Metabolism of lipids
... derived from acetyl CoA. The activated donor of the two-carbon units in the elongation step is malonyl-ACP (a three-carbon unit) but during the elongation, CO2 is released. This drives the reaction • The reducing agent is NADPH. • Elongation by FA synthase complex stops upon formation of C16 palmita ...
... derived from acetyl CoA. The activated donor of the two-carbon units in the elongation step is malonyl-ACP (a three-carbon unit) but during the elongation, CO2 is released. This drives the reaction • The reducing agent is NADPH. • Elongation by FA synthase complex stops upon formation of C16 palmita ...
File
... ◦ 1 ATP ◦ 1 FADH2 ◦ 3 NADH But, for each glucose you get two pyruvates, therefore you would have to double your numbers. ...
... ◦ 1 ATP ◦ 1 FADH2 ◦ 3 NADH But, for each glucose you get two pyruvates, therefore you would have to double your numbers. ...
Regulation of Elovl and fatty acid metabolism
... acids (FA) do not only serve as a major source of energy, but are also crucial structural components of membranes. Additionally, fatty acids may function as signaling molecules, thus exerting key biological functions, such as regulating fatty acid metabolism (Duplus and Forest, 2002). For example, p ...
... acids (FA) do not only serve as a major source of energy, but are also crucial structural components of membranes. Additionally, fatty acids may function as signaling molecules, thus exerting key biological functions, such as regulating fatty acid metabolism (Duplus and Forest, 2002). For example, p ...
Cholesterol Synthesis Regulation of cholesterol synthesis pathway
... bladder to contract releasing bile liver ...
... bladder to contract releasing bile liver ...
Functional Anatomy of the Liver
... 5) Blood clotting factors-Factors I, II, V, VII, VIII, IX, and X (vitamin K is needed for the synthesis of some factors) ...
... 5) Blood clotting factors-Factors I, II, V, VII, VIII, IX, and X (vitamin K is needed for the synthesis of some factors) ...
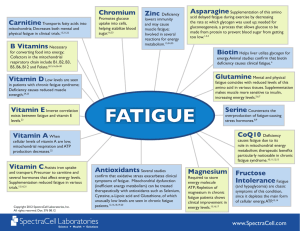
fatigue - Spectracell
... gluconeogenesis, a process that allows glucose to be made from protein to prevent blood sugar from getting too low.1,2,3 ...
... gluconeogenesis, a process that allows glucose to be made from protein to prevent blood sugar from getting too low.1,2,3 ...
chapter9_powerpoint
... Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle connect to many other metabolic pathways • Catabolic pathways funnel electrons from many kinds of organic molecules into cellular respiration • Glycolysis accepts a wide range of carbohydrates • Proteins must be digested to amino acids; amino groups can feed gly ...
... Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle connect to many other metabolic pathways • Catabolic pathways funnel electrons from many kinds of organic molecules into cellular respiration • Glycolysis accepts a wide range of carbohydrates • Proteins must be digested to amino acids; amino groups can feed gly ...
Examination 2: Chapters 8 through 11
... Increasing the free energy of the system so that the change in free energy is positive Increasing the free energy of the substrate so that it is greater than the free energy of the product C. Changing the equilibrium constant for the reaction D. Decreasing the free energy of activation E. Decreasing ...
... Increasing the free energy of the system so that the change in free energy is positive Increasing the free energy of the substrate so that it is greater than the free energy of the product C. Changing the equilibrium constant for the reaction D. Decreasing the free energy of activation E. Decreasing ...
Cellular Respiration - Ursuline High School
... most of the cell's energy in the form of NADH and FADH2… not ATP Does NOT require O2 The CO2 produced by the Krebs cycle is the CO2 animal exhale when they breathe. ...
... most of the cell's energy in the form of NADH and FADH2… not ATP Does NOT require O2 The CO2 produced by the Krebs cycle is the CO2 animal exhale when they breathe. ...
How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy
... • For each glucose molecule that enters cellular respiration, chemiosmosis produces up to 38 ATP molecules Cytoplasmic fluid ...
... • For each glucose molecule that enters cellular respiration, chemiosmosis produces up to 38 ATP molecules Cytoplasmic fluid ...
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... most of the cell's energy in the form of NADH and FADH2… not ATP Does NOT require O2 The CO2 produced by the Krebs cycle is the CO2 animal exhale when they breathe. ...
... most of the cell's energy in the form of NADH and FADH2… not ATP Does NOT require O2 The CO2 produced by the Krebs cycle is the CO2 animal exhale when they breathe. ...
Caldogcium – concentrated Calcium supplement containing Beta
... boosting phytonutrients are also available in their natural form. Vitamin D3, the naturally occurring form, is included in the formulation for its well-known association with Calcium to form and maintain bone mass. All of these nutrients being available and working synergistically, assists in the ut ...
... boosting phytonutrients are also available in their natural form. Vitamin D3, the naturally occurring form, is included in the formulation for its well-known association with Calcium to form and maintain bone mass. All of these nutrients being available and working synergistically, assists in the ut ...
medical chemistry and biochemistry
... Metabolism of dietary lipids Describe the process of digestion fatty acid and triglycerides. Describe the process of absorption fatty acid and triglycerides Describe the process of utilization of fatty acid and triglycerides. Explain medical ramification of lipid malabsorption, in particular, with r ...
... Metabolism of dietary lipids Describe the process of digestion fatty acid and triglycerides. Describe the process of absorption fatty acid and triglycerides Describe the process of utilization of fatty acid and triglycerides. Explain medical ramification of lipid malabsorption, in particular, with r ...
Chylomicron Remnants and Nonesterified Fatty Involved in Lipogenesis in Rats
... in starvation, they do not completely recapitulate the mechanism of dietary fat presentation to the liver, which is delivered via generated from the lymph of rats intubated with either safflower oil or lard. The remnants were added to the medium of primary rat hepatocytes in culture and the accumula ...
... in starvation, they do not completely recapitulate the mechanism of dietary fat presentation to the liver, which is delivered via generated from the lymph of rats intubated with either safflower oil or lard. The remnants were added to the medium of primary rat hepatocytes in culture and the accumula ...
I. Molecular mechanism for polyunsaturated fatty acid regulation of
... leads to enhanced fatty acid oxidation (24). Whether PUFA suppress malonyl-CoA levels in skeletal muscle and heart remains to be determined, but such a mechanism would be consistent with the higher rates of fatty acid oxidation observed in humans and animals fed diets rich in PUFA (6, 18). The reduc ...
... leads to enhanced fatty acid oxidation (24). Whether PUFA suppress malonyl-CoA levels in skeletal muscle and heart remains to be determined, but such a mechanism would be consistent with the higher rates of fatty acid oxidation observed in humans and animals fed diets rich in PUFA (6, 18). The reduc ...
26_Catabolism of tryacylglycerols oxidation of fatty acids a
... through the adipocyte membrane and enter bloodstream. • Glycerol is transported via the blood in free state and oxidized or converted to glucose in liver. • Fatty acids are traveled bound to albumin. • In heart, skeletal muscles and liver they are oxidized with energy release. ...
... through the adipocyte membrane and enter bloodstream. • Glycerol is transported via the blood in free state and oxidized or converted to glucose in liver. • Fatty acids are traveled bound to albumin. • In heart, skeletal muscles and liver they are oxidized with energy release. ...
Chapter 24
... the synthesis of palmitoyl-CoA, the synthesis of malonyl-CoA, and the overall reaction for the synthesis of palmitoyl-CoA from acetyl-CoA. Answer: Malonyl-CoA is synthesized as follows Acetyl-CoA + HCO3- + ATP4- malonyl-CoA- + ADP3- + Pi2- + H+ The carbons in the acetyl group of acetyl-CoA derive ...
... the synthesis of palmitoyl-CoA, the synthesis of malonyl-CoA, and the overall reaction for the synthesis of palmitoyl-CoA from acetyl-CoA. Answer: Malonyl-CoA is synthesized as follows Acetyl-CoA + HCO3- + ATP4- malonyl-CoA- + ADP3- + Pi2- + H+ The carbons in the acetyl group of acetyl-CoA derive ...
Nutrient Sensing through the Plasma Membrane of Eukaryotic Cells
... transporter [42], is induced only by low levels of glucose because its promoter has binding sites for the Mig1 glucose repressor, which represses transcription when glucose levels are high (Figure 3) [43]. By contrast, expression of HXT1, which encodes a low-affinity glucose transporter [42], is ind ...
... transporter [42], is induced only by low levels of glucose because its promoter has binding sites for the Mig1 glucose repressor, which represses transcription when glucose levels are high (Figure 3) [43]. By contrast, expression of HXT1, which encodes a low-affinity glucose transporter [42], is ind ...
respiration 2010
... Using ATP to do work? Cells can’t store ATP too unstable only used in cell that produces it only short term energy storage carbohydrates & fats are long term energy storage ...
... Using ATP to do work? Cells can’t store ATP too unstable only used in cell that produces it only short term energy storage carbohydrates & fats are long term energy storage ...
Cellular Respiration Explained
... made? The answer is in the mitochondria of cells. The overall reaction is C6H12O6 + 6O2→6CO2+ 6H2O+ Energy (ATP+ Heat). Notice that oxygen is required. When oxygen is used, it is called aerobic respiration. ANAEROBIC Respiration is called fermentation. No O2 used in fermentation. Without O2 there is ...
... made? The answer is in the mitochondria of cells. The overall reaction is C6H12O6 + 6O2→6CO2+ 6H2O+ Energy (ATP+ Heat). Notice that oxygen is required. When oxygen is used, it is called aerobic respiration. ANAEROBIC Respiration is called fermentation. No O2 used in fermentation. Without O2 there is ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... only one ATP from this pathway, which is a meager half of the exploitation of glucose in glycolysis. Due to this energetic limitation, this pathway is only used in aerobic bacteria that can use the NADH produced in the oxidation of glucose to gluconate and in the oxidation of G3P in a respiratory ch ...
... only one ATP from this pathway, which is a meager half of the exploitation of glucose in glycolysis. Due to this energetic limitation, this pathway is only used in aerobic bacteria that can use the NADH produced in the oxidation of glucose to gluconate and in the oxidation of G3P in a respiratory ch ...
Lipoic Acid 100 mg The Universal Antioxidant
... Alpha-lipoic acid is a nutritional coenzyme that participates in the energy metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates and fats, with a particular role in blood glucose disposal. It is also able to scavenge a number of free radicals. As both a fat and water-soluble, sulfur-containing coenzyme, alpha-lipo ...
... Alpha-lipoic acid is a nutritional coenzyme that participates in the energy metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates and fats, with a particular role in blood glucose disposal. It is also able to scavenge a number of free radicals. As both a fat and water-soluble, sulfur-containing coenzyme, alpha-lipo ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.