PAM2306 Description Features Pin Assignments Applications
... Products described herein may be covered by one or more United States, international or foreign patents pending. Product names and markings noted herein may also be covered by one or more United States, international or foreign trademarks. This document is written in English but may be translated in ...
... Products described herein may be covered by one or more United States, international or foreign patents pending. Product names and markings noted herein may also be covered by one or more United States, international or foreign trademarks. This document is written in English but may be translated in ...
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) Basics
... high input impedance and large bipolar current-carrying capability. Many designers view IGBT as a device with MOS input characteristics and bipolar output characteristic that is a voltage-controlled bipolar device. To make use of the advantages of both Power MOSFET and BJT, the IGBT has been introdu ...
... high input impedance and large bipolar current-carrying capability. Many designers view IGBT as a device with MOS input characteristics and bipolar output characteristic that is a voltage-controlled bipolar device. To make use of the advantages of both Power MOSFET and BJT, the IGBT has been introdu ...
A Fresh Approach to Switching Regulator Topologies and
... • Since VDS is reduced or zero at switch on, we have lower COSS switching losses and reduced EMI. • A QRC system has variable switching frequency defined by load and input voltage Note: In reality, the Snubber spike would probably be smaller • Since the DC link will always have some but this is show ...
... • Since VDS is reduced or zero at switch on, we have lower COSS switching losses and reduced EMI. • A QRC system has variable switching frequency defined by load and input voltage Note: In reality, the Snubber spike would probably be smaller • Since the DC link will always have some but this is show ...
TPS65283/-1 4.5- to 18-V Input Voltage, Maximum 3.5-/2.5
... from this voltage. Decouple this pin to power ground with a minimum 1-µF ceramic capacitor. The output voltage level of LDO is regulated to typical 6.3 V for optimal conduction on-resistances of internal power MOSFETs. In PCB design, the power ground and analog ground should have one-point common co ...
... from this voltage. Decouple this pin to power ground with a minimum 1-µF ceramic capacitor. The output voltage level of LDO is regulated to typical 6.3 V for optimal conduction on-resistances of internal power MOSFETs. In PCB design, the power ground and analog ground should have one-point common co ...
HGTG30N60A4D 600V, SMPS Series N
... essentially capacitors. Circuits that leave the gate opencircuited or floating should be avoided. These conditions can result in turn-on of the device due to voltage buildup on the input capacitor due to leakage currents or pickup. 7. Gate Protection - These devices do not have an internal monolithi ...
... essentially capacitors. Circuits that leave the gate opencircuited or floating should be avoided. These conditions can result in turn-on of the device due to voltage buildup on the input capacitor due to leakage currents or pickup. 7. Gate Protection - These devices do not have an internal monolithi ...
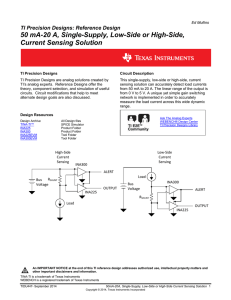
50mA-20A, Single-Supply, Low-Side or High
... effect of these two error sources upon the ability to monitor small levels of shunt current. Before a proper worst case error analysis can be performed the details and conditions surrounding the device specifications of offset and common mode rejection must be taken into account. Such conditions are ...
... effect of these two error sources upon the ability to monitor small levels of shunt current. Before a proper worst case error analysis can be performed the details and conditions surrounding the device specifications of offset and common mode rejection must be taken into account. Such conditions are ...
Characterization of an n-type 4 kV Silicon GTO for pulsed power
... [1], two common materials used as capacitive storage and conductors are considered, it is therein illustrated critical magnetic field strength values up to two orders of magnitude greater than critical electric field values are readily achievable. In light of these facts, one can see that capacitive ...
... [1], two common materials used as capacitive storage and conductors are considered, it is therein illustrated critical magnetic field strength values up to two orders of magnitude greater than critical electric field values are readily achievable. In light of these facts, one can see that capacitive ...
Introduction to Capacitor Technologies
... The charge on the capacitor at any time, t, is calculated by the following equation: Q = C x V x [1 - e-t/RC] The charging current decays according to the equation: I = V/R x e-t/RC Where e = 2.7182818, the so-called “natural number,” or the base of natural logarithm, ln(x). Many physical and even ...
... The charge on the capacitor at any time, t, is calculated by the following equation: Q = C x V x [1 - e-t/RC] The charging current decays according to the equation: I = V/R x e-t/RC Where e = 2.7182818, the so-called “natural number,” or the base of natural logarithm, ln(x). Many physical and even ...
Switching Ripple Characteristics of Space Vector PWM Schemes for
... of [12] is that the total flux HDF can only be obtained by means of the polygon approach if the HDFs of individual polygons are all at first determined and then accounted for in the total flux HDF evaluation. The results reported in [11] and [12] clearly show that the same value of a per-phase flux ...
... of [12] is that the total flux HDF can only be obtained by means of the polygon approach if the HDFs of individual polygons are all at first determined and then accounted for in the total flux HDF evaluation. The results reported in [11] and [12] clearly show that the same value of a per-phase flux ...
TBU-CX050-VTC-WH Datasheet
... the voltage across the TBU® device falls to the Vreset or below. Therefore, the TBU® device will automatically reset on lines which have no DC bias or have DC bias below Vreset (such as unpowered signal lines). If the line has a normal DC bias above Vreset, the voltage across the TBU® device may not ...
... the voltage across the TBU® device falls to the Vreset or below. Therefore, the TBU® device will automatically reset on lines which have no DC bias or have DC bias below Vreset (such as unpowered signal lines). If the line has a normal DC bias above Vreset, the voltage across the TBU® device may not ...
Memristor
The memristor (/ˈmɛmrɨstər/; a portmanteau of memory resistor) was a term coined in 1971 by circuit theorist Leon Chua as a missing non-linear passive two-terminal electrical component relating electric charge and magnetic flux linkage. The operation of RRAM devices was recently connected to the memristor concept According to the characterizing mathematical relations, the memristor would hypothetically operate in the following way: The memristor's electrical resistance is not constant but depends on the history of current that had previously flowed through the device, i.e., its present resistance depends on how much electric charge has flowed in what direction through it in the past. The device remembers its history - the so-called non-volatility property: When the electric power supply is turned off, the memristor remembers its most recent resistance until it is turned on again.Leon Chua has more recently argued that the definition could be generalized to cover all forms of two-terminal non-volatile memory devices based on resistance switching effects although some experimental evidence contradicts this claim, since a non-passive nanobattery effect is observable in resistance switching memory. Chua also argued that the memristor is the oldest known circuit element, with its effects predating the resistor, capacitor and inductor.In 2008, a team at HP Labs claimed to have found Chua's missing memristor based on an analysis of a thin film of titanium dioxide; the HP result was published in Nature. The memristor is currently under development by various teams including Hewlett-Packard, SK Hynix and HRL Laboratories.These devices are intended for applications in nanoelectronic memories, computer logic and neuromorphic/neuromemristive computer architectures. In October 2011, the HP team announced the commercial availability of memristor technology within 18 months, as a replacement for Flash, SSD, DRAM and SRAM. Commercial availability of new memory was more recently estimated as 2018. In March 2012, a team of researchers from HRL Laboratories and the University of Michigan announced the first functioning memristor array built on a CMOS chip.