Respiration 2 PPT
... • Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle connect to many other metabolic pathways • Our bodies generally use many sources of energy in respiration (fig 9.19) regulated by feedback inhibition (fig 9.20) • Carbohydrates simple sugars, enter glycolysis • Proteins amino acids (used to build new prot ...
... • Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle connect to many other metabolic pathways • Our bodies generally use many sources of energy in respiration (fig 9.19) regulated by feedback inhibition (fig 9.20) • Carbohydrates simple sugars, enter glycolysis • Proteins amino acids (used to build new prot ...
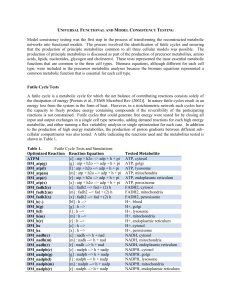
Universal Functional and Model Consistency Testing
... aminotransferase reaction and the mitochondrial alanine transporter ALAtm were both removed, based on the evidence that the mitochondrial alanine transaminase is present only on gluconeogenic tissues [DeRosa and Swick, J Biol Chem (1975)] and that there were no other alanine reactions in mitochondri ...
... aminotransferase reaction and the mitochondrial alanine transporter ALAtm were both removed, based on the evidence that the mitochondrial alanine transaminase is present only on gluconeogenic tissues [DeRosa and Swick, J Biol Chem (1975)] and that there were no other alanine reactions in mitochondri ...
espiration - WordPress.com
... muscle tissue in the presence of oxygen. The muscle preparation was able to respire some of the lactate and this provided the energy needed to convert the remaining lactate into glycogen. The diagram summarises the biochemical steps involved. ...
... muscle tissue in the presence of oxygen. The muscle preparation was able to respire some of the lactate and this provided the energy needed to convert the remaining lactate into glycogen. The diagram summarises the biochemical steps involved. ...
Module 3 Metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids
... D. All of the above E. None of the above 17. ATP is a cosubstrate of the enzyme PFK-1. In most species ATP is also an inhibitor of PFK-1 at higher concentrations. This seems to violate Le Chatelier's Principle. Which statement below would provide a suitable explanation? A. PFK-1 must be phosphorylat ...
... D. All of the above E. None of the above 17. ATP is a cosubstrate of the enzyme PFK-1. In most species ATP is also an inhibitor of PFK-1 at higher concentrations. This seems to violate Le Chatelier's Principle. Which statement below would provide a suitable explanation? A. PFK-1 must be phosphorylat ...
a method to produce insect resistance in plant by altering amino
... and Bemisia tabaci by altering concentration in artificial diet. We observed that higher concentration of D or/and E caused ~94-100 % mortality of both insects while higher concentration of N did not show any significant mortality. Deletion of such amino acids from normal diet did not show any effec ...
... and Bemisia tabaci by altering concentration in artificial diet. We observed that higher concentration of D or/and E caused ~94-100 % mortality of both insects while higher concentration of N did not show any significant mortality. Deletion of such amino acids from normal diet did not show any effec ...
Lipid Transport & Storage
... Brown adipose tissue is involved in metabolism particularly at times when heat generation is necessary ...
... Brown adipose tissue is involved in metabolism particularly at times when heat generation is necessary ...
Regulation of hepatic metabolism by AMPK - HAL
... levels following induction of fatty acid oxidation and thus may indirectly modulate the acetylation and activity of certain trancriptional regulators in addition to direct phosphorylation events [6]. AMPK phosphorylates the transcriptional coactivator peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor- coa ...
... levels following induction of fatty acid oxidation and thus may indirectly modulate the acetylation and activity of certain trancriptional regulators in addition to direct phosphorylation events [6]. AMPK phosphorylates the transcriptional coactivator peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor- coa ...
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... • Aerobic respiration consumes organic molecules and O2 and yields ATP • Anaerobic respiration is similar to aerobic respiration but consumes compounds other than O2 ...
... • Aerobic respiration consumes organic molecules and O2 and yields ATP • Anaerobic respiration is similar to aerobic respiration but consumes compounds other than O2 ...
Fatty acid desaturation and chain elongation in eukaryotes
... 2-carbon elongation process of long chain fatty acyl-CoA (Fig. 2). Condensation of fatty acyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA to ~-ketoacyl-CoA is the initial step. It is rate-limiting, determines fatty acyl specificity, and results in addition of the 2-carbon moiety. The second reaction is catalyzed by a reduc ...
... 2-carbon elongation process of long chain fatty acyl-CoA (Fig. 2). Condensation of fatty acyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA to ~-ketoacyl-CoA is the initial step. It is rate-limiting, determines fatty acyl specificity, and results in addition of the 2-carbon moiety. The second reaction is catalyzed by a reduc ...
Dual-Source Chromium
... protein, and fat metabolism. The biologically active form of chromium, sometimes called glucose tolerance factor (GTF), occurs naturally in brewers yeast. GTF has been proposed to be a complex of chromium, nicotinic acid (vitamin B-3), and possibly the amino acids glycine, cysteine and glutamic acid ...
... protein, and fat metabolism. The biologically active form of chromium, sometimes called glucose tolerance factor (GTF), occurs naturally in brewers yeast. GTF has been proposed to be a complex of chromium, nicotinic acid (vitamin B-3), and possibly the amino acids glycine, cysteine and glutamic acid ...
Enzyme Hydrolyzed Collagen Protein
... After water, protein is the next most plentiful component of our bodies. The body manufactures proteins to make up hair, muscles, nails, tendons, ligaments, and other body structures such as body fluids; but not bile or urine. Proteins also function as enzymes, hormones, and as important components ...
... After water, protein is the next most plentiful component of our bodies. The body manufactures proteins to make up hair, muscles, nails, tendons, ligaments, and other body structures such as body fluids; but not bile or urine. Proteins also function as enzymes, hormones, and as important components ...
Zygorrhynchus moelleri
... were removed from the Warburg flasks, adjusted to p H 4-4.5 with H,SO, and heated to 70". The precipitated protein was removed by Centrifugation and the supernatant diluted to 50 ml. with water. The acid anions were adsorbed on Amberlite IRA-400 and eluted with 1.0 N-( NH,),CO, (Bryant & Overell, 19 ...
... were removed from the Warburg flasks, adjusted to p H 4-4.5 with H,SO, and heated to 70". The precipitated protein was removed by Centrifugation and the supernatant diluted to 50 ml. with water. The acid anions were adsorbed on Amberlite IRA-400 and eluted with 1.0 N-( NH,),CO, (Bryant & Overell, 19 ...
Document
... cholesterol biosynthesis are regulated. To predict whether intracellular cholesterol synthesis will be up- or down-regulated in response to energy availability as influenced by diet, hormones and exercise. To distinguish the different mechanisms by which plasma cholesterol levels are controlled by c ...
... cholesterol biosynthesis are regulated. To predict whether intracellular cholesterol synthesis will be up- or down-regulated in response to energy availability as influenced by diet, hormones and exercise. To distinguish the different mechanisms by which plasma cholesterol levels are controlled by c ...
Conversion of amino acids to specialized products
... Outside the nervous system, norepinephrine and its methylated derivative, epinephrine regulates carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. They are released from storage vehicles in the adrenal medulla in response to stress (fright, exercise, cold, and low levels of blood glucose). They increase the degrada ...
... Outside the nervous system, norepinephrine and its methylated derivative, epinephrine regulates carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. They are released from storage vehicles in the adrenal medulla in response to stress (fright, exercise, cold, and low levels of blood glucose). They increase the degrada ...
Nutrition Nutrient – a substance that promotes normal growth
... Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Physiological implications of class IIa bacteriocin resistance in
... fermented and in a pure mixed-acid fermentation (i.e. no lactate formed and acetate and ethanol formed in a 1 : 1 ratio), 3 mol ATP is formed per mole of glucose fermented. The increased biomass observed in media to which glucose is added and the complete recovery of glucose in fermentation products ...
... fermented and in a pure mixed-acid fermentation (i.e. no lactate formed and acetate and ethanol formed in a 1 : 1 ratio), 3 mol ATP is formed per mole of glucose fermented. The increased biomass observed in media to which glucose is added and the complete recovery of glucose in fermentation products ...
a review on biochemical mechanism of fatty acids synthesis and oil
... Fig. 2. Metabolic pathways of fatty acid and lipid biosynthesis in seed. In embryo, G-6-P, PEP and pyruvate may produce through glycolytic pathway in cytosol using sucrose. The plastid envelopes contain transporters that pass those products into plastid from cytosol. In oilseed, glycolytic pathway i ...
... Fig. 2. Metabolic pathways of fatty acid and lipid biosynthesis in seed. In embryo, G-6-P, PEP and pyruvate may produce through glycolytic pathway in cytosol using sucrose. The plastid envelopes contain transporters that pass those products into plastid from cytosol. In oilseed, glycolytic pathway i ...
Chapter 9
... respiration enable cells to produce ATP without the use of oxygen • Most cellular respiration requires O2 to produce ATP • Without O2, the electron transport chain will cease to operate • In that case, glycolysis couples with fermentation or anaerobic respiration to produce ATP (37) ...
... respiration enable cells to produce ATP without the use of oxygen • Most cellular respiration requires O2 to produce ATP • Without O2, the electron transport chain will cease to operate • In that case, glycolysis couples with fermentation or anaerobic respiration to produce ATP (37) ...
檔案下載
... kerbs cycle克氏循環 : Sir Hans Krebs, who first investigated the pathway (1953 Nobel Prize) ...
... kerbs cycle克氏循環 : Sir Hans Krebs, who first investigated the pathway (1953 Nobel Prize) ...
Postexercise recovery of skeletal muscle malonyl-CoA, acetyl
... recently demonstrated an increase in energy expenditure over a 24-h period with high-intensity exercise. The data presented in the present study provide one possible explanation for a mechanism that allows this increase in fatty acid oxidation in the postexercise recovery period. Malonyl-CoA content ...
... recently demonstrated an increase in energy expenditure over a 24-h period with high-intensity exercise. The data presented in the present study provide one possible explanation for a mechanism that allows this increase in fatty acid oxidation in the postexercise recovery period. Malonyl-CoA content ...
4:6 Fermentation
... Fermentation allows the production of a small amount of ATP without oxygen. ...
... Fermentation allows the production of a small amount of ATP without oxygen. ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.