Quantum Theory
... when interacting with matter Even though it isn’t quite right to do so, you can think of light as a __________________ that travels as a wave A _________ is a massless bundle of light E photon=hv Some metals hold electrons more tightly than others and require ____________________ to move electrons ...
... when interacting with matter Even though it isn’t quite right to do so, you can think of light as a __________________ that travels as a wave A _________ is a massless bundle of light E photon=hv Some metals hold electrons more tightly than others and require ____________________ to move electrons ...
Notes on Quantum Theory
... the metal to escape the metal altogether). The photoelectric effect is the principle underlying the use of photovoltaic cells, i.e. “solar cells”, which absorb sunlight or other visible light and, through the release of electrons, produce electric current which can be used to operate switches, proce ...
... the metal to escape the metal altogether). The photoelectric effect is the principle underlying the use of photovoltaic cells, i.e. “solar cells”, which absorb sunlight or other visible light and, through the release of electrons, produce electric current which can be used to operate switches, proce ...
The electron-volt - Hockerill Students
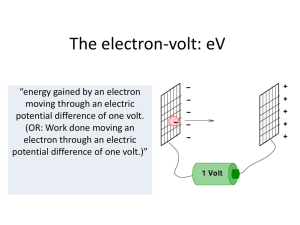
... (OR: Work done moving an electron through an electric potential difference of one volt.)” ...
... (OR: Work done moving an electron through an electric potential difference of one volt.)” ...
AN INTRODUCTION TO…
... behind the emitted electrons. Light strikes an electron at the electron vibrates with the frequency of the light ray. As more and more light rays hit this electron, it will gain energy. (Think pushing someone on a swing.) This is possible since resonance can do this… ...
... behind the emitted electrons. Light strikes an electron at the electron vibrates with the frequency of the light ray. As more and more light rays hit this electron, it will gain energy. (Think pushing someone on a swing.) This is possible since resonance can do this… ...
List the colors of visible light from low frequency to high frequency
... 1. List the colors of visible light from low frequency to high frequency. 2. Which EMR is the most harmful to living organisms? 3. A. A photon of energy having a wavelength of 1094 nm is released. What energy level was the electron before emitting the photon? B.What energy level is it on after emitt ...
... 1. List the colors of visible light from low frequency to high frequency. 2. Which EMR is the most harmful to living organisms? 3. A. A photon of energy having a wavelength of 1094 nm is released. What energy level was the electron before emitting the photon? B.What energy level is it on after emitt ...
Light
... By absorbing energy, the energy level rises to 2, 3, 4,or more (excited state) These electrons lose energy by emitting light when they return to lower energy levels. Atomic emission spectrum- frequencies of light emitted by an element separate into specific lines. ...
... By absorbing energy, the energy level rises to 2, 3, 4,or more (excited state) These electrons lose energy by emitting light when they return to lower energy levels. Atomic emission spectrum- frequencies of light emitted by an element separate into specific lines. ...
Brought to you by: Jonathan E. Mace
... Absorption and Emission of Light Electrons can only go to certain energy levels. They can only absorb certain frequencies of light. ...
... Absorption and Emission of Light Electrons can only go to certain energy levels. They can only absorb certain frequencies of light. ...
Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
... Called the dual wave-particle nature of light! Electromagnetic Radiation - form of E that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels thru space Electromagnetic Spectrum - all of the forms of electromagnetic radiation (visible light, x-rays, uv and infrared light, micro and radio waves) ...
... Called the dual wave-particle nature of light! Electromagnetic Radiation - form of E that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels thru space Electromagnetic Spectrum - all of the forms of electromagnetic radiation (visible light, x-rays, uv and infrared light, micro and radio waves) ...
At what intensity is the laser set?
... Though Einstein is most famous for his work in describing relativity in mechanics, his Nobel Prize was for understanding a very simple experiment. It was long understood that if you directed light of a certain wavelength at a piece of metal, it would emit electrons. In classical theory, the energy o ...
... Though Einstein is most famous for his work in describing relativity in mechanics, his Nobel Prize was for understanding a very simple experiment. It was long understood that if you directed light of a certain wavelength at a piece of metal, it would emit electrons. In classical theory, the energy o ...
photoelectric effect
... used to release it from the surface (i.e. to overcome the force of attraction between the electrons and the metal ions) and the rest of the energy is the kinetic energy of the electron as it leaves the metal. ...
... used to release it from the surface (i.e. to overcome the force of attraction between the electrons and the metal ions) and the rest of the energy is the kinetic energy of the electron as it leaves the metal. ...
Electrons in Atoms - Brunswick City Schools / Homepage
... • Did not answer why electrons are not pulled into atom’s “+” charged nucleus. ...
... • Did not answer why electrons are not pulled into atom’s “+” charged nucleus. ...
Sources and Nature of Light worksheet File
... The different ways of producing light depend on the different ways electrons can be forced to move to higher energy levels in their atoms. Although the electrons may be moved to higher energy levels in different ways, the light is always produced in the same way. ...
... The different ways of producing light depend on the different ways electrons can be forced to move to higher energy levels in their atoms. Although the electrons may be moved to higher energy levels in different ways, the light is always produced in the same way. ...
3. The nature of light 3.1 Light as a wave
... • Photon arriving at cathode absorbed by an electron. If energy of photon higher than material dependent work function Φ, then electron escapes from surface • Higher light intensity of light: more photons → more electrons • Φ, minimum energy needed, corresponding to minimum frequency fmin Visit the ...
... • Photon arriving at cathode absorbed by an electron. If energy of photon higher than material dependent work function Φ, then electron escapes from surface • Higher light intensity of light: more photons → more electrons • Φ, minimum energy needed, corresponding to minimum frequency fmin Visit the ...