C483 Final Exam Study Guide The final will be held in Morrison 007
... molecule that you store in your liver. Circle the pathways/cycles below that are part of this overall transformation. Cross out any that are not. Gluconeogenesis, pentose phosphate pathway, glycogen synthesis, glycolysis, citric acid cycle B. Trace the metabolic path of this glutamate molecule throu ...
... molecule that you store in your liver. Circle the pathways/cycles below that are part of this overall transformation. Cross out any that are not. Gluconeogenesis, pentose phosphate pathway, glycogen synthesis, glycolysis, citric acid cycle B. Trace the metabolic path of this glutamate molecule throu ...
Amino Acid Analysis
... HCl is dried in a Speedvac and the resulting amino acids dissolved in 100 µl Beckman sample buffer that contains 2 nmol homoserine with the latter acting as a second internal standard to independently monitor transfer of the sample onto the analyzer. The instrument is calibrated with a 2 nmol mixtur ...
... HCl is dried in a Speedvac and the resulting amino acids dissolved in 100 µl Beckman sample buffer that contains 2 nmol homoserine with the latter acting as a second internal standard to independently monitor transfer of the sample onto the analyzer. The instrument is calibrated with a 2 nmol mixtur ...
A1988L783100001
... light-catalysed isomerism of ABA to the biologically inactive 2.trans isomer that had been detected in plant extracts but could have been formed during the workup. By exploiting the optical rotation of the natural material and l4Clabelled (j )-ABA, we showed that about 4 percent of the ABA occurred ...
... light-catalysed isomerism of ABA to the biologically inactive 2.trans isomer that had been detected in plant extracts but could have been formed during the workup. By exploiting the optical rotation of the natural material and l4Clabelled (j )-ABA, we showed that about 4 percent of the ABA occurred ...
Ch. 3 Vocabs
... monomer: a simple molecule that can combine with other like or unlike molecules to make a polymer polymer: a large molecule that is formed by more than five monomers, or small units macromolecule: a very large organic molecule, usually a polymer, composed of hundreds or thousands of atoms co ...
... monomer: a simple molecule that can combine with other like or unlike molecules to make a polymer polymer: a large molecule that is formed by more than five monomers, or small units macromolecule: a very large organic molecule, usually a polymer, composed of hundreds or thousands of atoms co ...
NSAIDs - Virtual Medic
... b. Acidic drug tends to be lipid soluble; readily being absorp in through the GI mucosa 2. Most absorp at intestinal mucosa due to high surface area and low motility Distribution 1. Hydrolyzes by esterases in tissue and blood by a. Acetic acid b. Salicylate 2. Salicylate is highly plasma protein bou ...
... b. Acidic drug tends to be lipid soluble; readily being absorp in through the GI mucosa 2. Most absorp at intestinal mucosa due to high surface area and low motility Distribution 1. Hydrolyzes by esterases in tissue and blood by a. Acetic acid b. Salicylate 2. Salicylate is highly plasma protein bou ...
Other ways to make ATP
... – Enzymes for metabolizing it might not be present – Chemical may be used, but more expensive – These differences can be used for identification ...
... – Enzymes for metabolizing it might not be present – Chemical may be used, but more expensive – These differences can be used for identification ...
Solutions to Questions in the Cellular Respiration booklet
... occur in the cytoplasm. While Krebs’s Cycle or Citric Acid and Electron ...
... occur in the cytoplasm. While Krebs’s Cycle or Citric Acid and Electron ...
Energy Releasing Pathways
... stream and is transported to liver where it is converted back into pyruvic acid. Used to make cheese and yogurt ...
... stream and is transported to liver where it is converted back into pyruvic acid. Used to make cheese and yogurt ...
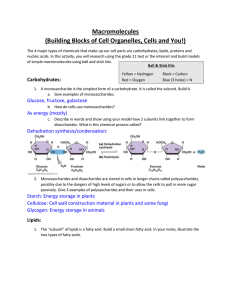
Macromolecules
... 3. Fatty acids can be attached (through dehydration synthesis) to different chemicals to perform different functions in the cell. Find two different types of lipids and record their function and the chemical that the fatty acids are attached to. ...
... 3. Fatty acids can be attached (through dehydration synthesis) to different chemicals to perform different functions in the cell. Find two different types of lipids and record their function and the chemical that the fatty acids are attached to. ...
Acid-Base Principles to Organic Acids
... ID structural features and reactive sites (alpha C, beta C, LG, etc.) ID Nu- and E+ use curved arrows to show bonds breaking and forming show delocalized electrons with resonance structures. Key ideas: Organic acids are weak, e.g., acetic acid pKa = 5 The charge on an acid depends on pH and pK (see ...
... ID structural features and reactive sites (alpha C, beta C, LG, etc.) ID Nu- and E+ use curved arrows to show bonds breaking and forming show delocalized electrons with resonance structures. Key ideas: Organic acids are weak, e.g., acetic acid pKa = 5 The charge on an acid depends on pH and pK (see ...
biochem study guide
... 7. Differentiate between the various levels of protein structure-primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary. Explain why proteins are so sensitive to changes in temperature and pH. 8. Diagram an individual nucleotide, identify the five-carbon sugar, the phosphate group and the nitrogenous base. 9. ...
... 7. Differentiate between the various levels of protein structure-primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary. Explain why proteins are so sensitive to changes in temperature and pH. 8. Diagram an individual nucleotide, identify the five-carbon sugar, the phosphate group and the nitrogenous base. 9. ...
Biochemistry PPT
... Found in all cells Makes up the cell membrane 2 layers of phospholipids lipid bilayer ...
... Found in all cells Makes up the cell membrane 2 layers of phospholipids lipid bilayer ...
Year 12 Chemistry: Chapter 14 From Organic Molecules to Medicines
... Felix Hoffman synthesis salicylic acid and replaced the OH functional group with an ester functional group to form acetylsalicylic acid. This is known commercially as aspirin. The production of a substance to be used as a medicine usually requires a number of chemical steps, known as synthetic pathw ...
... Felix Hoffman synthesis salicylic acid and replaced the OH functional group with an ester functional group to form acetylsalicylic acid. This is known commercially as aspirin. The production of a substance to be used as a medicine usually requires a number of chemical steps, known as synthetic pathw ...
Document
... 2. A Roundup Ready plant is one that has been genetically modified so that an enzyme (EPSP synthase) can no longer bind to the active ingredient (glyphosphate) which is a competitive inhibitor of A) shikimate (in the aromatic amino acid pathway). B) tryptophan. C) lysine. D) phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP ...
... 2. A Roundup Ready plant is one that has been genetically modified so that an enzyme (EPSP synthase) can no longer bind to the active ingredient (glyphosphate) which is a competitive inhibitor of A) shikimate (in the aromatic amino acid pathway). B) tryptophan. C) lysine. D) phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP ...
Amino acid Metabolism 2
... 2. A Roundup Ready plant is one that has been genetically modified so that an enzyme (EPSP synthase) can no longer bind to the active ingredient (glyphosphate) which is a competitive inhibitor of A) shikimate (in the aromatic amino acid pathway). B) tryptophan. C) lysine. D) phosphoenolpyruvate (P ...
... 2. A Roundup Ready plant is one that has been genetically modified so that an enzyme (EPSP synthase) can no longer bind to the active ingredient (glyphosphate) which is a competitive inhibitor of A) shikimate (in the aromatic amino acid pathway). B) tryptophan. C) lysine. D) phosphoenolpyruvate (P ...
An_explanation_of_the_pH_scale
... ion is an atom or a group of atoms that carries a positive or a negative charge as a result of having lost or gained one or more electrons. A free electron or other subatomic-charged particle is also referred to as an ion. ...
... ion is an atom or a group of atoms that carries a positive or a negative charge as a result of having lost or gained one or more electrons. A free electron or other subatomic-charged particle is also referred to as an ion. ...
9-5 fermentation reading KEY
... a. Biochemistry – in alcoholic fermentation, two steps turn pyruvate into a waste molecule (ethanol). In lactic acid fermentation, one step turns pyruvate into a waste molecule (lactic acid). In both cases, the sole purpose of wasting pyruvate like this is because in the process NADH is converted in ...
... a. Biochemistry – in alcoholic fermentation, two steps turn pyruvate into a waste molecule (ethanol). In lactic acid fermentation, one step turns pyruvate into a waste molecule (lactic acid). In both cases, the sole purpose of wasting pyruvate like this is because in the process NADH is converted in ...
BIo Exam Trashketball Review Questions
... when the microorganisms in the milk produce acid. Which of these processes would you expect to be key in the production of yogurt? a) b) c) d) ...
... when the microorganisms in the milk produce acid. Which of these processes would you expect to be key in the production of yogurt? a) b) c) d) ...
5 Lipid and Protein Metabolism
... fatty acid metabolism during fasting or carbohydrate restriction to use as energy instead of glucose • 2 of the 3 are used by the heart and brain and muscle for ATP synthesis – Picked up by cells and used to make acetyl-CoA – In the brain ...
... fatty acid metabolism during fasting or carbohydrate restriction to use as energy instead of glucose • 2 of the 3 are used by the heart and brain and muscle for ATP synthesis – Picked up by cells and used to make acetyl-CoA – In the brain ...
Fatty Acid Oxidation and Ketone Bodies
... Fed state: Malonyl-CoA formed in the fed state is a potent inhibitor of CPT-1. Under these conditions, free fatty acids enter the liver cell in low concentrations and are nearly all esterified to acylglycerols and transported out as VLDL. Starvation: Free fatty acid concentration increases with sta ...
... Fed state: Malonyl-CoA formed in the fed state is a potent inhibitor of CPT-1. Under these conditions, free fatty acids enter the liver cell in low concentrations and are nearly all esterified to acylglycerols and transported out as VLDL. Starvation: Free fatty acid concentration increases with sta ...
Enter o to this page the details for the document
... A popular cure for acid indigestion is to take an antacid, these stop acid indigestion by neutralising the acid in the stomach with a mild alkaline substance. Some of the more modern antacids work by stopping the stomach from producing the acid in the first place, often you can work out the differen ...
... A popular cure for acid indigestion is to take an antacid, these stop acid indigestion by neutralising the acid in the stomach with a mild alkaline substance. Some of the more modern antacids work by stopping the stomach from producing the acid in the first place, often you can work out the differen ...
Sample exam 1
... used for net synthesis of carbohydrates in animals, radioactive carbon from 14C-labeled acetate can be found in newly synthesized glucose (for example, in liver glycogen) in animal tracer studies. Explain which carbons of glucose you would expect to be the first to be labeled by the 14C-labeled acet ...
... used for net synthesis of carbohydrates in animals, radioactive carbon from 14C-labeled acetate can be found in newly synthesized glucose (for example, in liver glycogen) in animal tracer studies. Explain which carbons of glucose you would expect to be the first to be labeled by the 14C-labeled acet ...
Photosynthesis
... Step 4: Hydrogen is trapped by NADP Step 5: Oxygen is released to atmosphere when water is split ...
... Step 4: Hydrogen is trapped by NADP Step 5: Oxygen is released to atmosphere when water is split ...
Biosynthesis of Macromolecules
... Macromolecules Anabolism - use energy (ATP) from catabolism - use carbon from sugars, lipids, proteins, or any other carbon source (xenobiotics) to build cellular components ...
... Macromolecules Anabolism - use energy (ATP) from catabolism - use carbon from sugars, lipids, proteins, or any other carbon source (xenobiotics) to build cellular components ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.