Subject-Verb Agreement - the UCT Writing Centre
... Noun: A ‘naming’ word that names a person, a place, a thing or an idea. Verb: A ‘doing’ word that expresses an action or otherwise helps to make a statement. This means that a singular noun (e.g. ‘the cat’) takes a singular verb (e.g. ‘sleeps’); and a plural noun (e.g. ‘the cats’) takes a plural ...
... Noun: A ‘naming’ word that names a person, a place, a thing or an idea. Verb: A ‘doing’ word that expresses an action or otherwise helps to make a statement. This means that a singular noun (e.g. ‘the cat’) takes a singular verb (e.g. ‘sleeps’); and a plural noun (e.g. ‘the cats’) takes a plural ...
Year 2 - Crossley Fields
... Noun: A noun is a name of a person, place, animal or thing. Common nouns are the names given to general categories, such as ‘girl’, ‘city’, ‘dog’ and ‘car’. Proper nouns are the specific names of people, places, animals and things, such as ‘Beth’, ‘Edinburgh’, ‘Lassie’ and ‘Mercedes’. Concrete nouns ...
... Noun: A noun is a name of a person, place, animal or thing. Common nouns are the names given to general categories, such as ‘girl’, ‘city’, ‘dog’ and ‘car’. Proper nouns are the specific names of people, places, animals and things, such as ‘Beth’, ‘Edinburgh’, ‘Lassie’ and ‘Mercedes’. Concrete nouns ...
words - I blog di Unica - Università di Cagliari
... Pronouns Pronouns have a subject case, who, a possessive case, whose, and an object case, whom. They generally refer to persons. whom is falling into disuse except in formal written English. In expressions such as ‘TO WHOM IT MAY CONCERN” ; “he didn’t know to whom he had to address the letter (he d ...
... Pronouns Pronouns have a subject case, who, a possessive case, whose, and an object case, whom. They generally refer to persons. whom is falling into disuse except in formal written English. In expressions such as ‘TO WHOM IT MAY CONCERN” ; “he didn’t know to whom he had to address the letter (he d ...
WEEK 14 Monday 12.2
... Read each of the following sentences. Decide whether each sentence contains a verb that expresses action or being. Number 1 – 5 on your paper, and write A next to the number if that sentence contains an action verb. Write B next to the number if it contains a verb that expresses being. 1. Kwame took ...
... Read each of the following sentences. Decide whether each sentence contains a verb that expresses action or being. Number 1 – 5 on your paper, and write A next to the number if that sentence contains an action verb. Write B next to the number if it contains a verb that expresses being. 1. Kwame took ...
PARTS OF SPEECH NOTES Eight Parts of Speech: Noun: Pronoun:
... personal pronoun (refers to a specific person/thing or shows possession) first person: I, me, my, mine, we, us our, ours second person: you, your, yours third person: he, him, his, she, her, hers, it , its, they, them, their, theirs reflexive pronoun (has self/selves in it): myself, yourself, himsel ...
... personal pronoun (refers to a specific person/thing or shows possession) first person: I, me, my, mine, we, us our, ours second person: you, your, yours third person: he, him, his, she, her, hers, it , its, they, them, their, theirs reflexive pronoun (has self/selves in it): myself, yourself, himsel ...
Verbs Verbs are word which describes the action in a sentence (the
... An auxiliary verb (also know as a helping verb) determines the mood or tense of another verb in a phrase: "It will rain tonight." The primary auxiliaries are be, have, and do. The modal auxiliaries includecan, could, may, must, should, will, and would. A lexical verb (also known as a full or main ve ...
... An auxiliary verb (also know as a helping verb) determines the mood or tense of another verb in a phrase: "It will rain tonight." The primary auxiliaries are be, have, and do. The modal auxiliaries includecan, could, may, must, should, will, and would. A lexical verb (also known as a full or main ve ...
Latin Summer Assignment Latin III Mr. Pasquinelli 2016 If you have
... (2) Only third person possessive adjective F. Demonstrative Adjectives 1. Hic, Haec, Hoc a) Memorize Charts b) “This” c) Can also be pronouns 2. Ille, Illa, Illud a) Memorize Charts b) “That” c) Can also be pronouns IV. Verbs A. Definition: A word that indicates action or a state of bei ...
... (2) Only third person possessive adjective F. Demonstrative Adjectives 1. Hic, Haec, Hoc a) Memorize Charts b) “This” c) Can also be pronouns 2. Ille, Illa, Illud a) Memorize Charts b) “That” c) Can also be pronouns IV. Verbs A. Definition: A word that indicates action or a state of bei ...
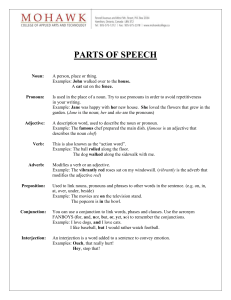
Parts of Speech - Mohawk College
... You can use a conjunction to link words, phases and clauses. Use the acronym FANBOYS (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so) to remember the conjunctions. Example: I love dogs, and I love cats. I like baseball, but I would rather watch football. ...
... You can use a conjunction to link words, phases and clauses. Use the acronym FANBOYS (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so) to remember the conjunctions. Example: I love dogs, and I love cats. I like baseball, but I would rather watch football. ...
Parts of Speech - Mohawk College
... You can use a conjunction to link words, phases and clauses. Use the acronym FANBOYS (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so) to remember the conjunctions. Example: I love dogs, and I love cats. I like baseball, but I would rather watch football. ...
... You can use a conjunction to link words, phases and clauses. Use the acronym FANBOYS (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so) to remember the conjunctions. Example: I love dogs, and I love cats. I like baseball, but I would rather watch football. ...
Verbs - HausauerAmLit
... the block. – They climbed the mountain that winter. – The dangerous storm stopped the trip. ...
... the block. – They climbed the mountain that winter. – The dangerous storm stopped the trip. ...
Unit 2: Verbs, Adverbs, Prepositions, Conjunctions and Interjections
... In what way? or How? To what extent? • Usually adverbs end in –ly, but not always ...
... In what way? or How? To what extent? • Usually adverbs end in –ly, but not always ...
PRONOUN REVIEW
... The copy that I read was from the library The people who live there are on vacation Demonstrative This, that, these, those This is the one I want. This seems to be my lucky day. Indefinite All, another, any, anybody, anyone, both, each, other, either, everybody, everyone, few, many, most, neither, n ...
... The copy that I read was from the library The people who live there are on vacation Demonstrative This, that, these, those This is the one I want. This seems to be my lucky day. Indefinite All, another, any, anybody, anyone, both, each, other, either, everybody, everyone, few, many, most, neither, n ...
Parts of Speech
... Linking verb example: “Jaleesa is adventurous.” Using the linking verb test, “Jaleesa = adventurous”, as a formula, is logical. Therefore, the “is” in this sentence is a linking verb. Helping verb example: “Jaleesa is practicing for her debate.” Here, the “is” does not function the same way. Preposi ...
... Linking verb example: “Jaleesa is adventurous.” Using the linking verb test, “Jaleesa = adventurous”, as a formula, is logical. Therefore, the “is” in this sentence is a linking verb. Helping verb example: “Jaleesa is practicing for her debate.” Here, the “is” does not function the same way. Preposi ...
Subject-Verb Agreement
... the subjects agree with the verbs. A plural verb goes with a plural subject. Below is a list of examples of subject-verb agreement. 1. When the subject of a sentence is composed of two or more nouns or pronouns connected by and, use a plural verb. Example: she and her friends are 2. When two or more ...
... the subjects agree with the verbs. A plural verb goes with a plural subject. Below is a list of examples of subject-verb agreement. 1. When the subject of a sentence is composed of two or more nouns or pronouns connected by and, use a plural verb. Example: she and her friends are 2. When two or more ...
the structure of english - I blog di Unica
... Pronouns Pronouns have a subject case, who, a possessive case, whose, and an object case, whom. They generally refer to persons. whom is falling into disuse except in formal written English. In expressions such as ‘TO WHOM IT MAY CONCERN” ; “he didn’t know to whom he had to address the letter (he d ...
... Pronouns Pronouns have a subject case, who, a possessive case, whose, and an object case, whom. They generally refer to persons. whom is falling into disuse except in formal written English. In expressions such as ‘TO WHOM IT MAY CONCERN” ; “he didn’t know to whom he had to address the letter (he d ...
Exactness and Vividness
... • Learn to look up synonyms for nouns • Make sure the synonym expresses your meaning exactly ...
... • Learn to look up synonyms for nouns • Make sure the synonym expresses your meaning exactly ...
Transitive and Intransitive Verbs
... Transitive and Intransitive Verbs There are three different kinds of verbs in the English language – transitive, intransitive and linking verbs. This handout will focus on both transitive and intransitive verbs. What is a transitive verb? A verb is a word that conveys action to the reader. A transit ...
... Transitive and Intransitive Verbs There are three different kinds of verbs in the English language – transitive, intransitive and linking verbs. This handout will focus on both transitive and intransitive verbs. What is a transitive verb? A verb is a word that conveys action to the reader. A transit ...
Year 2: To be introduced
... specification [for example, the blue butterfly, plain flour, the man in the moon] How the grammatical patterns in a sentence indicate its function as a statement, question, exclamation or command ...
... specification [for example, the blue butterfly, plain flour, the man in the moon] How the grammatical patterns in a sentence indicate its function as a statement, question, exclamation or command ...
Making English Grammar Meaningful and Useful Mini Lesson #1
... only have limited applicability to describing English. Take the word ‘conjugation’ for example. It is a useful word for languages whose verbs have different endings for different persons. Typically, conjugations are used for 6 persons: first singular and plural, second singular and plural, and third ...
... only have limited applicability to describing English. Take the word ‘conjugation’ for example. It is a useful word for languages whose verbs have different endings for different persons. Typically, conjugations are used for 6 persons: first singular and plural, second singular and plural, and third ...
Grammar for Writing
... When using verbs in past time, do not use a helper verb with the past form; however, use a helper verb with the past participle. This rule applies to all verbs, but focus on irregular verbs as their past tense and past participle forms are different from each other. For example: Mary took the le ...
... When using verbs in past time, do not use a helper verb with the past form; however, use a helper verb with the past participle. This rule applies to all verbs, but focus on irregular verbs as their past tense and past participle forms are different from each other. For example: Mary took the le ...
Fundamentals of English Grammar, Fourth Edition
... 5-4 Questions with who, who(m), and what . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119 5-5 Using what ⫹ a form of do . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121 5-6 Using which and what kind of . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123 ...
... 5-4 Questions with who, who(m), and what . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119 5-5 Using what ⫹ a form of do . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121 5-6 Using which and what kind of . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123 ...
Glossary of grammatical terms for parents
... Exclamation mark Indicates an interjection/surprise/strong ...
... Exclamation mark Indicates an interjection/surprise/strong ...