Light Students will learn about light.
... • Sometimes light acts as a particle • Light “particles” are called “photons” • Light colliding with a mirror makes very small “pings” • Photoelectric Effect: Light delivers energy through its frequency in order to excite and give electrons kinetic energy. Light energy (as photons): E = hf – H = 6.6 ...
... • Sometimes light acts as a particle • Light “particles” are called “photons” • Light colliding with a mirror makes very small “pings” • Photoelectric Effect: Light delivers energy through its frequency in order to excite and give electrons kinetic energy. Light energy (as photons): E = hf – H = 6.6 ...
The Compton Effect, or Compton scattering – conclusive evidence
... than the original x-ray photons. The scattered x-rays had lost energy. Where did the extra energy go? The energy lost by the x-ray photons, as evidenced by the photons’ increased wavelength, increases the kinetic energy of the scattered electrons. Sound like billiards? It should! The collision is in ...
... than the original x-ray photons. The scattered x-rays had lost energy. Where did the extra energy go? The energy lost by the x-ray photons, as evidenced by the photons’ increased wavelength, increases the kinetic energy of the scattered electrons. Sound like billiards? It should! The collision is in ...
Objective 1: Summarize the development of atomic theory
... necessary energy to break the bond? What type of electromagnetic radiation is this? ...
... necessary energy to break the bond? What type of electromagnetic radiation is this? ...
Chapter 4 Electron Configuration
... quantum) associated with each frequency of light The higher the frequency, the more the packet (quantum) contains E = hν E is energy in joules h is Plank’s constant (6.62 x 10-34 J sec ν is frequency ...
... quantum) associated with each frequency of light The higher the frequency, the more the packet (quantum) contains E = hν E is energy in joules h is Plank’s constant (6.62 x 10-34 J sec ν is frequency ...
Class 11 I : The speed of light
... We have seen that light can be understood as electromagnetic waves… they undergo diffraction and produce interference patterns BUT, light/electromagnetic-radiation can also behave as a stream of particles… Carries energy and momentum in discrete packets Can create a blip on a CCD chip This stran ...
... We have seen that light can be understood as electromagnetic waves… they undergo diffraction and produce interference patterns BUT, light/electromagnetic-radiation can also behave as a stream of particles… Carries energy and momentum in discrete packets Can create a blip on a CCD chip This stran ...
Hands-on Activities with LEDs and Light
... hands-on experiments with LEDs in order to find : Planck’s constant, electron’s charge, the energy required to light the LED, the frequency of light emitting from the LED? ...
... hands-on experiments with LEDs in order to find : Planck’s constant, electron’s charge, the energy required to light the LED, the frequency of light emitting from the LED? ...
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice – Magnetism and
... 32. Quantum concepts are critical in explaining all of the following EXCEPT (A) Rutherford's scattering experiments (B) Bohr's theory of the hydrogen atom (C) Compton scattering (D) the blackbody spectrum (E) the photoelectric effect 33. If photons of light of frequency f have momentum p, photons of ...
... 32. Quantum concepts are critical in explaining all of the following EXCEPT (A) Rutherford's scattering experiments (B) Bohr's theory of the hydrogen atom (C) Compton scattering (D) the blackbody spectrum (E) the photoelectric effect 33. If photons of light of frequency f have momentum p, photons of ...
Chapter 27 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom 27.1
... KE hf Increasing the intensity of light does not increase the energy of the photon. It does increase the number of photons, which increases the number of ejected electrons (more current). ...
... KE hf Increasing the intensity of light does not increase the energy of the photon. It does increase the number of photons, which increases the number of ejected electrons (more current). ...
Photoelectric Effect
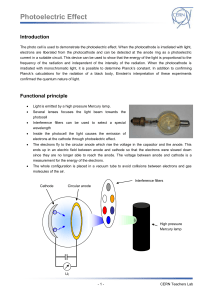
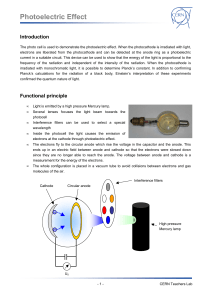
... The photo cell is used to demonstrate the photoelectric effect. When the photocathode is irradiated with light, electrons are liberated from the photocathode and can be detected at the anode ring as a photoelectric current in a suitable circuit. This device can be used to show that the energy of the ...
... The photo cell is used to demonstrate the photoelectric effect. When the photocathode is irradiated with light, electrons are liberated from the photocathode and can be detected at the anode ring as a photoelectric current in a suitable circuit. This device can be used to show that the energy of the ...
Click here to get the file
... 3. When electrons absorb a photon of the correct energy, the electron jumps to a higher energy level 4. When the electron falls to a lower energy level, a photon of only one certain energy is emitted The emitted photons have a discrete energy, frequency or wavelength that we observe in the spectrum ...
... 3. When electrons absorb a photon of the correct energy, the electron jumps to a higher energy level 4. When the electron falls to a lower energy level, a photon of only one certain energy is emitted The emitted photons have a discrete energy, frequency or wavelength that we observe in the spectrum ...
CHAPTER 3: The Experimental Basis of Quantum Theory
... The photoelectrons are emitted almost instantly following illumination of the photocathode, independent of the intensity of the light. ...
... The photoelectrons are emitted almost instantly following illumination of the photocathode, independent of the intensity of the light. ...
How many mL of 0.250 M sodium hydroxide is required to
... An orbit that is FARTHER from the nucleus means that the electron has MORE energy An orbit that is CLOSER to the nucleus means that the electron has LESS energy - Electrons may gain or lose energy by either ABSORBING (to gain) or EMITTING (to lose) a PHOTON of light. (Photon = particle or "packet" o ...
... An orbit that is FARTHER from the nucleus means that the electron has MORE energy An orbit that is CLOSER to the nucleus means that the electron has LESS energy - Electrons may gain or lose energy by either ABSORBING (to gain) or EMITTING (to lose) a PHOTON of light. (Photon = particle or "packet" o ...