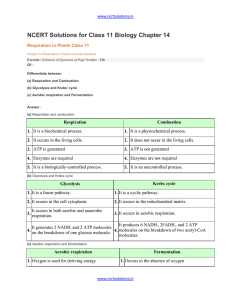
chapter_14_respiration_in_plants
... (c) Glucose molecule is assumed to be the only substrate while it is assumed that no other molecule enters the pathway at intermediate stages. (d) The intermediates produced during respiration are not utilized in any other process. ...
... (c) Glucose molecule is assumed to be the only substrate while it is assumed that no other molecule enters the pathway at intermediate stages. (d) The intermediates produced during respiration are not utilized in any other process. ...
Integrative Physiology Cardiac-Specific Deletion of Acetyl CoA
... myopathy in obesity and diabetes,12,13 it remains controversial whether enhancing FAO during the development of pathological cardiac hypertrophy will prevent metabolic remodeling and preserve myocardial energetics and function. The rate-limiting step of FAO is the import of long chain fatty acids (F ...
... myopathy in obesity and diabetes,12,13 it remains controversial whether enhancing FAO during the development of pathological cardiac hypertrophy will prevent metabolic remodeling and preserve myocardial energetics and function. The rate-limiting step of FAO is the import of long chain fatty acids (F ...
the relationship between calcium
... The citric acid levels were very low in the blood bones and joints and of difficulty in walking. From that time on she was subjected, without any satisfactory and high in the urine. The glomerular filtrate of results, to various therapeutic procedures, the details of citric acid was lower than the u ...
... The citric acid levels were very low in the blood bones and joints and of difficulty in walking. From that time on she was subjected, without any satisfactory and high in the urine. The glomerular filtrate of results, to various therapeutic procedures, the details of citric acid was lower than the u ...
View Full Page PDF - Advances in Physiology Education
... In the last three decades, the remarkable advances of molecular biology and molecular genetics have somewhat eclipsed areas of traditional biology, such as enzymology and metabolism. In recent years metabolism has reemerged as a central topic in biology (4, 30, 31). Nevertheless, recurring errors cr ...
... In the last three decades, the remarkable advances of molecular biology and molecular genetics have somewhat eclipsed areas of traditional biology, such as enzymology and metabolism. In recent years metabolism has reemerged as a central topic in biology (4, 30, 31). Nevertheless, recurring errors cr ...
Problem Set #3 Key
... (Hint: Be sure to account for energy used in activating the components of lactose so that they can enter glycolysis) B. As a belated Halloween joke, you have decided to give Kevin a batch of cookies containing an inhibitor of some enzyme associated with metabolism. After eating these delectable cook ...
... (Hint: Be sure to account for energy used in activating the components of lactose so that they can enter glycolysis) B. As a belated Halloween joke, you have decided to give Kevin a batch of cookies containing an inhibitor of some enzyme associated with metabolism. After eating these delectable cook ...
Table of Available Analyses - NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde
... Due to the complex range of tests performed, the HISS system offers over 500 biochemical tests. The following tables are a summary of the common tests and their salient pre-analytical features. Most tests are performed on heparinised plasma. Immunological tests however are best performed on serum sa ...
... Due to the complex range of tests performed, the HISS system offers over 500 biochemical tests. The following tables are a summary of the common tests and their salient pre-analytical features. Most tests are performed on heparinised plasma. Immunological tests however are best performed on serum sa ...
Lipids
... Sphingomyelin (or ceramide phosphorylcholine) consists of a ceramide unit with a phosphorylcholine moiety attached to position 1. It is thus the sphingolipid analogue of phosphatidylcholine. It is a ubiquitous component of animal cell membranes, where it is by far the most abundant sphingolipid. Ind ...
... Sphingomyelin (or ceramide phosphorylcholine) consists of a ceramide unit with a phosphorylcholine moiety attached to position 1. It is thus the sphingolipid analogue of phosphatidylcholine. It is a ubiquitous component of animal cell membranes, where it is by far the most abundant sphingolipid. Ind ...
05 Fermentations 2008
... In the presence of oxygen, reducing equivalents from glucose oxidation are transferred to oxygen, allowing the gain of an ...
... In the presence of oxygen, reducing equivalents from glucose oxidation are transferred to oxygen, allowing the gain of an ...
You Light Up My Life
... • When ATP levels rise high enough, glucose6-phosphate is diverted into glycogen synthesis (mainly in liver and muscle) • Glycogen is the main storage polysaccharide ...
... • When ATP levels rise high enough, glucose6-phosphate is diverted into glycogen synthesis (mainly in liver and muscle) • Glycogen is the main storage polysaccharide ...
The effect of short chain fatty acids on glucose homeostasis
... Feed intake elevates plasma glucose levels and subsequently insulin release is initiated to maintain glucose homeostasis. Insulin clears glucose from the blood by inhibiting endogenous glucose production and gluconeogenesis in the liver, and by stimulating glucose uptake in muscle- and adipose tissu ...
... Feed intake elevates plasma glucose levels and subsequently insulin release is initiated to maintain glucose homeostasis. Insulin clears glucose from the blood by inhibiting endogenous glucose production and gluconeogenesis in the liver, and by stimulating glucose uptake in muscle- and adipose tissu ...
Chapter 13 - TCA Cycle
... The inner membrane contains a transporter to move pyruvate into the matrix. ...
... The inner membrane contains a transporter to move pyruvate into the matrix. ...
BIOCHEMISTRY
... the management of patients. Biochemical tests are used extensively in medicine, both in relation to diseases that have an obvious metabolic basis (diabetes mellitus, hypo- or hyperthyroidism, etc.) and those in which biochemical changes are a consequence of the disease (malabsorption, renal failure, ...
... the management of patients. Biochemical tests are used extensively in medicine, both in relation to diseases that have an obvious metabolic basis (diabetes mellitus, hypo- or hyperthyroidism, etc.) and those in which biochemical changes are a consequence of the disease (malabsorption, renal failure, ...
The risks and benefits of feeding intact male swine in the United
... suggeststhat for this age group, the maximumingestivecapacitylies between2.0-2.2kg per day,and that diets of 3350-3465 kcal DE(14070-14550kJ)are required to maximize protein and fat growth. On a typical westernCanadian diet which lacks corn but is based on wheat, barley, and soybean meal as the grai ...
... suggeststhat for this age group, the maximumingestivecapacitylies between2.0-2.2kg per day,and that diets of 3350-3465 kcal DE(14070-14550kJ)are required to maximize protein and fat growth. On a typical westernCanadian diet which lacks corn but is based on wheat, barley, and soybean meal as the grai ...
respiration - sandsbiochem
... The role of glycolysis in oxidizing glucose to two molecules of pyruvate. The process that brings pyruvate from the cytosol into the mitochondria and introduces it into the citric acid cycle. How the process of chemiosmosis utilizes the electrons from NADH and FADH2 to produce ATP. ...
... The role of glycolysis in oxidizing glucose to two molecules of pyruvate. The process that brings pyruvate from the cytosol into the mitochondria and introduces it into the citric acid cycle. How the process of chemiosmosis utilizes the electrons from NADH and FADH2 to produce ATP. ...
Causes and interpretation of abnormal liver function tests
... Immunisation with Hepatitis B – See footnote (a) Anti-HBs ...
... Immunisation with Hepatitis B – See footnote (a) Anti-HBs ...
Ch18.doc
... 5. Both alanine and lactate have to be converted to pyruvate. From lactate, it is the lactate dehydrogenase reaction (1 NADH), then pyruvate gets oxidized by pyruvate dehydrogenase (1 NADH) and one turn of the CAC: yielding 3NADH, 1FADH2 and 1 GTP. Converting NADH and FADH2 to ATPs we use 1 NADH = 2 ...
... 5. Both alanine and lactate have to be converted to pyruvate. From lactate, it is the lactate dehydrogenase reaction (1 NADH), then pyruvate gets oxidized by pyruvate dehydrogenase (1 NADH) and one turn of the CAC: yielding 3NADH, 1FADH2 and 1 GTP. Converting NADH and FADH2 to ATPs we use 1 NADH = 2 ...
Novel regulatory roles of omega-3 fatty acids in metabolic pathways
... proteins involved in regulating lipid, carbohydrate, one-carbon, citric acid cycle and protein metabolism, suggesting integrated regulation of metabolic pathways. These novel proteins are potential targets to develop therapeutic strategies against metabolic disorders. ...
... proteins involved in regulating lipid, carbohydrate, one-carbon, citric acid cycle and protein metabolism, suggesting integrated regulation of metabolic pathways. These novel proteins are potential targets to develop therapeutic strategies against metabolic disorders. ...
part_4_cellular_respiration_stations
... Station 5: Special types of Anaerobic Respiration – Lactic Acid and Alcohol Fermentation Lactic acid fermentation is a type of anaerobic respiration that does not require oxygen. It occurs in muscle cells found in humans. Muscle cells normally use aerobic respiration when oxygen is sufficient. When ...
... Station 5: Special types of Anaerobic Respiration – Lactic Acid and Alcohol Fermentation Lactic acid fermentation is a type of anaerobic respiration that does not require oxygen. It occurs in muscle cells found in humans. Muscle cells normally use aerobic respiration when oxygen is sufficient. When ...
cellular-respiration 1
... 1. Despite a low yield of two ATP molecules, fermentation provides a quick burst of ATP energy for muscular activity. 2. Fermentation products are toxic to cells. a. When blood cannot remove all lactate from muscles, lactate changes pH and causes muscles to fatigue. b. The individual is in oxygen de ...
... 1. Despite a low yield of two ATP molecules, fermentation provides a quick burst of ATP energy for muscular activity. 2. Fermentation products are toxic to cells. a. When blood cannot remove all lactate from muscles, lactate changes pH and causes muscles to fatigue. b. The individual is in oxygen de ...
9.1 Catabolic Pathways yield energy by oxidizing organic fuels
... An Accounting of ATP Production by Cellular Respiration the overall function of cell respiration is harvesting the E of glucose for ATP synthesis During respiration, the E flows in this sequence: glucose NADH e- transport chain proton-motive force ATP 4 ATP are produced directly by sub ...
... An Accounting of ATP Production by Cellular Respiration the overall function of cell respiration is harvesting the E of glucose for ATP synthesis During respiration, the E flows in this sequence: glucose NADH e- transport chain proton-motive force ATP 4 ATP are produced directly by sub ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.