to a good English d ...
JEOPARDY - Bethesda Elem
... Name the direct object of the sentence: Last year I published a book. ...
... Name the direct object of the sentence: Last year I published a book. ...
Parts of Speech
... backyard. I sprinted as fast as I could and I still lost! (action verbs) I am hungry. (linking verb) I was hoping we could go together. (helping verbs) ...
... backyard. I sprinted as fast as I could and I still lost! (action verbs) I am hungry. (linking verb) I was hoping we could go together. (helping verbs) ...
Verb - starter activity
... If a verb only has one syllable and ends [consonant‐vowel‐consonant], you normally double the final consonant and add ‘ed’. ...
... If a verb only has one syllable and ends [consonant‐vowel‐consonant], you normally double the final consonant and add ‘ed’. ...