Slide 1
... ions act as a catalyst to increase the rate of the reaction and • Secondly it reacts with the water formed to shift the position of the equilibriumm to the right hand side (Le Chatelier’s principle) ensuring a good yield of product. • Note that unlike the acid and alcohol, an ester does not contain ...
... ions act as a catalyst to increase the rate of the reaction and • Secondly it reacts with the water formed to shift the position of the equilibriumm to the right hand side (Le Chatelier’s principle) ensuring a good yield of product. • Note that unlike the acid and alcohol, an ester does not contain ...
Pertubation of metabolism in IDD Q3-5 Joe - PBL-J-2015
... 3. Indicate the mechanisms by which beta ketoacid production is increased in response to oversupply of fatty acid to the liver, including the steps of the pathways of fatty acid metabolism that are up regulated The oversupply of fatty acids in the liver cells (in the absence of insulin) leads to the ...
... 3. Indicate the mechanisms by which beta ketoacid production is increased in response to oversupply of fatty acid to the liver, including the steps of the pathways of fatty acid metabolism that are up regulated The oversupply of fatty acids in the liver cells (in the absence of insulin) leads to the ...
碩命題橫式 - 國立彰化師範大學圖書館
... (a). xanthine oxidase (b). purine nucleoside phosphorylase (c). 5'-nucleotidase (d). adenosine deaminase (e). ribonucleotide reductase 10. The direct sources of nitrogen that are used to make urea via the Urea Cycle are: (a). citrulline and ornithine (b). arginine and aspartate (c). arginine and cit ...
... (a). xanthine oxidase (b). purine nucleoside phosphorylase (c). 5'-nucleotidase (d). adenosine deaminase (e). ribonucleotide reductase 10. The direct sources of nitrogen that are used to make urea via the Urea Cycle are: (a). citrulline and ornithine (b). arginine and aspartate (c). arginine and cit ...
Organic Molecule Building Block
... DNA has the information for the synthesis of proteins from amino acids. Some of these proteins are enzymes that control the rate of chemical reactions in a cell. ...
... DNA has the information for the synthesis of proteins from amino acids. Some of these proteins are enzymes that control the rate of chemical reactions in a cell. ...
Section 7-1
... Section 7-1 VOCABULARY REVIEW 1. Cellular respiration is the process in which cells make ATP by breaking down organic compounds. 2. Glycolysis is a biochemical pathway in which one molecule of glucose is oxidized to two molecules of pyruvic acid. 3. Lactic acid fermentation is an anaerobic pathway i ...
... Section 7-1 VOCABULARY REVIEW 1. Cellular respiration is the process in which cells make ATP by breaking down organic compounds. 2. Glycolysis is a biochemical pathway in which one molecule of glucose is oxidized to two molecules of pyruvic acid. 3. Lactic acid fermentation is an anaerobic pathway i ...
Assignment Chapter 12: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids 1
... An organic compound contains 69.77% carbon, 11.63% hydrogen and the rest is oxygen. The molecular mass of the compound is 86. It does not reduce Tollen’s reagent but forms an addition compound with sodium hydrogen sulphite and gives a positive iodoform test. On vigorous oxidation it gives ethanoic a ...
... An organic compound contains 69.77% carbon, 11.63% hydrogen and the rest is oxygen. The molecular mass of the compound is 86. It does not reduce Tollen’s reagent but forms an addition compound with sodium hydrogen sulphite and gives a positive iodoform test. On vigorous oxidation it gives ethanoic a ...
Data/hora: 16/04/2017 16:28:45 Provedor de dados: 36 País: Brazil
... Resumo: An ion chromatography procedure, employing an IonPac AC15 concentrator column was used to investigate on line preconcentration for the simultaneous determination of inorganic anions and organic acids in river water. Twelve organic acids and nine inorganic anions were separated without any in ...
... Resumo: An ion chromatography procedure, employing an IonPac AC15 concentrator column was used to investigate on line preconcentration for the simultaneous determination of inorganic anions and organic acids in river water. Twelve organic acids and nine inorganic anions were separated without any in ...
File
... Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Can occur in the cytoplasm of most animal cells, but the liver is the major site for this process Fatty acids are synthesized when the diet is low in fat or high in carbohydrate or protein (most from glucose via pyruvate) A large quantity of NADPH is needed for this process a ...
... Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Can occur in the cytoplasm of most animal cells, but the liver is the major site for this process Fatty acids are synthesized when the diet is low in fat or high in carbohydrate or protein (most from glucose via pyruvate) A large quantity of NADPH is needed for this process a ...
Chem 365 Problem set 10 answer key 1. Ketone bodies are formed
... Ketone bodies are formed primarily in the liver in the mitochondria. Ketone bodies are formed from the condensation of 2 molecules of acetyl CoA to form acetoacetic acid (a ketone body). The acetoacetic acid can be converted to β-hydoxybutyrate (another ketone body) by the enzyme β-hydroxybutyrate d ...
... Ketone bodies are formed primarily in the liver in the mitochondria. Ketone bodies are formed from the condensation of 2 molecules of acetyl CoA to form acetoacetic acid (a ketone body). The acetoacetic acid can be converted to β-hydoxybutyrate (another ketone body) by the enzyme β-hydroxybutyrate d ...
CHEM 220 Problem Set 3
... 9) Explain the structure of benzene and how the sigma and pi electrons contribute to its structure. Sketches are good. 10) Beginning with benzoic acid, indicate where the following substituting groups will locate on the benzene ring: a) -OH ...
... 9) Explain the structure of benzene and how the sigma and pi electrons contribute to its structure. Sketches are good. 10) Beginning with benzoic acid, indicate where the following substituting groups will locate on the benzene ring: a) -OH ...
documentation
... processes. It occurs naturally as an intermediate product in carbohydrate and protein metabolisms in the body. The six-carbon glucose molecule is broken down to two molecules of pyruvic acid in aerobic condition as the main input for Krebs cycle, whereas to two molecules of lactic acid (alpha hydrox ...
... processes. It occurs naturally as an intermediate product in carbohydrate and protein metabolisms in the body. The six-carbon glucose molecule is broken down to two molecules of pyruvic acid in aerobic condition as the main input for Krebs cycle, whereas to two molecules of lactic acid (alpha hydrox ...
Quantitative Analysis of Stearic Acid in Vulcanized Styrene
... acid content. There exists a need for a quantitative analytical method for the determination of stearic acid in rubber. This report illustrates two methods which can be used for the measurement of stearic acid in styrene butadiene rubber (SBR): thermal desorption (TD)-GC/MS and reactive thermal deso ...
... acid content. There exists a need for a quantitative analytical method for the determination of stearic acid in rubber. This report illustrates two methods which can be used for the measurement of stearic acid in styrene butadiene rubber (SBR): thermal desorption (TD)-GC/MS and reactive thermal deso ...
Fermentation Quiz
... 10. What is the net gain in ATP molecules produced during the reactions of glycolysis under anaerobic conditions? a) 0 b) 2 c) 4 d) 6 ...
... 10. What is the net gain in ATP molecules produced during the reactions of glycolysis under anaerobic conditions? a) 0 b) 2 c) 4 d) 6 ...
1. The table shows the number of carbon atoms contained in some
... The table shows the number of carbon atoms contained in some substances. Substance ...
... The table shows the number of carbon atoms contained in some substances. Substance ...
Volatile Fatty Acids
... Major VFA: acetic acid; propionic acid; butyric acid. Major VFAs are absorbed and used as primary energy source by ruminants. The tissue use of VFA is lower than tissue use of the sugars (e.g., glucose). ~10 % of energy consumed goes towards fermentation (methane). ...
... Major VFA: acetic acid; propionic acid; butyric acid. Major VFAs are absorbed and used as primary energy source by ruminants. The tissue use of VFA is lower than tissue use of the sugars (e.g., glucose). ~10 % of energy consumed goes towards fermentation (methane). ...
2015FallNSC408
... d. Pyruvate dehydrogenase Kinase-4 In cancer cells and diabetes, glucose oxidation via Krebs cycle is impaired. a. True b. False Obesity may contribute to diabetes by derailing normal mitochondrial oxidation of glucose. a. True b. False Which of the following compounds may increase the risk for colo ...
... d. Pyruvate dehydrogenase Kinase-4 In cancer cells and diabetes, glucose oxidation via Krebs cycle is impaired. a. True b. False Obesity may contribute to diabetes by derailing normal mitochondrial oxidation of glucose. a. True b. False Which of the following compounds may increase the risk for colo ...
nucleic acid - 4J Blog Server
... • The cellular functions of lipids. • How the sequence and subcomponents of lipids determine their properties. • The basic structure of a nucleic acid. • How changes in organic molecules would affect their function. ...
... • The cellular functions of lipids. • How the sequence and subcomponents of lipids determine their properties. • The basic structure of a nucleic acid. • How changes in organic molecules would affect their function. ...
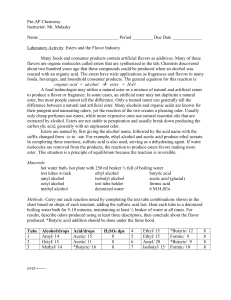
Pre-AP Chemistry
... Many foods and consumer products contain artificial flavors as additives. Many of these flavors are organic molecules called esters that are synthesized in the lab. Chemists discovered about two hundred years ago that these compounds could be produced when an alcohol was reacted with an organic acid ...
... Many foods and consumer products contain artificial flavors as additives. Many of these flavors are organic molecules called esters that are synthesized in the lab. Chemists discovered about two hundred years ago that these compounds could be produced when an alcohol was reacted with an organic acid ...
AS and A2 Biology resource
... A resource for A-level Biology students studying the digestive system. It could be used as an extension or homework task. Learning Objectives 1. Compare and discuss the anatomical differences of the digestive tract from different domestic species and relate these differences to their functions. 2. D ...
... A resource for A-level Biology students studying the digestive system. It could be used as an extension or homework task. Learning Objectives 1. Compare and discuss the anatomical differences of the digestive tract from different domestic species and relate these differences to their functions. 2. D ...
Organic Macromolecules
... Read Chapter 3 in your book and fill out this graphic organizer. You will use this when you do your Macromolecule Flapbook. Organic Molecule Simple Carbohydrate ...
... Read Chapter 3 in your book and fill out this graphic organizer. You will use this when you do your Macromolecule Flapbook. Organic Molecule Simple Carbohydrate ...
Butyric acid-producing anaerobic bacteria as a novel
... Butyric acid, produced within the intestinal lumen by bacterial fermentation of dietary carbohydrates, exerts a wide variety of effects on intestinal function (Hamer et al., 2008). First of all, butyric acid is the preferred source of energy for colonocytes. It affects cellular proliferation, differ ...
... Butyric acid, produced within the intestinal lumen by bacterial fermentation of dietary carbohydrates, exerts a wide variety of effects on intestinal function (Hamer et al., 2008). First of all, butyric acid is the preferred source of energy for colonocytes. It affects cellular proliferation, differ ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.