* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemistry TEST 4 Review and Answers
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Bremsstrahlung wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
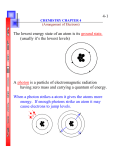
Chemistry TEST 5 Review and Answers Chapter 5 Electrons in atoms and Chapter 6.3 Periodic Trends TEST DAY: Friday, October 23, 2009 Consult class notes, activities, homework, and notes. Page 165 – 171 and 197 – 203 in textbook 5.1 Wave and Particle characteristics of Light 35 x rays , ultraviolet light, microwaves, radio waves 37 Phenomenon in which a metal emits electrons when light of a certain frequency shines on it 41 Red waves have longer wavelength and lower frequency λ=6.00x10-5 m; infrared radiation (use c=λν; c = 3.00x108 m/s) 46 E = 2.97x10-19 J (use E=hν; h = 6.626x10-34 J·s) 51 5.2 Quantum theory of the atom 61 Ground state – lowest energy; excited state – any energy state higher than ground state 63 3 dimensional region around nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found 70 2 electrons 5.3 Electron configuration and orbital diagrams 82 Pauli exclusion principle, aufbau principle, Hund’s rule 83 Oxygen: 1s2 2s2 2p4 Sulfur: 1s2 2s2 2p4 3s2 3p4 85 orbital diagrams – you’re on your own a. 1s2 2s2 c. 1s2 2s2 2p3 b. 1s2 2s2 2p4 3s2 3p1 d. 1s2 2s2 2p4 3s1 orbital diagrams – you’re on your own 6.3 Periodic trends 58 The energy needed to remove an electron from a neutral atom in its gaseous state 63 Atomic radii decrease left-to-right because the nuclear charge increases as the shielding of inner core electrons remains constant. The increased attraction of the nucleus for its electrons pulls the electrons inward, resulting in a decreased atomic size. 64 a. N; b. Ne; c. Li 65 Hydrogen and helium have a complete energy level with just two electrons (The first energy level is the 1s orbital, which holds a maximum of 2 electrons) 66a, b a. Ion is negative because the atom becomes smaller than neutral atom. b A is left of B – atomic radius in period decreases from left-to-right. 67 Group 1 has 1 electron (alkali metals); group 18 has 8 electrons (noble gases) 78 a. As; b. N; c. Be