Fatty acid productivity of Scenedesmus obliquus under nitrogen
... The protein contents of all the three ...
... The protein contents of all the three ...
Feeding Dogs for Agility
... this rate of sprinting exceeds the maximum rate at which oxygen can be taken up by the body. The extra energy for very rapid sprinting is generated without oxygen. This produces lactic acid which then builds up in the blood. In contrast, long distance running involves ‘sub-maximal’ exercise. The oxy ...
... this rate of sprinting exceeds the maximum rate at which oxygen can be taken up by the body. The extra energy for very rapid sprinting is generated without oxygen. This produces lactic acid which then builds up in the blood. In contrast, long distance running involves ‘sub-maximal’ exercise. The oxy ...
PDF - Biochemical Journal
... Green, 1958). The present method involves comacetate (PMA) (Hellerman, Schelphenylmercuric plete isotopic exchange in a solution formed by hot alkaline digestion of the sample, and determination lenberg & Reiss, 1958) and ADP (Frieden, 1959a, b) of the constant value of the diluted specific activity ...
... Green, 1958). The present method involves comacetate (PMA) (Hellerman, Schelphenylmercuric plete isotopic exchange in a solution formed by hot alkaline digestion of the sample, and determination lenberg & Reiss, 1958) and ADP (Frieden, 1959a, b) of the constant value of the diluted specific activity ...
Document
... • insulin does not function properly. • glucose levels are insufficient for energy needs. • fats are broken down to acetyl CoA. • ketone bodies form. ...
... • insulin does not function properly. • glucose levels are insufficient for energy needs. • fats are broken down to acetyl CoA. • ketone bodies form. ...
Introduction - American Society of Exercise Physiologists
... If you look at all of the diets, there is one key ingredient that they all eliminate: sugar. To be more specific, they eliminate simple carbohydrates (sugars), that is, the sugars that lead to long-term health problems such as type II diabetes, high blood pressure, and obesity. These types of carboh ...
... If you look at all of the diets, there is one key ingredient that they all eliminate: sugar. To be more specific, they eliminate simple carbohydrates (sugars), that is, the sugars that lead to long-term health problems such as type II diabetes, high blood pressure, and obesity. These types of carboh ...
MEDICAL GRAND ROUNDS PARKLAND
... enhancmg their tra ns port i nto the liver cells . and b) by Lncreasing proteolysis from plasma prot~ in and from hepatic cellular prot ei n (14) . NOTE : Although its glycogenolytic a ctivity is too well appr e ciated to r e quire e mphasis , glucagon's gluconeogenic activity is less well rec ogniz ...
... enhancmg their tra ns port i nto the liver cells . and b) by Lncreasing proteolysis from plasma prot~ in and from hepatic cellular prot ei n (14) . NOTE : Although its glycogenolytic a ctivity is too well appr e ciated to r e quire e mphasis , glucagon's gluconeogenic activity is less well rec ogniz ...
Document
... In animals and bacteria the extra step converts pyruvate to lactate (or lactic acid). This is a reduction, so NADH is used and NAD is regenerated, to be used in glycolysis. The reaction is reversible, so the energy remaining in the lactate molecule can be retrieved when oxygen becomes available and ...
... In animals and bacteria the extra step converts pyruvate to lactate (or lactic acid). This is a reduction, so NADH is used and NAD is regenerated, to be used in glycolysis. The reaction is reversible, so the energy remaining in the lactate molecule can be retrieved when oxygen becomes available and ...
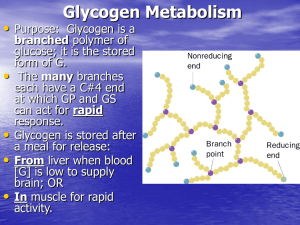
Glycogen Metabolism - http://www.utm.edu
... PEP pyr ACoA.) (These AAs are “ketogenic) So, these C’s of xs AA intake (in relation to need for protein synth) are used as fuel, just like dietary CH2O’s, fats. 2. Part (or all) of the C’s of 18 of the AAs can be converted to TCA intermediates, which can be converted to G (TCA int oxac PEP ...
... PEP pyr ACoA.) (These AAs are “ketogenic) So, these C’s of xs AA intake (in relation to need for protein synth) are used as fuel, just like dietary CH2O’s, fats. 2. Part (or all) of the C’s of 18 of the AAs can be converted to TCA intermediates, which can be converted to G (TCA int oxac PEP ...
Second Half of Glycolysis
... Glycolysis starts with glucose and ends with two pyruvate molecules, a total of four ATP molecules and two molecules of NADH. Two ATP molecules were used in the first half of the pathway to prepare the six-carbon ring for cleavage, so the cell has a net gain of two ATP molecules and 2 NADH molecules ...
... Glycolysis starts with glucose and ends with two pyruvate molecules, a total of four ATP molecules and two molecules of NADH. Two ATP molecules were used in the first half of the pathway to prepare the six-carbon ring for cleavage, so the cell has a net gain of two ATP molecules and 2 NADH molecules ...
NF96-251 A Comparative Study of Fiber Digestion and Subsequent
... minerals has occurred in the small intestine. Because the site of fiber digestion is after the small intestine, this means that little to no protein or amino acid utilization can occur during the microbial forage breakdown. Protein and amino acids are basically only absorbed in the small intestine w ...
... minerals has occurred in the small intestine. Because the site of fiber digestion is after the small intestine, this means that little to no protein or amino acid utilization can occur during the microbial forage breakdown. Protein and amino acids are basically only absorbed in the small intestine w ...
Excess of Free Fatty Acids as a Cause of Metabolic
... Although the etiology of obesity is multifactorial, main nutritional risk factors are an increase in total calorie intake and the consumption of high-fat diet (Astrup 2001). Obesity, especially with abdominal fat distribution, is frequently associated with metabolic alterations which predispose to t ...
... Although the etiology of obesity is multifactorial, main nutritional risk factors are an increase in total calorie intake and the consumption of high-fat diet (Astrup 2001). Obesity, especially with abdominal fat distribution, is frequently associated with metabolic alterations which predispose to t ...
document
... • For each glucose molecule that enters cellular respiration, chemiosmosis produces up to 38 ATP molecules Cytoplasmic fluid ...
... • For each glucose molecule that enters cellular respiration, chemiosmosis produces up to 38 ATP molecules Cytoplasmic fluid ...
Recent advances in biosynthesis of fatty acids derived products in
... the engineered strains still grew slower than the wild-type yeast strain. In addition, the use of A-ALD was only demonstrated by growth complementation and its energetic benefits for the synthesis of acetyl-CoA derived products still needs further evaluation. Recently, EcEutE was introduced into a f ...
... the engineered strains still grew slower than the wild-type yeast strain. In addition, the use of A-ALD was only demonstrated by growth complementation and its energetic benefits for the synthesis of acetyl-CoA derived products still needs further evaluation. Recently, EcEutE was introduced into a f ...
Final a
... cannot be processed via beta-oxidation. Outline the intermediates involved in converting ...
... cannot be processed via beta-oxidation. Outline the intermediates involved in converting ...
Influence of hepatic ammonia removal on ureagenesis, amino acid
... The mass transfers of O 2, glucose, NH 3, urea and amino acids across the portal-drained viscera (PDV) and the liver were quantified, by arterio–venous techniques, during the last 4 h of a 100 h infusion of 0 (basal), 150 or 400 mmol NH 4HCO 3/min into the mesenteric vein of three sheep given 800 g ...
... The mass transfers of O 2, glucose, NH 3, urea and amino acids across the portal-drained viscera (PDV) and the liver were quantified, by arterio–venous techniques, during the last 4 h of a 100 h infusion of 0 (basal), 150 or 400 mmol NH 4HCO 3/min into the mesenteric vein of three sheep given 800 g ...
Metabolic effects of glutamine on insulin sensitivity
... homeostasis and, in association with muscle, may increase its uptake. Unlike gluconeogenesis from other substrates, Gln mediated–gluconeogenesis represents an exergonic reaction with a net yield of 8 mol adenosine triphosphate (ATP) per mole of synthesized glucose (22, 23). ...
... homeostasis and, in association with muscle, may increase its uptake. Unlike gluconeogenesis from other substrates, Gln mediated–gluconeogenesis represents an exergonic reaction with a net yield of 8 mol adenosine triphosphate (ATP) per mole of synthesized glucose (22, 23). ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... – 36-38 ATP made from all 3 Stages – Oxidative Phosphorylation • Oxygen is final electron acceptor; water is formed • ADP is converted to ATP by adding phosphate group ...
... – 36-38 ATP made from all 3 Stages – Oxidative Phosphorylation • Oxygen is final electron acceptor; water is formed • ADP is converted to ATP by adding phosphate group ...
PP - Columbia University
... Exception #1: • 1) Water: 55 M (pure water) is considered the “unit” concentration in this case instead of 1M The concentration of water rarely changes during the course of an aqueous reaction, since water is at such a high concentration. • So when calulating Go, instead of writing in “55” when wat ...
... Exception #1: • 1) Water: 55 M (pure water) is considered the “unit” concentration in this case instead of 1M The concentration of water rarely changes during the course of an aqueous reaction, since water is at such a high concentration. • So when calulating Go, instead of writing in “55” when wat ...
Liver glucose metabolism in humans
... UDP-N-acetylglucosamine or follow the glycolytic pathway to generate pyruvate and then acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA may enter the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle to be oxidized or may be exported to the cytosol to synthesize fatty acids, when excess glucose is present within the hepatocyte. Finally, glucos ...
... UDP-N-acetylglucosamine or follow the glycolytic pathway to generate pyruvate and then acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA may enter the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle to be oxidized or may be exported to the cytosol to synthesize fatty acids, when excess glucose is present within the hepatocyte. Finally, glucos ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.