
CoA
... OBJECTIVES 1. Sequence leading from glucose to fatty acids via lipogenesis including roles of pyruvate carboxylase and pyruvate dehydrogenase. ...
... OBJECTIVES 1. Sequence leading from glucose to fatty acids via lipogenesis including roles of pyruvate carboxylase and pyruvate dehydrogenase. ...
B) Contain an alcohol - LSU School of Medicine
... superoxide radicals; binds to membrane receptors ...
... superoxide radicals; binds to membrane receptors ...
Chapter 7
... Now, recall that when amino acids are used for energy, they must first be deaminated. The remaining carbon chain ends up as glucose OR a derivative of glucose or fatty acids. Glycerol is actually a glucose derivative. So, when it comes to using chemicals for energy, cells really use glucose, fatty a ...
... Now, recall that when amino acids are used for energy, they must first be deaminated. The remaining carbon chain ends up as glucose OR a derivative of glucose or fatty acids. Glycerol is actually a glucose derivative. So, when it comes to using chemicals for energy, cells really use glucose, fatty a ...
Integrity and purity of the mitochondrial fraction
... by ERK1 and thus further evidence is needed to establish an influence of the kinase on this protein. There is extensive evidence for important effects of ROS on the activation of MAPKs. Low levels of H2O2 lead to ERK activation, whereas higher levels activate apoptotic signalling modules [12, 54, 55 ...
... by ERK1 and thus further evidence is needed to establish an influence of the kinase on this protein. There is extensive evidence for important effects of ROS on the activation of MAPKs. Low levels of H2O2 lead to ERK activation, whereas higher levels activate apoptotic signalling modules [12, 54, 55 ...
File
... 7a) Role of ATP Cellular respiration is a series of metabolic pathways that releases energy from food and generates a high energy compound called adenosine triphosphate (ATP) ATP is composed of adenosine and three inorganic phosphate (Pi) groups Energy is released from ATP when the bond attached to ...
... 7a) Role of ATP Cellular respiration is a series of metabolic pathways that releases energy from food and generates a high energy compound called adenosine triphosphate (ATP) ATP is composed of adenosine and three inorganic phosphate (Pi) groups Energy is released from ATP when the bond attached to ...
The Citric Acid Cycle
... Chapter 16: Summary In this chapter, we learned: • A large multi-subunit enzyme, pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, converts pyruvate into acetyl-CoA • Several cofactors are involved in reactions that harness the energy from pyruvate • Citric acid cycle is an important catabolic process: it makes GTP ...
... Chapter 16: Summary In this chapter, we learned: • A large multi-subunit enzyme, pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, converts pyruvate into acetyl-CoA • Several cofactors are involved in reactions that harness the energy from pyruvate • Citric acid cycle is an important catabolic process: it makes GTP ...
Summary of Metabolic Pathways
... • The net result of the citric acid cycle is conversion of an acetyl group to two carbon dioxide molecules, four molecules of reduced coenzymes, and one ATP molecule. -The reduced coenzyme molecules can pass electrons into the mitochondria, where they can result in generation of more ATP by oxidativ ...
... • The net result of the citric acid cycle is conversion of an acetyl group to two carbon dioxide molecules, four molecules of reduced coenzymes, and one ATP molecule. -The reduced coenzyme molecules can pass electrons into the mitochondria, where they can result in generation of more ATP by oxidativ ...
1 acetyl CoA - WordPress.com
... Under the mild conditions found in cells, there is insufficient energy to break the bond. ...
... Under the mild conditions found in cells, there is insufficient energy to break the bond. ...
Mixotrophic and photoheterotrophic metabolism in
... estimate the relative utilization of labelled carbon substrates (i.e. glucose, pyruvate and glycerol) and CO2 for metabolite synthesis under mixotrophic growth. Fig. 1 shows the central metabolic pathways in Cyanothece 51142 (http://www.genome.jp/kegg/). The labelling of five amino acids was analyse ...
... estimate the relative utilization of labelled carbon substrates (i.e. glucose, pyruvate and glycerol) and CO2 for metabolite synthesis under mixotrophic growth. Fig. 1 shows the central metabolic pathways in Cyanothece 51142 (http://www.genome.jp/kegg/). The labelling of five amino acids was analyse ...
Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Cloning of
... Local action of glucocorticoids depends on various processes such as passage through the cell membrane, binding to the glucocorticoid receptors, specific interaction of receptor–ligand complex with genes bearing glucocorticoid response element or with other transcription factors, and on intracellular ...
... Local action of glucocorticoids depends on various processes such as passage through the cell membrane, binding to the glucocorticoid receptors, specific interaction of receptor–ligand complex with genes bearing glucocorticoid response element or with other transcription factors, and on intracellular ...
sheet#30
... glutamate which gives ammonia. The resulted pyruvate may undergo gluconeogenesis and form glucose. That is why we call it glucose-alanine cycle. Then ammonia in the liver enters the urea cycle. Urea cycle: Urea compound: has two amino groups and carbonyl group. One amino group comes directly from fr ...
... glutamate which gives ammonia. The resulted pyruvate may undergo gluconeogenesis and form glucose. That is why we call it glucose-alanine cycle. Then ammonia in the liver enters the urea cycle. Urea cycle: Urea compound: has two amino groups and carbonyl group. One amino group comes directly from fr ...
Cellular Respiration Handout
... convert it into malate. And finally, another NAD+ oxidizes malate into oxaloacetate which joins with more acetyl CoA to enter the cycle again. The final products of oxidative decarboxylation and the Kreb’s cycle are: 8 NADH, 2 FADH2, 6 CO2, and 2 ATP’s. ...
... convert it into malate. And finally, another NAD+ oxidizes malate into oxaloacetate which joins with more acetyl CoA to enter the cycle again. The final products of oxidative decarboxylation and the Kreb’s cycle are: 8 NADH, 2 FADH2, 6 CO2, and 2 ATP’s. ...
Document
... a. ATP production results from a proton gradient established by the electron transport chain. b. The difference in pH between the intermembrane space and the cytosol drives the formation of ATP. c. The energy released by the reduction and subsequent oxidation of components of the electron transport ...
... a. ATP production results from a proton gradient established by the electron transport chain. b. The difference in pH between the intermembrane space and the cytosol drives the formation of ATP. c. The energy released by the reduction and subsequent oxidation of components of the electron transport ...
LESSON 2.2 WORKBOOK Metabolism: Glucose is the
... LESSON READINGS The energy in macronutrients is shuffled through many forms to generate ATP The release of energy from macronutrients involves breaking chemical bonds because that is where the energy is stored. Different types of bonds contain different amounts of energy, remember it is the combust ...
... LESSON READINGS The energy in macronutrients is shuffled through many forms to generate ATP The release of energy from macronutrients involves breaking chemical bonds because that is where the energy is stored. Different types of bonds contain different amounts of energy, remember it is the combust ...
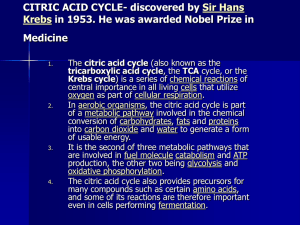
CITRIC ACID CYCLE
... It is the second of three metabolic pathways that are involved in fuel molecule catabolism and ATP production, the other two being glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation. The citric acid cycle also provides precursors for many compounds such as certain amino acids, and some of its reactions are th ...
... It is the second of three metabolic pathways that are involved in fuel molecule catabolism and ATP production, the other two being glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation. The citric acid cycle also provides precursors for many compounds such as certain amino acids, and some of its reactions are th ...
RESEARCH NOTES
... oil phen-2 isoloter showed appreciable growth on phenylpyruvote medium according to expectotionr (Brockmon et ol. 1959 Arch. Biochem. Biophyr. B&455), none of the phen-1 irolotes grew on this medium when compored to minim.1 &zum. Quantitative meorurements were mode on some phen-l isolates to check t ...
... oil phen-2 isoloter showed appreciable growth on phenylpyruvote medium according to expectotionr (Brockmon et ol. 1959 Arch. Biochem. Biophyr. B&455), none of the phen-1 irolotes grew on this medium when compored to minim.1 &zum. Quantitative meorurements were mode on some phen-l isolates to check t ...
Chapter 26
... • lipoprotein complexes transport lipids in the plasma – tiny droplets with a core of cholesterol and triglycerides – coated with protein and phospholipids • coating allows lipid to be suspended in blood • also serves as a recognition marker for cells that absorb them ...
... • lipoprotein complexes transport lipids in the plasma – tiny droplets with a core of cholesterol and triglycerides – coated with protein and phospholipids • coating allows lipid to be suspended in blood • also serves as a recognition marker for cells that absorb them ...
Lecture 27
... • Pancreatic and b cells directly sense the dietary and energy state of the organism through [glucose] in the blood. cells respond to low blood glucose by secreting glucagon. b cells respond to the high blood glucose by secreting insulin. • Both involved in glycogen metabolism. • These hormo ...
... • Pancreatic and b cells directly sense the dietary and energy state of the organism through [glucose] in the blood. cells respond to low blood glucose by secreting glucagon. b cells respond to the high blood glucose by secreting insulin. • Both involved in glycogen metabolism. • These hormo ...
- Wiley Online Library
... in two enzyme-mediated steps: anaplerosis of pyruvate into oxaloacetate (OAA) catalyzed by pyruvate carboxylase (PC), followed by conversion of OAA into PEP mediated by PEP carboxykinase (PEPCK). PEPCK is commonly considered the control point for liver gluconeogenesis and its overexpression leads to ...
... in two enzyme-mediated steps: anaplerosis of pyruvate into oxaloacetate (OAA) catalyzed by pyruvate carboxylase (PC), followed by conversion of OAA into PEP mediated by PEP carboxykinase (PEPCK). PEPCK is commonly considered the control point for liver gluconeogenesis and its overexpression leads to ...
Chapter 8 Worksheet
... Exercise 2 – Glycolysis (8.2) Glycolysis is the first of three steps in cellular respiration. Review glycolysis by matching each phrase on the right with a term on the left. Some terms are used tw ...
... Exercise 2 – Glycolysis (8.2) Glycolysis is the first of three steps in cellular respiration. Review glycolysis by matching each phrase on the right with a term on the left. Some terms are used tw ...
Chapter 1
... • Final substrate-level dehydration in the pathway • Phosphoenolpyruvate serves as donor of the phosphoryl group transferred to ADP by pyruvate kinase making ATP and releasing water – Pyruvate is the final product of glycolysis – A coupled reaction in which hydrolysis of the phosphoester bond provid ...
... • Final substrate-level dehydration in the pathway • Phosphoenolpyruvate serves as donor of the phosphoryl group transferred to ADP by pyruvate kinase making ATP and releasing water – Pyruvate is the final product of glycolysis – A coupled reaction in which hydrolysis of the phosphoester bond provid ...
[j26]Chapter 5#
... ___ 13. Anaerobic respiration (or lactic acid fermentation) yields a net gain of two ATP molecules. ___ 14. Anaerobic respiration (or lactic acid fermentation) in the cell does not require the presence of oxygen in the conversion of one glucose molecule to two molecules of lactic acid. ___ 15. It is ...
... ___ 13. Anaerobic respiration (or lactic acid fermentation) yields a net gain of two ATP molecules. ___ 14. Anaerobic respiration (or lactic acid fermentation) in the cell does not require the presence of oxygen in the conversion of one glucose molecule to two molecules of lactic acid. ___ 15. It is ...
Metabolic production and renal disposal of hydrogen ions
... In contrast to the above, the metabolism of anions to neutral species to species. The two possible pathways are in fact end-products will remove hydrogen ions. Again, following equivalent in their net effects on acid-base balance. We begin by through on the above example of protein metabolism, 100 c ...
... In contrast to the above, the metabolism of anions to neutral species to species. The two possible pathways are in fact end-products will remove hydrogen ions. Again, following equivalent in their net effects on acid-base balance. We begin by through on the above example of protein metabolism, 100 c ...
AMINO ACIDS METABOLISM ** Dr. Mohammed Abdullateef **
... 8. Cystathionine β-synthase: enzyme involved in cysteine biosynthesis, deficiencies are most common cause of homocystinurias 9. Glycine cleavage complex: also called glycine decarboxylase, enzyme catabolizing glycine, defects in activity cause glycine encephalopathy 10. Phenylketonuria (PKU): a part ...
... 8. Cystathionine β-synthase: enzyme involved in cysteine biosynthesis, deficiencies are most common cause of homocystinurias 9. Glycine cleavage complex: also called glycine decarboxylase, enzyme catabolizing glycine, defects in activity cause glycine encephalopathy 10. Phenylketonuria (PKU): a part ...
Glyceroneogenesis

Glyceroneogenesis is a metabolic pathway which synthesizes glycerol 3-phosphate or triglyceride from precursors other than glucose. Usually glycerol 3-phosphate is generated from glucose by glycolysis, but when glucose concentration drops in the cytosol, it is generated by another pathway called glyceroneogenesis. Glyceroneogenesis uses pyruvate, alanine, glutamine or any substances from the TCA cycle as precursors for glycerol 3-phophate. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPC-K), which is an enzyme that catalyses the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate is the main regulator for this pathway. Glyceroneogenesis can be observed in adipose tissue and also liver. It is a significant biochemical pathway which regulates cytosolic lipid levels. Intense suppression of glyceroneogenesis may lead to metabolic disorder such as type 2 diabetes.




















![[j26]Chapter 5#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/013325615_1-93c4a55e793afe312f3604738fdd639e-300x300.png)

