* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Christian`s Parts of Speech Notes
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Morphology (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Untranslatability wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Comparison (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Russian declension wikipedia , lookup
Russian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Contraction (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sotho parts of speech wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
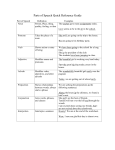
Parts of Speech Notes Noun: Person, place, thing or idea. Anything that affects your five senses is a NOUN! So. . . .Anything you can see, hear, taste, touch (feel) or smell is a NOUN! Can you put “a,” “an” or “the” in front of the word? Verb: They link ideas together, help other verbs OR they show ACTION! To find the verb ask “What is being done?” Look to see what word is hooking things together! Helping verbs/Auxiliary verbs: There are 23! Am, is, are, was, were, being, been, be, have, has, had, do, does, did, can could, shall, should, may, might, must, will, would. Adjective: Describe nouns They answer the questions “What kind?” “Which one?” and “How many?” They can usually fit well into one of these two sentences: o I see a ______________________ house. o She was a ___________________ girl. Adverbs: Words that describe verbs, adjectives and other adverbs. All “ly” words are adverbs They answer the questions “How?” “When” “Where” and “To what extent?” Not or n’t are ALWAYS adverbs! Pronouns: Take the place of nouns They are words like he, she, it, they, them, you, I, those, we, her They may look like nouns because you can touch them, but they don’t NAME a noun, so they are taking the place of a noun. If you can replace the word with a person’s name or a specific thing, it is a pronoun! Conjunctions: Joining words The words and, but, yet, so, or, for, nor are ALWAYS conjunctions. Prepositions: A group of words working together to provide more information about things happening in the sentence They usually fit in this sentence: The cat is __________ the house or The school is ________________ the road. Prepositions get lonely, so they have to work in a phrase. The preposition is always the first word in the phrase. EX: down the road, about a year, without my mom, etc. They sometimes feel like adverbs because they are directional words, but they aren’t because they can’t stand alone when they are used as a preposition. Interjections: Words that interrupt a sentence with an emotional outburst. These are words we say that interrupt our regular speech pattern! Like, “OMG! She was cute!” or “Stop! That drink is poison. Articles: A, An, The are ALWAYS articles! *******************************************************Other information (not a part of speech) How do you find a simple subject? Ask “Who or what is doing something?” How do you find the simple predicate? Ask “What are they doing?”