4 - Clark College
... • Describe what substrates enter and what products exit glycolysis, when oxygen is available to the cell. • Name the coenzyme of glycolysis and its role in metabolism. • Identify where in the cell the reactions of glycolysis occurs. Citric Acid Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation • Describe what sub ...
... • Describe what substrates enter and what products exit glycolysis, when oxygen is available to the cell. • Name the coenzyme of glycolysis and its role in metabolism. • Identify where in the cell the reactions of glycolysis occurs. Citric Acid Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation • Describe what sub ...
In Vivo Characterization of 3-Ketoacyl-acyl-carrier protein
... 2Center for Biorenewable Chemicals (CBiRC), Iowa State University, Ames, IA 50010 Introduction: 3-ketoacyl-acyl-carrier protein (ACP) synthase III (KASIII) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction acetylCoA + malonyl-ACP acetoacetyl-ACP + CoA + CO2. This enzyme participates in fatty acid ...
... 2Center for Biorenewable Chemicals (CBiRC), Iowa State University, Ames, IA 50010 Introduction: 3-ketoacyl-acyl-carrier protein (ACP) synthase III (KASIII) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction acetylCoA + malonyl-ACP acetoacetyl-ACP + CoA + CO2. This enzyme participates in fatty acid ...
aerobic vs anerobic ws - Hicksville Public Schools
... 16. Glycolysis begins with glucose and produces a. starch` c. acetyl CoA b. lactic acid d. pyruvic acid 17. Energy is released from ATP when the bond is broken between a. two phosphate groups c. ribose and a phosphate group b. adenine and ribose d. adenine and a phosphate group 18. Glycolysis takes ...
... 16. Glycolysis begins with glucose and produces a. starch` c. acetyl CoA b. lactic acid d. pyruvic acid 17. Energy is released from ATP when the bond is broken between a. two phosphate groups c. ribose and a phosphate group b. adenine and ribose d. adenine and a phosphate group 18. Glycolysis takes ...
26,6 Synthesis of omino ocids
... seen, cr-ketoglutarateaccepts amino groups from other amino acids in transamination to give glutamic acid, and arginine is formed in the urea cycle. TWo other nonessential amino acids-aspartic acid and alaninemay be qmthesized directly from cr-ketoacidsbecausethe reactions catalyzed by the transamin ...
... seen, cr-ketoglutarateaccepts amino groups from other amino acids in transamination to give glutamic acid, and arginine is formed in the urea cycle. TWo other nonessential amino acids-aspartic acid and alaninemay be qmthesized directly from cr-ketoacidsbecausethe reactions catalyzed by the transamin ...
Genetics Lab - Identification of a Nucleic Acid
... Each group will be given a nucleic acid sample to analyze over the next few weeks. You must determine whether the nucleic acid is DNA or RNA, whether it is single-stranded or double-stranded. Based on this information, you should be able to identify the Virulent Virus. The following equipment and re ...
... Each group will be given a nucleic acid sample to analyze over the next few weeks. You must determine whether the nucleic acid is DNA or RNA, whether it is single-stranded or double-stranded. Based on this information, you should be able to identify the Virulent Virus. The following equipment and re ...
Diversity of Metabolism in Procaryotes
... level phosphorylations that occur during the Embden Meyerhof pathway, but they occur in all other fermentation pathways which have an Embden-Meyerhof component. (c) is a substrate level phosphorylation found in Clostridium and Bifidobacterium. These are two anaerobic (fermentative) bacteria who lear ...
... level phosphorylations that occur during the Embden Meyerhof pathway, but they occur in all other fermentation pathways which have an Embden-Meyerhof component. (c) is a substrate level phosphorylation found in Clostridium and Bifidobacterium. These are two anaerobic (fermentative) bacteria who lear ...
Capryloyl Salicylic Acid Technical Data Sheet
... Capryloyl Salicylic Acid is an exfoliant, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic. It’s used to treat the appearance of dry damaged skin, reducing dry patches/flaking and restoring suppleness to the skin. This means that they not only exfoliate the upper layer of skin, but also penetrate deep through the e ...
... Capryloyl Salicylic Acid is an exfoliant, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic. It’s used to treat the appearance of dry damaged skin, reducing dry patches/flaking and restoring suppleness to the skin. This means that they not only exfoliate the upper layer of skin, but also penetrate deep through the e ...
Fermentation (Anaerobic Respiration)
... Calorie- amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 g of water 1 °C. Unit of measurement for energy found in food. ...
... Calorie- amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 g of water 1 °C. Unit of measurement for energy found in food. ...
Requirements for Test Review-Solutions-Acid-Base-Grade 11-2015
... know experimentally which is the stronger electrolyte) (answer: light bulb experiment (which is brighter, more dim), rate of reaction with metal and metal carbonate for acids, measurement of pH) ...
... know experimentally which is the stronger electrolyte) (answer: light bulb experiment (which is brighter, more dim), rate of reaction with metal and metal carbonate for acids, measurement of pH) ...
PRODUCT FACT SHEET - Taylormade Horse Supplies
... Equine exertional rhabdomyolysis (Tying-Up). ER occurs when there is an inadequate flow of blood to the muscles of an exercising horse. The muscle cells, lacking in oxygen, begin to function anaerobically to produce the needed ATP. The anaerobic work creates a buildup of waste products, acid, and he ...
... Equine exertional rhabdomyolysis (Tying-Up). ER occurs when there is an inadequate flow of blood to the muscles of an exercising horse. The muscle cells, lacking in oxygen, begin to function anaerobically to produce the needed ATP. The anaerobic work creates a buildup of waste products, acid, and he ...
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 7-1 Glycolysis and Fermentation
... Short Answer-Answer the following questions in complete sentences. 1. In what part of the mitochondria does the Krebs cycle take place? ___________________ 2. In what part of the mitochondria does the electron transport chain occur? _____________ _____________________________________________________ ...
... Short Answer-Answer the following questions in complete sentences. 1. In what part of the mitochondria does the Krebs cycle take place? ___________________ 2. In what part of the mitochondria does the electron transport chain occur? _____________ _____________________________________________________ ...
REVISED Review 4 - Bonham Chemistry
... 5. A glycosidic bond occurs when a ____________ functional group on a sugar reacts with a __________________ functional group on another sugar. 6. Draw the reaction which results in trans fatty acids in processed foods. ...
... 5. A glycosidic bond occurs when a ____________ functional group on a sugar reacts with a __________________ functional group on another sugar. 6. Draw the reaction which results in trans fatty acids in processed foods. ...
6O2 + C6H12O6 ------------------------
... d. Uses NAD+ and FAD which are coenzymes made from Vitamin C III. Aerobic Respiration: Occurs when oxygen ______ available. a. Occurs in ______________________________________________ b. Two parts—Kreb’s cycle and Electron Transport chain ...
... d. Uses NAD+ and FAD which are coenzymes made from Vitamin C III. Aerobic Respiration: Occurs when oxygen ______ available. a. Occurs in ______________________________________________ b. Two parts—Kreb’s cycle and Electron Transport chain ...
Buffers - Philadelphia University
... raw materials and the specific roles of of molecules in life processes. – Do not reflect the composition of the biosphere – Examples on per atom basis, H in organisms = 49%, H in Earth’s crust = 0.22 %, Si in organisms = 0.033%, Si in Earth’s crust = 28%) ...
... raw materials and the specific roles of of molecules in life processes. – Do not reflect the composition of the biosphere – Examples on per atom basis, H in organisms = 49%, H in Earth’s crust = 0.22 %, Si in organisms = 0.033%, Si in Earth’s crust = 28%) ...
Unit 5: Hypercholesterolemia Section 1: Cholesterol A lipid that
... proteins are embedded. An HDL particle carries less cholesterol than a related lipoprotein, LDL, & may be correlated with a decreased risk of blood vessel blockage. A cholesterol-carrying particle in the blood, made up of cholesterol & other lipids surrounded by a single layer of phospholipids in wh ...
... proteins are embedded. An HDL particle carries less cholesterol than a related lipoprotein, LDL, & may be correlated with a decreased risk of blood vessel blockage. A cholesterol-carrying particle in the blood, made up of cholesterol & other lipids surrounded by a single layer of phospholipids in wh ...
Metabolic engineering Synthetic Biology
... Artemisinin : extracted from the leaves of Artemisia annua, or sweet wormwood, and has been used for more than 2,000 years by the Chinese as a herbal medicine called qinghaosu. The parasite that causes malaria has become at least partly resistant to every other treatment tried so far. Artemisinin is ...
... Artemisinin : extracted from the leaves of Artemisia annua, or sweet wormwood, and has been used for more than 2,000 years by the Chinese as a herbal medicine called qinghaosu. The parasite that causes malaria has become at least partly resistant to every other treatment tried so far. Artemisinin is ...
Bonding is more than attraction
... - It is a long chain of smaller molecules called nucleotides. • What is a nucleotide? - A nucleotide has three parts: a sugar, a base, and a phosphate group, which contains phosphorus and oxygen atoms. ...
... - It is a long chain of smaller molecules called nucleotides. • What is a nucleotide? - A nucleotide has three parts: a sugar, a base, and a phosphate group, which contains phosphorus and oxygen atoms. ...
Ch. 16 Calendar
... acids or only bases … mixtures of acids and bases is covered in the next chapter). *Perform calculations relating pH, pOH, pKa, pKb, Ka, Kb, Kw, [H3O+], [OH-], [HA], [B], % ionization in solutions containing one or more acid or one or more base. *Calculate or estimate the pH and/or concentration of ...
... acids or only bases … mixtures of acids and bases is covered in the next chapter). *Perform calculations relating pH, pOH, pKa, pKb, Ka, Kb, Kw, [H3O+], [OH-], [HA], [B], % ionization in solutions containing one or more acid or one or more base. *Calculate or estimate the pH and/or concentration of ...
Pantothenic Acid - Pure Encapsulations
... Nutrient Metabolism and Organ Function: Pantothenic acid is a precursor of coenzyme A (CoA), an important cofactor and acyl group carrier in cells. One of the main functions for CoA is the formation of acetyl-CoA, vital for cellular respiration and the metabolism of carbohydrates and fatty acids thr ...
... Nutrient Metabolism and Organ Function: Pantothenic acid is a precursor of coenzyme A (CoA), an important cofactor and acyl group carrier in cells. One of the main functions for CoA is the formation of acetyl-CoA, vital for cellular respiration and the metabolism of carbohydrates and fatty acids thr ...
Review of Glucose Metabolism File
... Review of Glucose Metabolism Match each of the following occurrences to the correct part of the glucose metabolism process. If more than one answer is correct, write all letters in the blank. A. Glycolysis B. Fermentation C. Cellular Respiration (aerobic) D. Krebs Cycle E. Electron Transport Chain _ ...
... Review of Glucose Metabolism Match each of the following occurrences to the correct part of the glucose metabolism process. If more than one answer is correct, write all letters in the blank. A. Glycolysis B. Fermentation C. Cellular Respiration (aerobic) D. Krebs Cycle E. Electron Transport Chain _ ...
Review over Glucose Metabolism
... Review over Glucose Metabolism Match each of the following occurrences to the correct part of the glucose metabolism process. If more than one answer is correct, write all letters in the blank. A. Glycolysis B. Fermentation C. Cellular Respiration (aerobic) D. Krebs Cycle E. Electron Transport Chain ...
... Review over Glucose Metabolism Match each of the following occurrences to the correct part of the glucose metabolism process. If more than one answer is correct, write all letters in the blank. A. Glycolysis B. Fermentation C. Cellular Respiration (aerobic) D. Krebs Cycle E. Electron Transport Chain ...
CHEM-643 Intermediary Metabolism Checklist for final group assignment on:
... Conclusions that are supported by well-analyzed data and associated discussion Conclusions that are supported by multiple tests Exceptional elements that show depth of investigation, understanding, and presentation. ...
... Conclusions that are supported by well-analyzed data and associated discussion Conclusions that are supported by multiple tests Exceptional elements that show depth of investigation, understanding, and presentation. ...
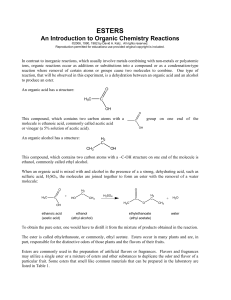
Esters - chymist.com
... In contrast to inorganic reactions, which usually involve metals combining with non-metals or polyatomic ions, organic reactions occur as additions or substitutions into a compound or as a condensation-type reaction where removal of certain atoms or groups cause two molecules to combine. One type of ...
... In contrast to inorganic reactions, which usually involve metals combining with non-metals or polyatomic ions, organic reactions occur as additions or substitutions into a compound or as a condensation-type reaction where removal of certain atoms or groups cause two molecules to combine. One type of ...
2016 department of medicine research day
... Co-Investigators: Jieping Yang, Mark Hsu, David Heber ...
... Co-Investigators: Jieping Yang, Mark Hsu, David Heber ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.