Cadet College Okara
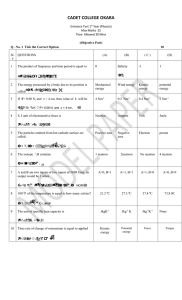
... Entrance Test 1st Year (Physics) Max Marks 25 Time Allowed 30 Mins (Objective Part) Q . No. 1 Tick the Correct Option. ...
... Entrance Test 1st Year (Physics) Max Marks 25 Time Allowed 30 Mins (Objective Part) Q . No. 1 Tick the Correct Option. ...
p30chap6S
... A student is making an analogy for light as a photon (quantized) and light as a wave (continuous). The analogy she uses involves walking to a height using a ramp or stairs. ...
... A student is making an analogy for light as a photon (quantized) and light as a wave (continuous). The analogy she uses involves walking to a height using a ramp or stairs. ...
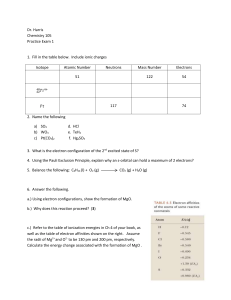
Dr. Harris Chemistry 105 Practice Exam 1 Isotope Atomic Number
... 14. A laser emits 200mJ of energy per hour. Given that the wavelength of the photons in the beam is 300 nm, and assuming that the emission rate is constant, how many photons are emitted per minute? ...
... 14. A laser emits 200mJ of energy per hour. Given that the wavelength of the photons in the beam is 300 nm, and assuming that the emission rate is constant, how many photons are emitted per minute? ...
Worksheet 6 - KFUPM Faculty List
... (b) It takes 208.4 kJ of energy to remove 1 mole of electrons from an atom of the surface of rubidium (Rb) metal. What is the maximum wavelength of light capable of removing an electron from an atom on the surface of solid Rb? ...
... (b) It takes 208.4 kJ of energy to remove 1 mole of electrons from an atom of the surface of rubidium (Rb) metal. What is the maximum wavelength of light capable of removing an electron from an atom on the surface of solid Rb? ...
Photoelectric Effect
... Using the an investigation into special relativity, we see that E = mc2. Knowing that “waves” can act like “particles” might mean that “particles” can act like “waves”. This is the de Broglie wavelengths. This leads to the conclusion of wave-particle duality. ...
... Using the an investigation into special relativity, we see that E = mc2. Knowing that “waves” can act like “particles” might mean that “particles” can act like “waves”. This is the de Broglie wavelengths. This leads to the conclusion of wave-particle duality. ...
Physics 222 - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... Photoelectric Effect Existence of a threshold voltage Current increases with intensity Threshold is a function of light frequency No intensity threshold No time delay Fairly monochromatic electron energies ...
... Photoelectric Effect Existence of a threshold voltage Current increases with intensity Threshold is a function of light frequency No intensity threshold No time delay Fairly monochromatic electron energies ...
Topic 7_1_Ext B__Photons and the photoelectric effect
... FYI: The ramifications of the particle-wave duality of light will be explored later. calculations agree with experimental observations. In 1905 Elbert Einstein published a paper on the photoelectric effect, in which he postulated that energy quantization is a fundamental property of electromagnetic ...
... FYI: The ramifications of the particle-wave duality of light will be explored later. calculations agree with experimental observations. In 1905 Elbert Einstein published a paper on the photoelectric effect, in which he postulated that energy quantization is a fundamental property of electromagnetic ...