Principles of BIOCHEMISTRY
... • Glyoxylate cycle leads from 2-carbon compounds to glucose • In animals, acetyl CoA is not a carbon source for the net formation of glucose (2 carbons of acetyl CoA enter cycle, 2 are released as 2 CO2) ...
... • Glyoxylate cycle leads from 2-carbon compounds to glucose • In animals, acetyl CoA is not a carbon source for the net formation of glucose (2 carbons of acetyl CoA enter cycle, 2 are released as 2 CO2) ...
A futile metabolic cycle activated in adipocytes by - Zen-Bio
... puzzle. TZDs might have direct effects on muscle and liver; however, the concentration of PPAR-γ is very low in these tissues, particularly skeletal muscle. As a result, much attention has been paid to the effects of TZDs on the adipocyte. Indeed, TZDs regulate the expression of several adipocyte-se ...
... puzzle. TZDs might have direct effects on muscle and liver; however, the concentration of PPAR-γ is very low in these tissues, particularly skeletal muscle. As a result, much attention has been paid to the effects of TZDs on the adipocyte. Indeed, TZDs regulate the expression of several adipocyte-se ...
R-lipoic acid inhibits mammalian pyruvate
... and cofactor of key metabolic enzyme complexes catalyzing the decarboxylation of alpha-keto acids. Racemic LA (rac-LA) has shown promise in treating diabetic polyneuropathy, and some studies suggest that it improves glucose homeostasis in patients with type 2 diabetes. We examined the effects of R-L ...
... and cofactor of key metabolic enzyme complexes catalyzing the decarboxylation of alpha-keto acids. Racemic LA (rac-LA) has shown promise in treating diabetic polyneuropathy, and some studies suggest that it improves glucose homeostasis in patients with type 2 diabetes. We examined the effects of R-L ...
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... the Pyruvic acid is first converted to Acetic Acid by losing a carbon atom and 2 oxygens as CO2. The Acetic acid then must enter the matrix region of the mitochondria. The CO2 produced is the CO2 animals exhale when they breathe. ...
... the Pyruvic acid is first converted to Acetic Acid by losing a carbon atom and 2 oxygens as CO2. The Acetic acid then must enter the matrix region of the mitochondria. The CO2 produced is the CO2 animals exhale when they breathe. ...
Glycolysi
... Propionic acid & CO2 milk protein precipitation & holes Kimchi, soy sauce Low pH prevents growth of microorganisms ...
... Propionic acid & CO2 milk protein precipitation & holes Kimchi, soy sauce Low pH prevents growth of microorganisms ...
Adventures in Chemistry Julie T. Millard, Colby College
... pathway (cellular respiration) or converted to lactic acid in the anaerobic pathway (fermentation). 3. The rate at which oxygen is delivered to the muscles (VO2 max) dictates the level of activity that can be sustained under aerobic conditions. ...
... pathway (cellular respiration) or converted to lactic acid in the anaerobic pathway (fermentation). 3. The rate at which oxygen is delivered to the muscles (VO2 max) dictates the level of activity that can be sustained under aerobic conditions. ...
Chemistry and the Gym
... pathway (cellular respiration) or converted to lactic acid in the anaerobic pathway (fermentation). 3. The rate at which oxygen is delivered to the muscles (VO2 max) dictates the level of activity that can be sustained under aerobic conditions. ...
... pathway (cellular respiration) or converted to lactic acid in the anaerobic pathway (fermentation). 3. The rate at which oxygen is delivered to the muscles (VO2 max) dictates the level of activity that can be sustained under aerobic conditions. ...
- humans ingest more proteins than needed for replacement of
... - humans ingest more proteins than needed for replacement of endogenous proteins; excess amino acids can’t be stored catabolized; - figure 1, 18-2 - any amino acid that can be degraded to pyruvate or citric acid cycle intermediate can serve as precursor in liver for synthesis of glucose (glycogeni ...
... - humans ingest more proteins than needed for replacement of endogenous proteins; excess amino acids can’t be stored catabolized; - figure 1, 18-2 - any amino acid that can be degraded to pyruvate or citric acid cycle intermediate can serve as precursor in liver for synthesis of glucose (glycogeni ...
a new equation for calculating the number of atp molecules
... penetration. Upon reaching the cytosol, several processes should take place in order for the fatty acids to be transferred from the cytosol to the mitochondrial matrix where the betaoxidation process takes place.[12-18] In the mitochondrial matrix, fatty acids undergo beta-oxidation process in which ...
... penetration. Upon reaching the cytosol, several processes should take place in order for the fatty acids to be transferred from the cytosol to the mitochondrial matrix where the betaoxidation process takes place.[12-18] In the mitochondrial matrix, fatty acids undergo beta-oxidation process in which ...
Chapter 6
... Cells can use the energy in fats and proteins as well. – Fats are digested into fatty acids and glycerol. – Proteins are digested into amino acids. Cells must convert fats and proteins into molecules that can enter and be metabolized by the enzymes of glycolysis or the Kreb’s cycle. Copyright © The ...
... Cells can use the energy in fats and proteins as well. – Fats are digested into fatty acids and glycerol. – Proteins are digested into amino acids. Cells must convert fats and proteins into molecules that can enter and be metabolized by the enzymes of glycolysis or the Kreb’s cycle. Copyright © The ...
Nutrient Metabolism
... deficiency when dietary protein is restricted and energy demand increased, such as during strenuous exercise. Addition of limiting amino acids may also reduce the risk of protein deficiency. This study also tested the hypothesis that acid-base ...
... deficiency when dietary protein is restricted and energy demand increased, such as during strenuous exercise. Addition of limiting amino acids may also reduce the risk of protein deficiency. This study also tested the hypothesis that acid-base ...
IN VIVO CUSCUTA EPITHYMUM PLANT AGAINST CCL INDUCED LIVER DAMAGE ANIMAL MODEL
... Liver has a pivotal role in the maintenance of normal physiological process through its multiple and diverse functions, such as metabolism, secretion, storage and detoxification of variety of drugs. In the absence of reliable liver protective drugs in modern medicine, in India, a number of medical p ...
... Liver has a pivotal role in the maintenance of normal physiological process through its multiple and diverse functions, such as metabolism, secretion, storage and detoxification of variety of drugs. In the absence of reliable liver protective drugs in modern medicine, in India, a number of medical p ...
CNM
... Cellulose is structural material of ……………………. It is a …………………… polymer. Human don’t have the …………… required to break these beta (1,4) glycosidic bonds, so cellulose is not digestible by humans and is often referred to as ……………. ………….. Some animals, particularly ………………. and …………………., can digest cellu ...
... Cellulose is structural material of ……………………. It is a …………………… polymer. Human don’t have the …………… required to break these beta (1,4) glycosidic bonds, so cellulose is not digestible by humans and is often referred to as ……………. ………….. Some animals, particularly ………………. and …………………., can digest cellu ...
Muscle Metabolism - White Plains Public Schools
... Ionic disturbances are the most likely cause of muscle fatigue: Potassium ion lost from the muscle cells Interference of Calcium regulation ...
... Ionic disturbances are the most likely cause of muscle fatigue: Potassium ion lost from the muscle cells Interference of Calcium regulation ...
Amino Acid Analysis Recommendations
... determined at two wavelengths (λ= 570 nm and λ= 440 nm). Signal ratios at these wavelengths have to be determined for proper identification of the individual amino acids and detection of co-eluting interferences. Control plasma or urine samples are analysed in each series of plasma or urine amino ac ...
... determined at two wavelengths (λ= 570 nm and λ= 440 nm). Signal ratios at these wavelengths have to be determined for proper identification of the individual amino acids and detection of co-eluting interferences. Control plasma or urine samples are analysed in each series of plasma or urine amino ac ...
The citric acid cycle is the
... transformation of acetyl-CoA to oxaloacetate. Thus, for every succinate that enters the reversed cycle, two succinates are returned, making the cycle highly autocatalytic. • Because TCA cycle intermediates are involved in many biosynthetic pathways, a reversed TCA cycle would be a bountifuland broad ...
... transformation of acetyl-CoA to oxaloacetate. Thus, for every succinate that enters the reversed cycle, two succinates are returned, making the cycle highly autocatalytic. • Because TCA cycle intermediates are involved in many biosynthetic pathways, a reversed TCA cycle would be a bountifuland broad ...
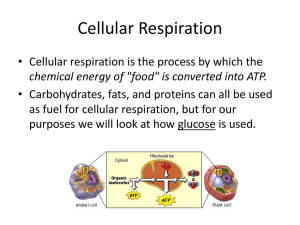
Cellular Respiration
... • Following glycolysis if oxygen is present, pyruvate is metabolized in two processes called: – The Kreb Cycle – Electron Transport Chain ...
... • Following glycolysis if oxygen is present, pyruvate is metabolized in two processes called: – The Kreb Cycle – Electron Transport Chain ...
Guideline for the investigation of hyperammonaemia
... collection or a delay in analysis. Plasma ammonia levels should be taken from a free flowing venous sample and should be taken directly to the biochemistry laboratory. It is important to inform the laboratory that an ammonia sample is being taken before drawing the blood. Hyperammonaemia can be caus ...
... collection or a delay in analysis. Plasma ammonia levels should be taken from a free flowing venous sample and should be taken directly to the biochemistry laboratory. It is important to inform the laboratory that an ammonia sample is being taken before drawing the blood. Hyperammonaemia can be caus ...
Fatty and Amino acids composition of Bactrocera zonata as affected
... amino acids, sugars and simpler fatty acids. Lipids were the major food reserves of insects, probably occurring in the form of triglycerides in which the fatty acids are combined with glycerols. Fatty acids combined in the triglycerides were usually long acid chains, both saturated and unsaturated w ...
... amino acids, sugars and simpler fatty acids. Lipids were the major food reserves of insects, probably occurring in the form of triglycerides in which the fatty acids are combined with glycerols. Fatty acids combined in the triglycerides were usually long acid chains, both saturated and unsaturated w ...
Phospholipid Ester-linked Fatty Acid Biomarkers of
... acetoxidans (5579, which are all sulphate-reducingbacteria that oxidize acetate. A thermophilic sulphate reducer, Desulfovibrio thermophilus, and two sulphur-reducingbacteria, Desulfuromonas acetoxidans (1 1070) and a Cumpylobacter-like spirillum (5175), were also studied. The Desulfobacter spp. wer ...
... acetoxidans (5579, which are all sulphate-reducingbacteria that oxidize acetate. A thermophilic sulphate reducer, Desulfovibrio thermophilus, and two sulphur-reducingbacteria, Desulfuromonas acetoxidans (1 1070) and a Cumpylobacter-like spirillum (5175), were also studied. The Desulfobacter spp. wer ...
Physiology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in anaerobic glucose
... (Postma et al., 1989a), and also after a glucose pulse to an aerobic culture pregrown at a low dilution rate (van Urk et al., 1988). In the presence of excess sugar, aerobic fermentation of glucose to ethanol provides a substantial part of the energy required for the formation of biomass. At first s ...
... (Postma et al., 1989a), and also after a glucose pulse to an aerobic culture pregrown at a low dilution rate (van Urk et al., 1988). In the presence of excess sugar, aerobic fermentation of glucose to ethanol provides a substantial part of the energy required for the formation of biomass. At first s ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.