English Notes
... *Are words that can be substituted for nouns in naming people, places, and things. *Personal pronouns refer to people or animals: I, you, she, he, it, we, they, me, him, her, us, them *Possessive pronouns are personal pronouns used to show possession: my, mine, your(s), his, her(s), our(s), their(s) ...
... *Are words that can be substituted for nouns in naming people, places, and things. *Personal pronouns refer to people or animals: I, you, she, he, it, we, they, me, him, her, us, them *Possessive pronouns are personal pronouns used to show possession: my, mine, your(s), his, her(s), our(s), their(s) ...
verbs - SCA Moodle
... 3. Be Verbs – am, are, is, was, were, be, being, been – If one of the previously listed be verbs is the main verb in the sentence, the sentence has to have a noun, a pronoun, an adjective, or an adverb of time or place to complete the thought. 4. Helping or Auxiliary Verbs – form verb phrases. A ver ...
... 3. Be Verbs – am, are, is, was, were, be, being, been – If one of the previously listed be verbs is the main verb in the sentence, the sentence has to have a noun, a pronoun, an adjective, or an adverb of time or place to complete the thought. 4. Helping or Auxiliary Verbs – form verb phrases. A ver ...
File
... A: There are some students. (This is a small number but the number is not known.) Or.... Q: Are there any students in the classroom? A: There aren't any students. (This is zero ( nul/geen een), or a very, very small number and the number is not known.) NOTE: Any is only used in question and negative ...
... A: There are some students. (This is a small number but the number is not known.) Or.... Q: Are there any students in the classroom? A: There aren't any students. (This is zero ( nul/geen een), or a very, very small number and the number is not known.) NOTE: Any is only used in question and negative ...
Verbs--Part I File
... Linking verbs—shows a state of being; shows someone or something exists, but they do not show action; links the subject of the sentence to a noun or an adjective. The most common linking verbs are forms of the verb be: is, am, are, was, were, been, being. Example: He is happy. Smell, look, taste ...
... Linking verbs—shows a state of being; shows someone or something exists, but they do not show action; links the subject of the sentence to a noun or an adjective. The most common linking verbs are forms of the verb be: is, am, are, was, were, been, being. Example: He is happy. Smell, look, taste ...
The Eight Parts of Speech
... Takes the place of a person’s name but may also take the place of things. Ex: Monica is a dancer. She has the lead in the school musical. ...
... Takes the place of a person’s name but may also take the place of things. Ex: Monica is a dancer. She has the lead in the school musical. ...
verbs - WordPress.com
... an object buy, bring) and intransitive ( they require no objectstay, fly) Based on their availability to be used in continuous tenses we group them as: action verbs (sing = singing) and state verbs (love, hate but not loving, hating) ...
... an object buy, bring) and intransitive ( they require no objectstay, fly) Based on their availability to be used in continuous tenses we group them as: action verbs (sing = singing) and state verbs (love, hate but not loving, hating) ...
COMMON MISTAKES IN GRAMMAR Faulty Parallelism
... My son ate the last piece of cake. Please call your mother. An intransitive verb does not need a direct object to complete its meaning. Example: The baby laughed. Prepositions A preposition is a word used to connect and relate a noun or pronoun to some other word. Examples: about/as/at/for/from/in/o ...
... My son ate the last piece of cake. Please call your mother. An intransitive verb does not need a direct object to complete its meaning. Example: The baby laughed. Prepositions A preposition is a word used to connect and relate a noun or pronoun to some other word. Examples: about/as/at/for/from/in/o ...
COMMON MISTAKES IN GRAMMAR Faulty Parallelism
... My son ate the last piece of cake. Please call your mother. An intransitive verb does not need a direct object to complete its meaning. Example: The baby laughed. Prepositions A preposition is a word used to connect and relate a noun or pronoun to some other word. Examples: about/as/at/for/from/in/o ...
... My son ate the last piece of cake. Please call your mother. An intransitive verb does not need a direct object to complete its meaning. Example: The baby laughed. Prepositions A preposition is a word used to connect and relate a noun or pronoun to some other word. Examples: about/as/at/for/from/in/o ...
Transforming verbs to nouns
... paper while joining, thus avoiding having to push awkwardly across the page. If the ink or pencil trace disappears, do not tell them they have to produce a joining mark. However, do ensure they are joining just above the paper, rather than printing. Left-handers may also want to produce a sharper, m ...
... paper while joining, thus avoiding having to push awkwardly across the page. If the ink or pencil trace disappears, do not tell them they have to produce a joining mark. However, do ensure they are joining just above the paper, rather than printing. Left-handers may also want to produce a sharper, m ...
Grammar Cards, Ch. 1
... [EXAMPLES: tall, funny, new, loud, scary, many, few, 2, 11th, several] 2. adjectives use virtually the same Latin endings as nouns (“declensions”), with few exceptions 1. an action word [run, swim, laugh] or a word denoting existence or state of being [be] 2. verbs have special endings in Latin, div ...
... [EXAMPLES: tall, funny, new, loud, scary, many, few, 2, 11th, several] 2. adjectives use virtually the same Latin endings as nouns (“declensions”), with few exceptions 1. an action word [run, swim, laugh] or a word denoting existence or state of being [be] 2. verbs have special endings in Latin, div ...
-Ar ending verbs
... In Spanish, there are three classes (or conjugations) of verbs; those that end in –AR, those that end in –ER, and those that end in –IR. This is important because the conjugation determines the endings you put on the verbs. ...
... In Spanish, there are three classes (or conjugations) of verbs; those that end in –AR, those that end in –ER, and those that end in –IR. This is important because the conjugation determines the endings you put on the verbs. ...
Pronoun antecedent - Clarkstown Central School District
... verbs. (There are two parts to these things.) ...
... verbs. (There are two parts to these things.) ...
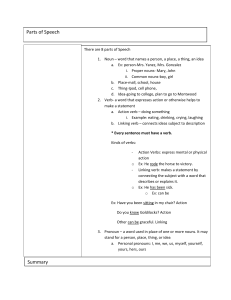
Parts of Speech Summary
... Ex: Have you been sitting in my chair? Action Do you know Goldilocks? Action Other can be graceful. Linking 3. Pronoun – a word used in place of one or more nouns. It may stand for a person, place, thing, or idea a. Personal pronouns: I, me, we, us, myself, yourself, yours, hers, ours ...
... Ex: Have you been sitting in my chair? Action Do you know Goldilocks? Action Other can be graceful. Linking 3. Pronoun – a word used in place of one or more nouns. It may stand for a person, place, thing, or idea a. Personal pronouns: I, me, we, us, myself, yourself, yours, hers, ours ...
The FOUR LEVELS OF ANALYSIS
... • PRONOUNS ARE VAGUE AND TAKE THE PLACE OF A NOUN. THEY ARE LAZY: • HE, US, SHE, IT, WE, THEY, THEM, THAT…. • THEY CAN ONLY BE USED AFTER THE ANTECEDENT IS SET. ...
... • PRONOUNS ARE VAGUE AND TAKE THE PLACE OF A NOUN. THEY ARE LAZY: • HE, US, SHE, IT, WE, THEY, THEM, THAT…. • THEY CAN ONLY BE USED AFTER THE ANTECEDENT IS SET. ...
Subjects – who or what a clause, phrase, or sentence is about
... Prepositional Phrases Made up of a preposition plus its object and any modifiers. Common prepositions – about, above, according to, across, after, against, along, among, around, at , ...
... Prepositional Phrases Made up of a preposition plus its object and any modifiers. Common prepositions – about, above, according to, across, after, against, along, among, around, at , ...
Nouns and Verbs
... matters whether it is a Chihuahua or a Doberman. If a father allows his teenager to drive his car, it matters whether it’s a sleek sedan or a rusty station wagon. To make the image as vivid as possible, be as specific as possible in your choice of nouns. ...
... matters whether it is a Chihuahua or a Doberman. If a father allows his teenager to drive his car, it matters whether it’s a sleek sedan or a rusty station wagon. To make the image as vivid as possible, be as specific as possible in your choice of nouns. ...
Grammar Glossary
... A pronoun is a word that stands in for a noun. There are different classes ofpronoun, the main types are: 1. Personal pronouns refer to people or things, such as ‘I’ or ‘you’. 2. Reflexive pronouns refer to people or things that are also the subject of the sentence and end with ‘-self’ or ‘-selves’. ...
... A pronoun is a word that stands in for a noun. There are different classes ofpronoun, the main types are: 1. Personal pronouns refer to people or things, such as ‘I’ or ‘you’. 2. Reflexive pronouns refer to people or things that are also the subject of the sentence and end with ‘-self’ or ‘-selves’. ...
Chapter 4 - Tony Morris
... Compound nouns in the possessive case are the simplest. An –‘s is added to the end of the compound phrase to create the possessive Joint possessives involve two or more roughly equal nouns in common possession of something else. Possessive ending only for the final noun. But don’t join two possessiv ...
... Compound nouns in the possessive case are the simplest. An –‘s is added to the end of the compound phrase to create the possessive Joint possessives involve two or more roughly equal nouns in common possession of something else. Possessive ending only for the final noun. But don’t join two possessiv ...
Verbs - colonelenglish9
... Precise verb- They tell what and how something is done. Regular verb- Forms its past and past participle by adding –d or –ed. Transitive verb- Verb that expresses an action toward a person, place, or thing. Troublesome Verb- verb that is written in different forms. ...
... Precise verb- They tell what and how something is done. Regular verb- Forms its past and past participle by adding –d or –ed. Transitive verb- Verb that expresses an action toward a person, place, or thing. Troublesome Verb- verb that is written in different forms. ...
Subject
... • Several of the women are pilots. • A few in the crowd were rowdy. • Have both tried harder? ...
... • Several of the women are pilots. • A few in the crowd were rowdy. • Have both tried harder? ...
Subject-verb agreement
... one this either each that neither All pronouns ending in one, body, and thing (everyone, anybody, nothing) • Everyone needs to buy a ticket. • Each of the boys cleans his room. • Neither of the sandwiches is fresh. ...
... one this either each that neither All pronouns ending in one, body, and thing (everyone, anybody, nothing) • Everyone needs to buy a ticket. • Each of the boys cleans his room. • Neither of the sandwiches is fresh. ...
Parts of Speech - Flagstaff High School
... * Others express an action you usually can’t see (abstract) ...
... * Others express an action you usually can’t see (abstract) ...