17 The Citric Acid Cycle: The latabolism of Acetyl
... I The major function of the citric acid cycle is to act I the final common pathway for the oxidation of carihydrate, lipids, and protein, since glucose, fatty Is, and many amino acids are all metabolized to tylCoA or intermediates of the cycle. It also plays |major role in gluconeogenesis, transamin ...
... I The major function of the citric acid cycle is to act I the final common pathway for the oxidation of carihydrate, lipids, and protein, since glucose, fatty Is, and many amino acids are all metabolized to tylCoA or intermediates of the cycle. It also plays |major role in gluconeogenesis, transamin ...
Impact of Malolactic Fermentation Strain on Wine Composition
... acid as a very poor carbon and energy source in the fermenter and in the bottle. • Conversion of malic to lactic acid by a controlled malolactic fermentation prior to bottling eliminates the instability. • It can be a problem to start, very slow activity, long time to finish and can start and stop. ...
... acid as a very poor carbon and energy source in the fermenter and in the bottle. • Conversion of malic to lactic acid by a controlled malolactic fermentation prior to bottling eliminates the instability. • It can be a problem to start, very slow activity, long time to finish and can start and stop. ...
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... Electron Transport Chain • Electron Transport Chain uses the electron carriers (NADH and FADH2) to pass electrons down the protein chain and slowly release energy that is used to form ATP and water molecules • Electron Transport Chain transfers the most energy ...
... Electron Transport Chain • Electron Transport Chain uses the electron carriers (NADH and FADH2) to pass electrons down the protein chain and slowly release energy that is used to form ATP and water molecules • Electron Transport Chain transfers the most energy ...
Document
... Pathway of conversion of (A) galactose to glucose in the liver and (B) glucose to lactose in the lactating mammary gland. ...
... Pathway of conversion of (A) galactose to glucose in the liver and (B) glucose to lactose in the lactating mammary gland. ...
Final Exam: Multiple Choice Portion Biochem Block Spring 2016
... C) glucose is produced from carbon dioxide D) electrons flow from NADH to oxygen, producing ATP 25. Which statement describes best what happens in the citric acid cycle? A) citrate condenses to form a protein B) glucose is cleaved into two molecules of pyruvate, releasing energy C) acetyl CoA is oxi ...
... C) glucose is produced from carbon dioxide D) electrons flow from NADH to oxygen, producing ATP 25. Which statement describes best what happens in the citric acid cycle? A) citrate condenses to form a protein B) glucose is cleaved into two molecules of pyruvate, releasing energy C) acetyl CoA is oxi ...
FERMENTATION: an anaerobic biological reaction process in which
... fermentation: catabolic reactions producing ATP in which organic compounds serve as both the primary electron donor and ultimate electron acceptor and ATP is produced by substrate level phosophorylation ...
... fermentation: catabolic reactions producing ATP in which organic compounds serve as both the primary electron donor and ultimate electron acceptor and ATP is produced by substrate level phosophorylation ...
Folic acid
... • Can be used iv with caution • Toxicity primarily nephro- and neurotoxicity – Expected to have low selective toxicity because of detergent effects on cell membranes. ...
... • Can be used iv with caution • Toxicity primarily nephro- and neurotoxicity – Expected to have low selective toxicity because of detergent effects on cell membranes. ...
1. Triglyceride degradation is not influenced by: A cAMP B Glucagon
... A 5 molecules of mevalonate B 6 isoprene units C 15 molecules of acetyl CoA D 3 molecules of farnesyl pyrophosphate 8. Which of the following lipoproteins participates in reverse cholesterol transport: A VLDL B HDL C LDL D chylomicrons 9. Which of the following occurs when cholesterol enters cells: ...
... A 5 molecules of mevalonate B 6 isoprene units C 15 molecules of acetyl CoA D 3 molecules of farnesyl pyrophosphate 8. Which of the following lipoproteins participates in reverse cholesterol transport: A VLDL B HDL C LDL D chylomicrons 9. Which of the following occurs when cholesterol enters cells: ...
C483 Final Exam Study Guide The final will be held in Chemistry
... concepts for the course. It will be about 1/3 multiple choice, 1/3 short answer, and 1/3 problems, some of which are taken directly from the list below. These questions will also serve as a good review for the major topics of the course. You are encouraged to use them as a study guide. You may work ...
... concepts for the course. It will be about 1/3 multiple choice, 1/3 short answer, and 1/3 problems, some of which are taken directly from the list below. These questions will also serve as a good review for the major topics of the course. You are encouraged to use them as a study guide. You may work ...
fatty acid synthesis
... synthesis. Phosphorylation of ACC, for example a result of activation of PKA by stress or exercise switches on fatty acid oxidation (via phosphorylation and inhibition of ACC-2 resulting in decreased malonyl CoA levels) while switching off fatty acid synthesis (via phosphorylation and inhibition of ...
... synthesis. Phosphorylation of ACC, for example a result of activation of PKA by stress or exercise switches on fatty acid oxidation (via phosphorylation and inhibition of ACC-2 resulting in decreased malonyl CoA levels) while switching off fatty acid synthesis (via phosphorylation and inhibition of ...
Begin by going to the address below
... 3. What is the most important monosaccharide on the earth? ...
... 3. What is the most important monosaccharide on the earth? ...
ORGANIC ACIDS – Ketone/Fatty Acids (urine)
... urine collection. The organic acid tests assess a wide range of cellular and physiological processes including intestinal dysbiosis, energy production, nutrient cofactor requirements and neurotransmitter metabolism. Marked accumulation of specific organic acids detected in urine often signals a meta ...
... urine collection. The organic acid tests assess a wide range of cellular and physiological processes including intestinal dysbiosis, energy production, nutrient cofactor requirements and neurotransmitter metabolism. Marked accumulation of specific organic acids detected in urine often signals a meta ...
Revision - Exercise Phys
... The Aerobic System The Aerobic system produces its energy by utilising oxygen. It is performed through a series of chemical reactions known as the Krebs Cycle. Here we have the continued breakdown of glycogen from when it becomes pyruvic acid and enters the mitochondria. Fats (and in extreme circum ...
... The Aerobic System The Aerobic system produces its energy by utilising oxygen. It is performed through a series of chemical reactions known as the Krebs Cycle. Here we have the continued breakdown of glycogen from when it becomes pyruvic acid and enters the mitochondria. Fats (and in extreme circum ...
Metabolism II
... Electrons flow from carriers with more negative E0 to carriers with more positive E0 ...
... Electrons flow from carriers with more negative E0 to carriers with more positive E0 ...
BIOCHEMISTRY (CHEM 360)
... Many cancer cells grow anaerobically, and PDH is not active in these cells. Speculate the effect of DCA on cancer cells. Outline your train of thought. Inhibiting PDH-phosphorylase kinase would activate PDH, which allow the citric acid cycle to function at its full rate, thus maintain aerobic condit ...
... Many cancer cells grow anaerobically, and PDH is not active in these cells. Speculate the effect of DCA on cancer cells. Outline your train of thought. Inhibiting PDH-phosphorylase kinase would activate PDH, which allow the citric acid cycle to function at its full rate, thus maintain aerobic condit ...
Review 1 - Allen ISD
... a. composed of building blocks called amino acids b. insoluble in water and are used by the body for energy storage and insulation c. complex biomolecules that store genetic information d. organic compounds used by cells to store and release energy ...
... a. composed of building blocks called amino acids b. insoluble in water and are used by the body for energy storage and insulation c. complex biomolecules that store genetic information d. organic compounds used by cells to store and release energy ...
nucleic acids
... a. composed of building blocks called amino acids b. insoluble in water and are used by the body for energy storage and insulation c. complex biomolecules that store genetic information d. organic compounds used by cells to store and release energy ...
... a. composed of building blocks called amino acids b. insoluble in water and are used by the body for energy storage and insulation c. complex biomolecules that store genetic information d. organic compounds used by cells to store and release energy ...
Document
... This overview of the metabolic networks show why we now need computers, particulary if we want to predict cell behaviour! In recent years these needs have led to the development of ”Systems Biology”, which involves mathematical analysis and modelling of living cells. Hint: think about this figure b ...
... This overview of the metabolic networks show why we now need computers, particulary if we want to predict cell behaviour! In recent years these needs have led to the development of ”Systems Biology”, which involves mathematical analysis and modelling of living cells. Hint: think about this figure b ...
Chemical Equation Interpretations – Match the chemical equation
... Chemical Equation Interpretations – Match the chemical equation with the appropriate interpretation. __ 1. 2CH4O(l) + O2(g) 2CH2O(l) + 2H2O(l) __ 2. NH2Cl(g) NH2Cl(aq) ...
... Chemical Equation Interpretations – Match the chemical equation with the appropriate interpretation. __ 1. 2CH4O(l) + O2(g) 2CH2O(l) + 2H2O(l) __ 2. NH2Cl(g) NH2Cl(aq) ...
Alpha-Lipoic Acid The Universal Antioxidant
... glucose disposal. This important coenzyme appears to be necessary for the normal transport of blood glucose into the cell. This may be explained by its functions in the glucose-metabolizing enzymes, PDH and alphaKGDH, but some researchers suspect a more direct role in cellular glucose uptake at the ...
... glucose disposal. This important coenzyme appears to be necessary for the normal transport of blood glucose into the cell. This may be explained by its functions in the glucose-metabolizing enzymes, PDH and alphaKGDH, but some researchers suspect a more direct role in cellular glucose uptake at the ...
Section 2.3 - Father Michael McGivney Catholic Academy
... backed up. • NADH cannot get recycled back to NAD+ to pick up more electrons. • Organisms have evolved a way to recycle NAD+ and allow glycolysis to continue. ...
... backed up. • NADH cannot get recycled back to NAD+ to pick up more electrons. • Organisms have evolved a way to recycle NAD+ and allow glycolysis to continue. ...
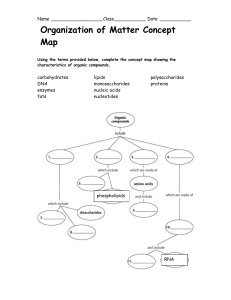
Polymers vs. monomers wkst. and concept map
... Nucleic Acids 19. You notice a thin layer of a substance that is slimy and doesn’t mix with water. It is also liquid at room temperature, and was found in the kitchen. You may infer that it is EXACTLY what type of macromolecule? (The macromolecule AND the kind of macromolecule. Look in your notes!) ...
... Nucleic Acids 19. You notice a thin layer of a substance that is slimy and doesn’t mix with water. It is also liquid at room temperature, and was found in the kitchen. You may infer that it is EXACTLY what type of macromolecule? (The macromolecule AND the kind of macromolecule. Look in your notes!) ...
2.1 Molecules and metabolism
... • Anabolism is the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler molecules including the formation of macromolecules from monomers by condensation reactions. • Catabolism is the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules including the hydrolysis of macromolecules into monomers. Applications ...
... • Anabolism is the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler molecules including the formation of macromolecules from monomers by condensation reactions. • Catabolism is the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules including the hydrolysis of macromolecules into monomers. Applications ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.