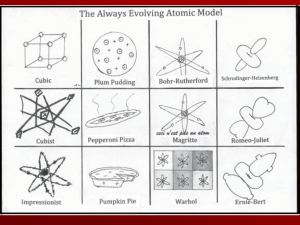
2.8-2.9 - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... Perform the simulation with several sets of parameters. Write a paragraph about how the simulation supports the discussion of the photoelectric effect from the book and any insights you gained from performing the simulation. You may include figures or a table if you'd like. ...
... Perform the simulation with several sets of parameters. Write a paragraph about how the simulation supports the discussion of the photoelectric effect from the book and any insights you gained from performing the simulation. You may include figures or a table if you'd like. ...
Determination of Planck`s Constant
... where νo is the threshold frequency below which no photoemission occurs, and h is a constant. The value of h, Planck’s constant, (6.626 × 10–34 J·s = 4.136 × 10–15 eV·s), is always the same, whereas νo varies with the particular metal being illuminated. Also, within the limits of experimental accura ...
... where νo is the threshold frequency below which no photoemission occurs, and h is a constant. The value of h, Planck’s constant, (6.626 × 10–34 J·s = 4.136 × 10–15 eV·s), is always the same, whereas νo varies with the particular metal being illuminated. Also, within the limits of experimental accura ...
photoeffect
... the ejecting surface and the collector plate, Lenard was able to: – Determine that the particles had a negative charge. – Determine the kinetic energy of the ejected particles. ...
... the ejecting surface and the collector plate, Lenard was able to: – Determine that the particles had a negative charge. – Determine the kinetic energy of the ejected particles. ...
6.4 - Hockerill Students
... The intensity of the incident light does not affect the energy of the emitted electrons (only their number) ...
... The intensity of the incident light does not affect the energy of the emitted electrons (only their number) ...
chapter-27
... Photoelectric Effect (Example) A metal whose work function is 1.5 eV is illuminated with 600 nm wavelength light. Will any electrons be ejected from the metal? If so, what is the maximum possible kinetic energy of the ejected electrons? ...
... Photoelectric Effect (Example) A metal whose work function is 1.5 eV is illuminated with 600 nm wavelength light. Will any electrons be ejected from the metal? If so, what is the maximum possible kinetic energy of the ejected electrons? ...
Chapter 7 - Colby College Wiki
... The energy required to break a carboncarbon bond is approximately 360 KJ/mol. What wavelength of electromagnetic radiation can supply this amount of energy? ...
... The energy required to break a carboncarbon bond is approximately 360 KJ/mol. What wavelength of electromagnetic radiation can supply this amount of energy? ...
It is sometimes difficult to find the polarity of an
... Also, light of any frequency should cause emission if it is intense enough. But there are cutoff frequencies below which emission does not occur, even at high intensity. ...
... Also, light of any frequency should cause emission if it is intense enough. But there are cutoff frequencies below which emission does not occur, even at high intensity. ...
Atoms and Energies
... the energy of emitted electrons does not depend on the intensity of light electrons are ejected immediately the frequency of light does affect the maximum kinetic energy of electrons; kinetic energy is linearly dependent on frequency intensity of light determines number of emitted electrons (photocu ...
... the energy of emitted electrons does not depend on the intensity of light electrons are ejected immediately the frequency of light does affect the maximum kinetic energy of electrons; kinetic energy is linearly dependent on frequency intensity of light determines number of emitted electrons (photocu ...
The Photoelectric effect - University of Toronto Physics
... In 1899, J.J. Thomson discovered that when a metal target is irradiated by ultraviolet light it emits negative charges. These charges were found to have the same charge/mass ratio as the electron. This effect was named the photoelectric effect, and the emitted electrons called photoelectrons. To exp ...
... In 1899, J.J. Thomson discovered that when a metal target is irradiated by ultraviolet light it emits negative charges. These charges were found to have the same charge/mass ratio as the electron. This effect was named the photoelectric effect, and the emitted electrons called photoelectrons. To exp ...
CHAPTER 3: The Experimental Basis of Quantum
... Field emission: A strong external electric field pulls the electron out of the material. Photoelectric effect: Incident light (electromagnetic radiation) shining on the material transfers energy to the electrons, allowing them to escape. We call the ejected electrons photoelectrons. ...
... Field emission: A strong external electric field pulls the electron out of the material. Photoelectric effect: Incident light (electromagnetic radiation) shining on the material transfers energy to the electrons, allowing them to escape. We call the ejected electrons photoelectrons. ...
5.2 Quantum Theory and the Atom
... Atomic Emission Spectrum (Bright Line Spectrum) • The set of frequencies of light emitted by atoms of a given element • Each element has its own unique atomic emission spectrum (LIKE A FINGER PRINT) • Used to determine the composition of stars ...
... Atomic Emission Spectrum (Bright Line Spectrum) • The set of frequencies of light emitted by atoms of a given element • Each element has its own unique atomic emission spectrum (LIKE A FINGER PRINT) • Used to determine the composition of stars ...
Modern Physics
... No photoelectrons are emitted if the frequency falls below some cut-off frequency fc The maximum energy of the photons is independent of the light intensity The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons increases with increasing frequency Photoelectrons are emitted almost instantaneously from the ...
... No photoelectrons are emitted if the frequency falls below some cut-off frequency fc The maximum energy of the photons is independent of the light intensity The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons increases with increasing frequency Photoelectrons are emitted almost instantaneously from the ...
Physics and the Quantum Mechanical Model
... frequencies, depending on the element Each frequency is a different color The light is emitted as electrons fall from one energy level to another, like from n=4 to n=1 They are like atomic fingerprints- every element is ...
... frequencies, depending on the element Each frequency is a different color The light is emitted as electrons fall from one energy level to another, like from n=4 to n=1 They are like atomic fingerprints- every element is ...
Light and the electron
... and can be used to determine if that element is part of an unknown compound. Pg. 126 ...
... and can be used to determine if that element is part of an unknown compound. Pg. 126 ...
THE PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT
... THEORY: When light (or other electromagnetic radiation) is incident on a metal surface, electrons can be released from the metal. This is the photoelectric effect. According to classical theory, the electrons are shaken loose from atoms by the electric field of the incident light, and so a brighter ...
... THEORY: When light (or other electromagnetic radiation) is incident on a metal surface, electrons can be released from the metal. This is the photoelectric effect. According to classical theory, the electrons are shaken loose from atoms by the electric field of the incident light, and so a brighter ...