CHAP Twenty-Five - Foothill College
... C) Sequencing via Selective Cleavage i) With aqueous acid at every peptide bond ii) Edman Degradation: N terminus iii) DNFB to identify N-terminus iv) Chymotripsin at C-terminus v) With cyanogen bromide BrCN at methionine C terminus vi) With chymotripsin at C end of phe, tyr, trp vii) With Tripsin a ...
... C) Sequencing via Selective Cleavage i) With aqueous acid at every peptide bond ii) Edman Degradation: N terminus iii) DNFB to identify N-terminus iv) Chymotripsin at C-terminus v) With cyanogen bromide BrCN at methionine C terminus vi) With chymotripsin at C end of phe, tyr, trp vii) With Tripsin a ...
Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism
... b. The final electron acceptor in aerobic respiration is molecular oxygen; in anaerobic respiration, it is another inorganic molecule. c. In cyclic photophosphorylation, electrons are returned to chlorophyll. In noncyclic photophosphorylation, chlorophyll receives electrons from ...
... b. The final electron acceptor in aerobic respiration is molecular oxygen; in anaerobic respiration, it is another inorganic molecule. c. In cyclic photophosphorylation, electrons are returned to chlorophyll. In noncyclic photophosphorylation, chlorophyll receives electrons from ...
SLIB biochemistry homework
... reaction occurring and use the formulae on Table 22 of the Data Booklet to write a balanced equation. 27) Olive oil has an energy value that is about twice that of cane sugar. Explain why the energy value of a fat is much higher than a carbohydrate. 28) Outline the difference between a micronutrient ...
... reaction occurring and use the formulae on Table 22 of the Data Booklet to write a balanced equation. 27) Olive oil has an energy value that is about twice that of cane sugar. Explain why the energy value of a fat is much higher than a carbohydrate. 28) Outline the difference between a micronutrient ...
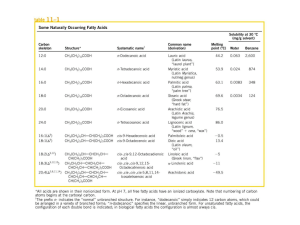
Free Fatty acids - Sheffield Metabolic Laboratory
... metabolites (IMs), include lactate, pyruvate, acetoacetate as well as 3-hydroxybutyrate and free fatty acids (or non-esterified, NEFA). All are normally present in blood and have a vital role in energy metabolism. These compounds are linked through a number of different pathways, which interact depe ...
... metabolites (IMs), include lactate, pyruvate, acetoacetate as well as 3-hydroxybutyrate and free fatty acids (or non-esterified, NEFA). All are normally present in blood and have a vital role in energy metabolism. These compounds are linked through a number of different pathways, which interact depe ...
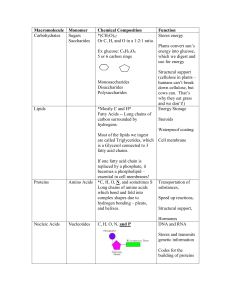
Chapter 3 Review Questions
... 10. _____Lipids___________ are a source of long-term stored energy. 11. Organic molecules that have the same chemical formula but different structural arrangements are called __isomers_________. 12. Carbohydrates are important because they __are the main source of energy for living things. 13. Meat, ...
... 10. _____Lipids___________ are a source of long-term stored energy. 11. Organic molecules that have the same chemical formula but different structural arrangements are called __isomers_________. 12. Carbohydrates are important because they __are the main source of energy for living things. 13. Meat, ...
L -Glutamic acid (G1251) - Product Information Sheet - Sigma
... L-Glutamic acid is one of the two amino acids that contains a carboxylic acid group in its side chains. Glutamic acid is commonly referred to as "glutamate", because its carboxylic acid side chain will be deprotonated and thus negatively charged in its anionic form at physiological pH. In amino acid ...
... L-Glutamic acid is one of the two amino acids that contains a carboxylic acid group in its side chains. Glutamic acid is commonly referred to as "glutamate", because its carboxylic acid side chain will be deprotonated and thus negatively charged in its anionic form at physiological pH. In amino acid ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... NADH and FADH2 are put through the chain so that their energy can be used to convert ADP into ATP These reactions require oxygen, which accepts the H+ ions to form water Occurs in the mitochondria The entire process of aerobic respiration produces 36 ATP molecules ...
... NADH and FADH2 are put through the chain so that their energy can be used to convert ADP into ATP These reactions require oxygen, which accepts the H+ ions to form water Occurs in the mitochondria The entire process of aerobic respiration produces 36 ATP molecules ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... NADH and FADH2 are put through the chain so that their energy can be used to convert ADP into ATP These reactions require oxygen, which accepts the H+ ions to form water Occurs in the mitochondria The entire process of aerobic respiration produces 36 ATP molecules ...
... NADH and FADH2 are put through the chain so that their energy can be used to convert ADP into ATP These reactions require oxygen, which accepts the H+ ions to form water Occurs in the mitochondria The entire process of aerobic respiration produces 36 ATP molecules ...
Fermentation
... sugars. Small amounts of ethanol and isopropanol may also be formed. • Butanol and acetone were discovered as the main end products of fermentation by Clostridium ...
... sugars. Small amounts of ethanol and isopropanol may also be formed. • Butanol and acetone were discovered as the main end products of fermentation by Clostridium ...
CHM 105 - Test 3 Review
... 23. Give two other names for the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. 24. Glycolysis begins with the molecule _____________ and ends with the molecule ______________. 25. What organelle produces most of the cell’s ATP? By what pathway? 26. The conversion of glucose to CO2 yields approximately ____ ATP. 2 ...
... 23. Give two other names for the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. 24. Glycolysis begins with the molecule _____________ and ends with the molecule ______________. 25. What organelle produces most of the cell’s ATP? By what pathway? 26. The conversion of glucose to CO2 yields approximately ____ ATP. 2 ...
Regulation of metabolism by PPARs and Angiopoietin like proteins
... fasting-induced adipose factor) leads to a rapid reduction in adipose tissue LPL activity during fasting. The collective data point to a scenario where ANGPTL4 is the central component of a feedback mechanism that regulates plasma triglyceride hydrolysis and subsequent tissue fatty acid uptake in re ...
... fasting-induced adipose factor) leads to a rapid reduction in adipose tissue LPL activity during fasting. The collective data point to a scenario where ANGPTL4 is the central component of a feedback mechanism that regulates plasma triglyceride hydrolysis and subsequent tissue fatty acid uptake in re ...
02.Products of Biochemical Engineering.web
... BC) – isopropanol --- acetone – sorbitol --- sorbose (manufacture of vit.C) ...
... BC) – isopropanol --- acetone – sorbitol --- sorbose (manufacture of vit.C) ...
(i)
... with formation of hydrogen/ NADH2 which reduce pyruvic acid to ethanol and carbon dioxide (c) Glucose is the substrate of glycolysis and therefore adding glucose to tube A accounts for its fastest rate. (d) C > B / A> A/B In test tube C, fluoride inhibits the step of Glycerate phosphate to PEP, with ...
... with formation of hydrogen/ NADH2 which reduce pyruvic acid to ethanol and carbon dioxide (c) Glucose is the substrate of glycolysis and therefore adding glucose to tube A accounts for its fastest rate. (d) C > B / A> A/B In test tube C, fluoride inhibits the step of Glycerate phosphate to PEP, with ...
Cellular Respiration
... Decomposition of glucose to pyruvate Nine intermediate products are formed ...
... Decomposition of glucose to pyruvate Nine intermediate products are formed ...
Biochemistry Test Review
... List the five natural elements which make up 96% of the human body. What is an organic compound vs. inorganic? List the total number of atoms in the following compound: C18H36O2 Elements with a different number of neutrons that protons such as Carbon-13 and Carbon-14 are considered______________. Ex ...
... List the five natural elements which make up 96% of the human body. What is an organic compound vs. inorganic? List the total number of atoms in the following compound: C18H36O2 Elements with a different number of neutrons that protons such as Carbon-13 and Carbon-14 are considered______________. Ex ...
BDS Ist YEAR EXAMINATION 2008-09
... Define isoenzymes. Discuss the role of isoenzymes in clinical diagnosis with suitable examples. ...
... Define isoenzymes. Discuss the role of isoenzymes in clinical diagnosis with suitable examples. ...
C h e m g u id e –... AMINO ACIDS: INTRODUCTION
... R-CH-COOb) There will be ionic bonds between the separate molecules, and these take more energy to break that other intermolecular forces. c) There are attractions between the very polar water molecules and the zwitterions which help to supply the energy needed to break up the amino acid crystal. d) ...
... R-CH-COOb) There will be ionic bonds between the separate molecules, and these take more energy to break that other intermolecular forces. c) There are attractions between the very polar water molecules and the zwitterions which help to supply the energy needed to break up the amino acid crystal. d) ...
Learning Check
... in the presence of water and heat. What will be the products of this reaction? To write the hydrolysis products, separate the compound at the ester bond. Complete the formula of the carboxylic acid by adding –OH (from water) to the carbonyl group and –H (from water) to the alcohol. ...
... in the presence of water and heat. What will be the products of this reaction? To write the hydrolysis products, separate the compound at the ester bond. Complete the formula of the carboxylic acid by adding –OH (from water) to the carbonyl group and –H (from water) to the alcohol. ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.