Modern Atomic Theory (aka the electron chapter!)
... draw the line spectra (all of the lines) and ...
... draw the line spectra (all of the lines) and ...
PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT Introduction
... the electrons in the metal absorb a sufficient amount of energy from the light to escape from the metal. This energy is called the binding energy or work function Φ. The work function is different for each type of metal. Energy absorbed in excess of this binding energy is carried off by the electron ...
... the electrons in the metal absorb a sufficient amount of energy from the light to escape from the metal. This energy is called the binding energy or work function Φ. The work function is different for each type of metal. Energy absorbed in excess of this binding energy is carried off by the electron ...
Phys 12 Investigating the Photoelectric Effect 1a) List three
... 7) How does this amount of potential energy compare to the electron’s initial kinetic energy? This potential energy would be the initial kinetic energy of the electrons. 8) Predict what will happen to the stopping potential when we increase the intensity of the wave. Remember, the intensity of a wav ...
... 7) How does this amount of potential energy compare to the electron’s initial kinetic energy? This potential energy would be the initial kinetic energy of the electrons. 8) Predict what will happen to the stopping potential when we increase the intensity of the wave. Remember, the intensity of a wav ...
Chemistry I Unit Review: The Atom Text Chapters 2 and 7 1. The
... Determine the number of valence electrons and draw the dot diagram for the following atoms: ...
... Determine the number of valence electrons and draw the dot diagram for the following atoms: ...
force on moving charge
... When UV light shines on a clean metal surface, electrons are emitted. What is unusual is the way they are emitted. They are emitted immediately, even in weak light. According to the wave interpretation of light, a time delay is needed for enough energy at a given spot to build up to release an elect ...
... When UV light shines on a clean metal surface, electrons are emitted. What is unusual is the way they are emitted. They are emitted immediately, even in weak light. According to the wave interpretation of light, a time delay is needed for enough energy at a given spot to build up to release an elect ...
Photoelectric Effect
... the cathode. When a photon of frequency strikes the cathode, then an electron can be ejected from the metal (external photoelectric effect) provided the photon has sufficient energy. Some of these ejected electrons reach the (unilluminated) anode so that a potential difference is set up between an ...
... the cathode. When a photon of frequency strikes the cathode, then an electron can be ejected from the metal (external photoelectric effect) provided the photon has sufficient energy. Some of these ejected electrons reach the (unilluminated) anode so that a potential difference is set up between an ...
Chemistry TEST 4 Review and Answers
... Page 165 – 171 and 197 – 203 in textbook 5.1 Wave and Particle characteristics of Light ...
... Page 165 – 171 and 197 – 203 in textbook 5.1 Wave and Particle characteristics of Light ...
Modern Physics P age | 1 AP Physics B
... a. All stable nuclei have Z= N. b. Only heavy stable nuclei have Z = N. c. Heavy stable nuclei tend to have Z < N. d. All light stable nuclei have Z < N. e. All light stable nuclei have Z > N. 45. When 10B is bombarded by neutrons, a neutron can be absorbed and an alpha particle ( 4He) emitted. If t ...
... a. All stable nuclei have Z= N. b. Only heavy stable nuclei have Z = N. c. Heavy stable nuclei tend to have Z < N. d. All light stable nuclei have Z < N. e. All light stable nuclei have Z > N. 45. When 10B is bombarded by neutrons, a neutron can be absorbed and an alpha particle ( 4He) emitted. If t ...
Electricity & Optics Physics 24100 Lecture 22 – Chapter 31 sec. 1-4,6
... • Albert Einstein: particle theory of light to explain photoelectric effect • Quantum Mechanics naturally accounts for both of these effects, not just for light but for all forms of matter. ...
... • Albert Einstein: particle theory of light to explain photoelectric effect • Quantum Mechanics naturally accounts for both of these effects, not just for light but for all forms of matter. ...
ch_24_poss_elmo
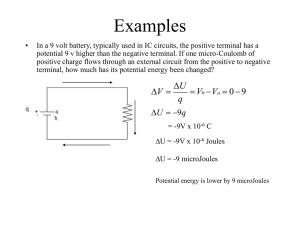
... Examples A proton is placed in an electric field of E=105 V/m and released. After going 10 cm, what is its speed? Use conservation of energy. a ...
... Examples A proton is placed in an electric field of E=105 V/m and released. After going 10 cm, what is its speed? Use conservation of energy. a ...
Quantum Physics
... and Planck’s constant for the description of matter in terms of waves or particles. • Demonstrate your understanding of the photoelectric effect, the stopping potential, and the deBroglie wavelength. • Explain and solve problems similar to those presented in this unit. ...
... and Planck’s constant for the description of matter in terms of waves or particles. • Demonstrate your understanding of the photoelectric effect, the stopping potential, and the deBroglie wavelength. • Explain and solve problems similar to those presented in this unit. ...
PHYS 212 Modern Physics Lab Photoelectric Effect
... effect. He argued that light was not a wave--it was particulate--and it travels in little energy bundles called photons. The energy of one of these photons is hf, where h is the fundamental constant of nature recently proposed by Max Planck to explain blackbody radiation, and f is the frequency of t ...
... effect. He argued that light was not a wave--it was particulate--and it travels in little energy bundles called photons. The energy of one of these photons is hf, where h is the fundamental constant of nature recently proposed by Max Planck to explain blackbody radiation, and f is the frequency of t ...
Blackbody Radiation
... degrees Celsius. At what wavelength does the radiation emitted from the skin ...
... degrees Celsius. At what wavelength does the radiation emitted from the skin ...
Atomic Physics
... 1/ When the incident light is monochromatic, the number of photoelectrons emitted per second ( current I ) is proportional to the light intensity ( I’). Such an emission ...
... 1/ When the incident light is monochromatic, the number of photoelectrons emitted per second ( current I ) is proportional to the light intensity ( I’). Such an emission ...
1. Millikan did his experiments with the balance of
... repeating this experiment several times, he found that the values measured are always multiples of the same number. He then interpreted that this number is the charge of an electron: 1602 × 10-19 coulomb (SI unit for electric charge). ...
... repeating this experiment several times, he found that the values measured are always multiples of the same number. He then interpreted that this number is the charge of an electron: 1602 × 10-19 coulomb (SI unit for electric charge). ...