C483 Practice Final Exam
... D. produce 6 ATP for every pass through the cycle. E. More than one of the above 22. ______ The standard reduction potential for the reaction of oxaloacetate and NADH to produce malate is A. + 0.149 V B. - 0.149 V C. + 0.481 V D. - 0.481 V 23. ______ In humans, a full rotation of the ATP synthase ro ...
... D. produce 6 ATP for every pass through the cycle. E. More than one of the above 22. ______ The standard reduction potential for the reaction of oxaloacetate and NADH to produce malate is A. + 0.149 V B. - 0.149 V C. + 0.481 V D. - 0.481 V 23. ______ In humans, a full rotation of the ATP synthase ro ...
AP Bio Cellular Respiration Define
... Why are NAD+ and FAD +2 important to cellular respiration? _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ What are the 3 parts of c ...
... Why are NAD+ and FAD +2 important to cellular respiration? _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ What are the 3 parts of c ...
BHS 150.1 – Biochemistry II Date: 2/8/2013, 2sndhalf Notetaker: Kim
... 12. Ascorbate in the aqueous is needed by the cornea for which two of the following functions: antioxidant properties collagen synthesis 13. A missense mutation occurs when the: amino acid sequence changes 14. During fasting, what are some possible sources of carbons for gluconeogenesis: amino acids ...
... 12. Ascorbate in the aqueous is needed by the cornea for which two of the following functions: antioxidant properties collagen synthesis 13. A missense mutation occurs when the: amino acid sequence changes 14. During fasting, what are some possible sources of carbons for gluconeogenesis: amino acids ...
palm butter - In
... 45/50% of oil and has consistency like soft butter at room temperature. Palm Butter may be used in the lipidic phase of an emulsion or of a lipogel acting both as a vegetal triglycerids and as consistency factor (it can substitute the whole oil phase of an emulsion), moreover it makes the skin soft ...
... 45/50% of oil and has consistency like soft butter at room temperature. Palm Butter may be used in the lipidic phase of an emulsion or of a lipogel acting both as a vegetal triglycerids and as consistency factor (it can substitute the whole oil phase of an emulsion), moreover it makes the skin soft ...
Adenosine Triphosphate-ATP: The main molecule used by cells for
... Fat: Most commonly molecules composed of glycerol linked by ester bonds to one, two or three fatty acid tails. Fatty acid: A molecule consisting of a carboxyl group bonded to a hydrocarbon chain. Fatty acids are commonly bonded to a glycerol to make up fats or phospholipids. Glycerol: A type of alco ...
... Fat: Most commonly molecules composed of glycerol linked by ester bonds to one, two or three fatty acid tails. Fatty acid: A molecule consisting of a carboxyl group bonded to a hydrocarbon chain. Fatty acids are commonly bonded to a glycerol to make up fats or phospholipids. Glycerol: A type of alco ...
Review 1 - Allen ISD
... with one phosphate group, is formed. c. Energy is released, which can be used by the cell. d. Energy is lost in the process. ...
... with one phosphate group, is formed. c. Energy is released, which can be used by the cell. d. Energy is lost in the process. ...
nucleic acids
... with one phosphate group, is formed. c. Energy is released, which can be used by the cell. d. Energy is lost in the process. ...
... with one phosphate group, is formed. c. Energy is released, which can be used by the cell. d. Energy is lost in the process. ...
Chapter 3 Review Questions
... A. It forms short, simple carbon chains. B. It forms large, complex, diverse molecules. C. It forms covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. D. It forms covalent bonds that can exist in a single plane. 2. What reaction or process forms a polymer from 2 monomers? A. glycolysis B. hydrolysis C. photosy ...
... A. It forms short, simple carbon chains. B. It forms large, complex, diverse molecules. C. It forms covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. D. It forms covalent bonds that can exist in a single plane. 2. What reaction or process forms a polymer from 2 monomers? A. glycolysis B. hydrolysis C. photosy ...
Chemical Equation Interpretations – Match the chemical equation
... __ 5. Hg(l) Hg(g) __ 6. C16H30O2(s) + H2(g) C16H32O2(s) __ 7. CaO(s) + H2O(l) Ca(OH)2 (s) ...
... __ 5. Hg(l) Hg(g) __ 6. C16H30O2(s) + H2(g) C16H32O2(s) __ 7. CaO(s) + H2O(l) Ca(OH)2 (s) ...
QUIZ #7 NUCLEOTIDE METABOLISM
... Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate is: a. Formed during a regulated step in purine synthesis b. Formed by the action of phosphoribosyl synthetase c. A substrate for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis d. Hydrolyzed by the action of inorganic pyrophosphate phosphatase e. 1), 2) and 3) are correct ...
... Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate is: a. Formed during a regulated step in purine synthesis b. Formed by the action of phosphoribosyl synthetase c. A substrate for both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis d. Hydrolyzed by the action of inorganic pyrophosphate phosphatase e. 1), 2) and 3) are correct ...
Slide ()
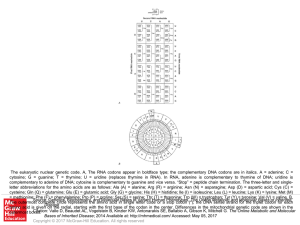
... The eukaryotic nuclear genetic code. A, The RNA codons appear in boldface type; the complementary DNA codons are in italics. A = adenine; C = cytosine; G = guanine; T = thymine; U = uridine (replaces thymine in RNA). In RNA, adenine is complementary to thymine of DNA; uridine is complementary to ade ...
... The eukaryotic nuclear genetic code. A, The RNA codons appear in boldface type; the complementary DNA codons are in italics. A = adenine; C = cytosine; G = guanine; T = thymine; U = uridine (replaces thymine in RNA). In RNA, adenine is complementary to thymine of DNA; uridine is complementary to ade ...
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE DEPARTMENT OF BIOCHEMISTRY ADVANCED PLACEMENT TEST (SAMPLE)
... 1. Which of the following statements about the biophysical property of water is INCORRECT? A. Water molecule forms H-bonds B. Water retains heat well C. Water is dielectrict D. Water at freezing point has the highest density E. Water is polar 2. Which of the following is NOT a strong electrolyte and ...
... 1. Which of the following statements about the biophysical property of water is INCORRECT? A. Water molecule forms H-bonds B. Water retains heat well C. Water is dielectrict D. Water at freezing point has the highest density E. Water is polar 2. Which of the following is NOT a strong electrolyte and ...
Slide 1
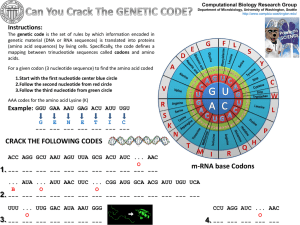
... The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences) is translated into proteins (amino acid sequences) by living cells. Specifically, the code defines a mapping between trinucleotide sequences called codons and amino acids. For a given codon ( ...
... The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences) is translated into proteins (amino acid sequences) by living cells. Specifically, the code defines a mapping between trinucleotide sequences called codons and amino acids. For a given codon ( ...
Amino Acids - Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC INTERNATIONAL
... Determination of free and/or total proteinogenic L-α-amino acids and taurine (as shown in Table 1) in all forms of infant, adult, and/or pediatric formulas (powders, ready-to-feed liquids, and liquid concentrates). For amino acids sensitive to modification during handling and/or processing (primarily ...
... Determination of free and/or total proteinogenic L-α-amino acids and taurine (as shown in Table 1) in all forms of infant, adult, and/or pediatric formulas (powders, ready-to-feed liquids, and liquid concentrates). For amino acids sensitive to modification during handling and/or processing (primarily ...
C483 Final Exam Study Guide The final will be held in Morrison 007
... B. A DNA melting curve for a poly(AT) sequence and a poly(GC) sequence (indicate which is poly(AT) and which is poly(GC)) C. A plot of initial velocity versus substrate concentration for a Michaelis-Menton enzyme. D. The same plot as (B), but the enzyme is treated with a competitive inhibitor E. a p ...
... B. A DNA melting curve for a poly(AT) sequence and a poly(GC) sequence (indicate which is poly(AT) and which is poly(GC)) C. A plot of initial velocity versus substrate concentration for a Michaelis-Menton enzyme. D. The same plot as (B), but the enzyme is treated with a competitive inhibitor E. a p ...
BIO C211 - BITS Pilani
... 1. Classification of vitamins 2. Structures and functions of some important vitamins. D. Biochemical Energetics 3 Ch. 1. The concept of free energy 2. Energy rich compounds 3. Coupling of reactions 4. Oxidation-Reduction E. Carbohydrate Metabolism 9 Ch. 1. Glycolysis 2. Reversal of Glycolytic sequen ...
... 1. Classification of vitamins 2. Structures and functions of some important vitamins. D. Biochemical Energetics 3 Ch. 1. The concept of free energy 2. Energy rich compounds 3. Coupling of reactions 4. Oxidation-Reduction E. Carbohydrate Metabolism 9 Ch. 1. Glycolysis 2. Reversal of Glycolytic sequen ...
Physiology Objectives 33
... Titratable acid: amount of filtered acid that has been changed from salt to acid form as it accepts H+ from tubular secretion ...
... Titratable acid: amount of filtered acid that has been changed from salt to acid form as it accepts H+ from tubular secretion ...
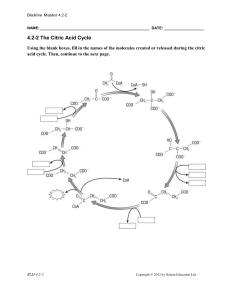
Blackline Master 4.2-2 NAME: DATE: 4.2
... ________________enters the cycle and then combines with ________________ to make the six-carbon compound ________________. During the eight steps of the citric cycle, ________________ undergoes a number of reactions, releasing _______ and ______ in a number of steps. ________________ is eventually c ...
... ________________enters the cycle and then combines with ________________ to make the six-carbon compound ________________. During the eight steps of the citric cycle, ________________ undergoes a number of reactions, releasing _______ and ______ in a number of steps. ________________ is eventually c ...
Lactate Inflection Point & Recovery
... This fatigue is generally considered to be a consequence of a greater reliance on the anaerobic systems to supply the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and the resultant accumulation of the by-products of anaerobic metabolism Lactic acid and hydrogen ions ...
... This fatigue is generally considered to be a consequence of a greater reliance on the anaerobic systems to supply the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and the resultant accumulation of the by-products of anaerobic metabolism Lactic acid and hydrogen ions ...
M. PHARM. 1. Sildenafil is used in the following disorder: A) Systolic
... A) Reserpic acid + methyl alcohol + trimethoxy cinnamic acid. B) Reserpic acid + acetic acid + trimethoxy benzaldehyde. C) Reserpic acid + methyl alcohol + trimethoxy benzoic acid. D) Reserpic acid + methyl alcohol + trimethoxy cinnamaldehyde. ...
... A) Reserpic acid + methyl alcohol + trimethoxy cinnamic acid. B) Reserpic acid + acetic acid + trimethoxy benzaldehyde. C) Reserpic acid + methyl alcohol + trimethoxy benzoic acid. D) Reserpic acid + methyl alcohol + trimethoxy cinnamaldehyde. ...
CHEM131 Quiz 5_AA
... b. Circle the acidic R group in the tirpeptide you drew in question part a and draw an arrow pointing out each peptide bond. 4. Answer questions a-c about the Fisher projection of the amino acid shown on the right. (3 pts) a) Briefly explain what is wrong with this Fisher projection. ...
... b. Circle the acidic R group in the tirpeptide you drew in question part a and draw an arrow pointing out each peptide bond. 4. Answer questions a-c about the Fisher projection of the amino acid shown on the right. (3 pts) a) Briefly explain what is wrong with this Fisher projection. ...
what are cannabinoid receptors?
... Receptors are akin to ”locks,” and the ligand compounds that bind to them are akin to ”keys” in a lock & key system. They have about seven sections that pass through the outer cell membrane. Cannabinoid receptors are also coupled to G-proteins, where a lot of the signaling ”magic” happens when a mol ...
... Receptors are akin to ”locks,” and the ligand compounds that bind to them are akin to ”keys” in a lock & key system. They have about seven sections that pass through the outer cell membrane. Cannabinoid receptors are also coupled to G-proteins, where a lot of the signaling ”magic” happens when a mol ...
Hepoxilin

Hepoxilins (HxA3 and HxB3) are nonclassic eicosanoid hormones involved in inflammation.