Balancing Reactions 1
... 4. Assign Oxidation numbers to the element specified in each group of compounds. a. N in: i. NO v. N2H4 ii. N2O3 vi. NH2OH iii. N2O4 vii. HNO2 iv. NH3 viii. HNO3 b. Cr in: i. CrO2-1 iii. CrO4-2 ...
... 4. Assign Oxidation numbers to the element specified in each group of compounds. a. N in: i. NO v. N2H4 ii. N2O3 vi. NH2OH iii. N2O4 vii. HNO2 iv. NH3 viii. HNO3 b. Cr in: i. CrO2-1 iii. CrO4-2 ...
PARA-AMINOBENZOIC ACID (PABA) Functions of
... Helps utilization of pantothenic acid (B-5); Topical application protects against skin cancer; Topically applied sunscreen — prevents & soothes pain & damage of sunburn; Said to soothe pain of burns even better than vitamin E; Useful for treating some parasitic diseases, including Rocky Mountain spo ...
... Helps utilization of pantothenic acid (B-5); Topical application protects against skin cancer; Topically applied sunscreen — prevents & soothes pain & damage of sunburn; Said to soothe pain of burns even better than vitamin E; Useful for treating some parasitic diseases, including Rocky Mountain spo ...
BIOLOGY
... in the mitochondria. In this chain, electrons are transferred from one protein to another, RELEASING energy in the process. OXYGEN is the final electron acceptor in this process. Oxygen reacts with hydrogen and electrons to form water (H2O). Oxygen is important in the body since without it the prote ...
... in the mitochondria. In this chain, electrons are transferred from one protein to another, RELEASING energy in the process. OXYGEN is the final electron acceptor in this process. Oxygen reacts with hydrogen and electrons to form water (H2O). Oxygen is important in the body since without it the prote ...
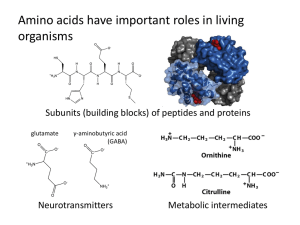
5.Amino acids
... rod capable of growing on a simple mineral salt medium with glucose, provided that biotin is also added. Production of L-glutamic acid by C. glutamicum is maximal at a critical biotin concentration of 0.5 mg g-1 of dry cells, which is suboptimal for growth Detergents like Tween-40, addition of penic ...
... rod capable of growing on a simple mineral salt medium with glucose, provided that biotin is also added. Production of L-glutamic acid by C. glutamicum is maximal at a critical biotin concentration of 0.5 mg g-1 of dry cells, which is suboptimal for growth Detergents like Tween-40, addition of penic ...
Vitamin-similar substances
... • Ubiquinone is another name for CoQ10, a potent antioxidant naturally produced by the body and important to cell functioning and development. Ubiquinone naturally decreases with aging, and it is used in cosmetics and personal care products (in a wide variety of formulas) as an anti-aging ingredien ...
... • Ubiquinone is another name for CoQ10, a potent antioxidant naturally produced by the body and important to cell functioning and development. Ubiquinone naturally decreases with aging, and it is used in cosmetics and personal care products (in a wide variety of formulas) as an anti-aging ingredien ...
Glycolysis in the Cytoplasm
... -splits one molecule of glucose (6 carbon molecule) into two molecules of a 3-carbon acid - pyruvic acid (pyruvate). Glycolysis occurs in two phases: 1. Glycolysis I - Energy Investment Phase ATP is used to split the 6-carbon molecule into two 3-carbon molecules 2. Glycolysis II - Energy Payoff Phas ...
... -splits one molecule of glucose (6 carbon molecule) into two molecules of a 3-carbon acid - pyruvic acid (pyruvate). Glycolysis occurs in two phases: 1. Glycolysis I - Energy Investment Phase ATP is used to split the 6-carbon molecule into two 3-carbon molecules 2. Glycolysis II - Energy Payoff Phas ...
Introduction to 9th Grade Biology
... • Our body needs them for insulation, cushioning, and energy storage. • Three important groups – Fats & Oils – Phospholipids (cell membrane) – Steroids (cholesterol) ...
... • Our body needs them for insulation, cushioning, and energy storage. • Three important groups – Fats & Oils – Phospholipids (cell membrane) – Steroids (cholesterol) ...
Fish Oil - Sundown Naturals
... Health experts agree: not all fat is bad for you. Omega-3 fatty acids are considered some of the “good” fats important for cellular, heart and metabolic health.* Getting an adequate amount of fatty acids to promote heart health is not easy.* Sundown Naturals’ Fish Oil 1000 mg contains eicosapentaeno ...
... Health experts agree: not all fat is bad for you. Omega-3 fatty acids are considered some of the “good” fats important for cellular, heart and metabolic health.* Getting an adequate amount of fatty acids to promote heart health is not easy.* Sundown Naturals’ Fish Oil 1000 mg contains eicosapentaeno ...
MAKEUP: Briefly discuss functions of the liver
... o Protein synthesis Lipoproteins - Catabolic Functions: o CHO: Glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis (via acetyl CoA formation from fatty acid breakdown) → maintain BSL o Fats: ↑lipolysis Ketone body formation Bile Acid formation (for fat absorption) o Proteins Ammonium formation (via glutathione ...
... o Protein synthesis Lipoproteins - Catabolic Functions: o CHO: Glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis (via acetyl CoA formation from fatty acid breakdown) → maintain BSL o Fats: ↑lipolysis Ketone body formation Bile Acid formation (for fat absorption) o Proteins Ammonium formation (via glutathione ...
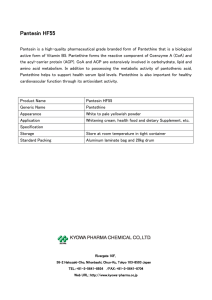
Pantesin HF55
... Pantesin HF55 Pantesin is a high-quality pharmaceutical grade branded form of Pantethine that is a biological active form of Vitamin B5. Pantethine forms the reactive component of Coenzyme A (CoA) and the acyl-carrier protein (ACP). CoA and ACP are extensively involved in carbohydrate, lipid and ami ...
... Pantesin HF55 Pantesin is a high-quality pharmaceutical grade branded form of Pantethine that is a biological active form of Vitamin B5. Pantethine forms the reactive component of Coenzyme A (CoA) and the acyl-carrier protein (ACP). CoA and ACP are extensively involved in carbohydrate, lipid and ami ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... II. State whether the following are true or false, if false, give reason ...
... II. State whether the following are true or false, if false, give reason ...
Fermentation and Biosynthetic Pathways File
... Microorganisms synthesize sugars and polysaccharides. The carbon atoms required to synthesize glucose are derived from the intermediates produced during glycolysis, Krebs cycle and from lipids or amino acids. Bacteria may assemble it into the more complex polysaccharides. Biosynthesis of Lipids Lipi ...
... Microorganisms synthesize sugars and polysaccharides. The carbon atoms required to synthesize glucose are derived from the intermediates produced during glycolysis, Krebs cycle and from lipids or amino acids. Bacteria may assemble it into the more complex polysaccharides. Biosynthesis of Lipids Lipi ...
2008 VFA Absorption
... • Total viscera requires 25% of the total energy requirement • Use of VFAs as an energy source spares glucose • Relatively minor use ...
... • Total viscera requires 25% of the total energy requirement • Use of VFAs as an energy source spares glucose • Relatively minor use ...
Monoammonium glutamate
... Monoammonium glutamate is the ammonium acid salt of glutamic acid, which is a natural essential amino acid. It is the most common excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain and is present in all complete proteins. Monoammonium glutamate has the ability to make bland and tasteless foods taste wonderful ...
... Monoammonium glutamate is the ammonium acid salt of glutamic acid, which is a natural essential amino acid. It is the most common excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain and is present in all complete proteins. Monoammonium glutamate has the ability to make bland and tasteless foods taste wonderful ...
ETC Details
... • How cells take molecules from food and turn them into molecules for growth and repair • Aka Metabolic Pool • Intermediaries of all cycles can be removed and used to build molecules! • Ex. pyruvate glucose • Acetyl CoA fatty acids ...
... • How cells take molecules from food and turn them into molecules for growth and repair • Aka Metabolic Pool • Intermediaries of all cycles can be removed and used to build molecules! • Ex. pyruvate glucose • Acetyl CoA fatty acids ...
Name
... Purpose: To model dehydration synthesis reactions resulting in the formation of either protein or lipid molecules. Materials: 14 black carbon atoms 13 red oxygen atoms ...
... Purpose: To model dehydration synthesis reactions resulting in the formation of either protein or lipid molecules. Materials: 14 black carbon atoms 13 red oxygen atoms ...
Slide 1
... Esters have strong, fragrant aromas and are the cause of the odors and flavors of pineapple, banana, wintergreen and oranges. Ex. The smell of pineapples is due to ethyl butyrate ethanol + butanoic acid water (alcohol) ...
... Esters have strong, fragrant aromas and are the cause of the odors and flavors of pineapple, banana, wintergreen and oranges. Ex. The smell of pineapples is due to ethyl butyrate ethanol + butanoic acid water (alcohol) ...
AP Bio Cellular Respiration Define
... _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Why are NAD+ and FAD +2 important to cellular respiration? _______________________________________________________________________ _________________________ ...
... _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Why are NAD+ and FAD +2 important to cellular respiration? _______________________________________________________________________ _________________________ ...
Biomolecules Review
... 14. To which of the four classes of amino acid does cysteine belong? 15. Draw the structure of a generic dipeptide using H3N+-CHR-CO2-. What type of bond links the amino acids? Draw an arrow to this bond. 16. What are the four levels of protein structure? What level is given for this tripeptide? ala ...
... 14. To which of the four classes of amino acid does cysteine belong? 15. Draw the structure of a generic dipeptide using H3N+-CHR-CO2-. What type of bond links the amino acids? Draw an arrow to this bond. 16. What are the four levels of protein structure? What level is given for this tripeptide? ala ...
Fatty Acid Spiral
... – Fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and grains tend to be high in some and low in others. They do not contain similar ratios to that needed by humans. Thus, they should be consumed such that the amino acids they contain will ‘complement’ each other. ...
... – Fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and grains tend to be high in some and low in others. They do not contain similar ratios to that needed by humans. Thus, they should be consumed such that the amino acids they contain will ‘complement’ each other. ...
Document
... – Fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and grains tend to be high in some and low in others. They do not contain similar ratios to that needed by humans. Thus, they should be consumed such that the amino acids they contain will ‘complement’ each other. ...
... – Fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and grains tend to be high in some and low in others. They do not contain similar ratios to that needed by humans. Thus, they should be consumed such that the amino acids they contain will ‘complement’ each other. ...
The pathway from “activated acetic acid” to fatty acids and terpenes
... Fatty Acid Synthesis-Intermediates Attached to acyl carrier protein ...
... Fatty Acid Synthesis-Intermediates Attached to acyl carrier protein ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.