* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download At what intensity is the laser set?
Survey
Document related concepts
Optical coherence tomography wikipedia , lookup
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Harold Hopkins (physicist) wikipedia , lookup
Spectral density wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Photoacoustic effect wikipedia , lookup
Optical amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Photonic laser thruster wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
Mode-locking wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
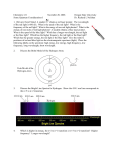
(VCL) Assignment - Photoelectric Effect Experiment Introduction Though Einstein is most famous for his work in describing relativity in mechanics, his Nobel Prize was for understanding a very simple experiment. It was long understood that if you directed light of a certain wavelength at a piece of metal, it would emit electrons. In classical theory, the energy of light was thought to be based on its intensity and not its frequency. However, the results of the photoelectric effect contradicted classical theory. These inconsistencies lead Einstein to suggest that we need to think of light as being composed of particles and not just as waves. You will have a chance to recreate some of the measurements that led to Einstein’s theory. Procedure / Observations 1. Enter the Quantum Lab in VCL. 2. Set up the optics table for this experiment by selecting Photoelectric Effect (1) on the clipboard (in the stockroom). What source is used in this experiment and what does it do? At what intensity is the laser set? At what wavelength is the laser set? Which metal foil is used in this experiment? What detector is used in this experiment and what does it measure? What does the signal on the phosphor screen indicate about the laser light shining on the Na foil? 3. Decrease the laser power to 1 photon/second. How does the signal change? 4. Increase the power to 1kW. How does the signal change? 5. Change the power back to 1 nW. Now increase the wavelength to 650 nm. What do you observe? Does the frequency of light increase or decrease as wavelength is increased? Does a lower frequency correspond to a lower or higher energy? 6. Change the laser power to determine whether you can get the signal back to what it was beford. Can you get the signal back? What is the difference between wavelength and intensity? Discussion