Lecture 33 - University of Arizona
... cAMP triggers two types of phosphorylation circuits in muscle cells; one that stimulates glycogen degradation and a second that inhibits glycogen synthesis. ...
... cAMP triggers two types of phosphorylation circuits in muscle cells; one that stimulates glycogen degradation and a second that inhibits glycogen synthesis. ...
Molecular Cloning, Characterization, and mRNA Expression of
... internal water filled cavity. Due to this protein specially found in mature enterocytes, I-FABP was thought to be crucial in fatty acids trafficking, and targeting ligands to specific organelle for metabolic process. Even so, the specific function of I-FABP in animal intestine remains elusive. LCFAs ...
... internal water filled cavity. Due to this protein specially found in mature enterocytes, I-FABP was thought to be crucial in fatty acids trafficking, and targeting ligands to specific organelle for metabolic process. Even so, the specific function of I-FABP in animal intestine remains elusive. LCFAs ...
unit 1: introduction to biology
... which prevents free diffusion of these solutes cross this barrier; they can only pass the membrane through selective membrane openings (= pores) cells tap the potential energy conserved in a proton (= H+) gradient to synthesize ATP with the help of a highly specialized enzyme system, called ATP-sy ...
... which prevents free diffusion of these solutes cross this barrier; they can only pass the membrane through selective membrane openings (= pores) cells tap the potential energy conserved in a proton (= H+) gradient to synthesize ATP with the help of a highly specialized enzyme system, called ATP-sy ...
Document
... Loss of electrons from one substance = oxidation. Addition of electrons to a substance = reduction. Oxidizing agent - accepts electrons. Reducing agent - gives up electrons. ...
... Loss of electrons from one substance = oxidation. Addition of electrons to a substance = reduction. Oxidizing agent - accepts electrons. Reducing agent - gives up electrons. ...
Reaction of glycolysis
... tissues, such as actively metabolizing muscle. NAD+ is recycled in the process • In some organisms, pyruvate is converted to ethanol in a process requiring thiamine pyrophosphate as a coenzyme ...
... tissues, such as actively metabolizing muscle. NAD+ is recycled in the process • In some organisms, pyruvate is converted to ethanol in a process requiring thiamine pyrophosphate as a coenzyme ...
Slide 1
... and FADH2 molecules With the help of CoA, the acetyl (two-carbon) compound enters the citric acid cycle – At this point, the acetyl group associates with a fourcarbon molecule forming a six-carbon molecule – The six-carbon molecule then passes through a series of redox reactions that regenerate th ...
... and FADH2 molecules With the help of CoA, the acetyl (two-carbon) compound enters the citric acid cycle – At this point, the acetyl group associates with a fourcarbon molecule forming a six-carbon molecule – The six-carbon molecule then passes through a series of redox reactions that regenerate th ...
The Syndrome of Carnitine Deficiency: Morphological and Metabolic
... cases have been published (Markesbery et al., 1974; Vandyke et al., 1975; Karpati et al., 1975; Smyth et al., 1975; Angelini et al., 1976; Boudin et al., 1976; Isaacs et al., 1977; Cornelio et al., 1977; Engel et al., 1977). From these studies, it is possible to recognize two types of carnitine defi ...
... cases have been published (Markesbery et al., 1974; Vandyke et al., 1975; Karpati et al., 1975; Smyth et al., 1975; Angelini et al., 1976; Boudin et al., 1976; Isaacs et al., 1977; Cornelio et al., 1977; Engel et al., 1977). From these studies, it is possible to recognize two types of carnitine defi ...
The malonyl CoA axis as a potential target for treating ischaemic
... 5. Regulation of malonyl CoA As mentioned previously, malonyl CoA is a potent endogenous inhibitor of CPT-I, the rate-limiting enzyme in the mitochondrial uptake of fatty acids. Thus, malonyl CoA decreases the uptake of fatty acids into the mitochondria, thereby reducing mitochondrial fatty acid b-o ...
... 5. Regulation of malonyl CoA As mentioned previously, malonyl CoA is a potent endogenous inhibitor of CPT-I, the rate-limiting enzyme in the mitochondrial uptake of fatty acids. Thus, malonyl CoA decreases the uptake of fatty acids into the mitochondria, thereby reducing mitochondrial fatty acid b-o ...
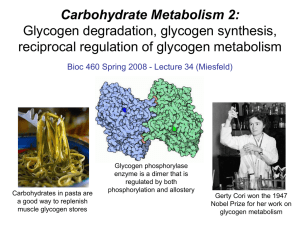
inclusion of a glycogen regulation mathematical model into a
... biochemical processes that make up metabolic pathways are regulated on many levels, such as by metabolites, hormones and enzymes, and also at a pre-protein level through transcription. While the model developed here does not include all levels of metabolic ...
... biochemical processes that make up metabolic pathways are regulated on many levels, such as by metabolites, hormones and enzymes, and also at a pre-protein level through transcription. While the model developed here does not include all levels of metabolic ...
Corn Syrups: Clearing up the Confusion
... syrups range from a low of 20 to above 73 DE. Spray or vacuum drum driers are used to make dried corn syrups (corn syrup solids), which function the same as liquid products when rehydrated. HFCS contains both fructose and glucose (a key distinguishing feature from regular corn syrups), and are not c ...
... syrups range from a low of 20 to above 73 DE. Spray or vacuum drum driers are used to make dried corn syrups (corn syrup solids), which function the same as liquid products when rehydrated. HFCS contains both fructose and glucose (a key distinguishing feature from regular corn syrups), and are not c ...
Understanding fatty acid synthesis in developing - Shachar
... for fatty acid synthesis is in the form of acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) which cannot cross the plastidic membrane (Weaire and Kekwick, 1975; Roughan et al., 1979). Precursors for acetylCoA synthesis must thus be generated in the plastid or imported from the cytosol. In heterotrophic oilseeds, lipi ...
... for fatty acid synthesis is in the form of acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) which cannot cross the plastidic membrane (Weaire and Kekwick, 1975; Roughan et al., 1979). Precursors for acetylCoA synthesis must thus be generated in the plastid or imported from the cytosol. In heterotrophic oilseeds, lipi ...
Introduction to Biochemistry
... Because vitamin A is a fat soluble vitamin, it can be stored in our body. We can actually get too much, although this is not very common. Too much vitamin A, just like too little, can cause birth defects. Some prescriptions, such as accutane for severe acne, are similar to high levels of vitamin A ...
... Because vitamin A is a fat soluble vitamin, it can be stored in our body. We can actually get too much, although this is not very common. Too much vitamin A, just like too little, can cause birth defects. Some prescriptions, such as accutane for severe acne, are similar to high levels of vitamin A ...
electron transport chain.
... and fatty acids (used in generating acetyl CoA). • Fatty acids are broken down by beta oxidation and yield acetyl CoA. • An oxidized gram of fat produces more than twice as much ATP as an oxidized gram of carbohydrate. ...
... and fatty acids (used in generating acetyl CoA). • Fatty acids are broken down by beta oxidation and yield acetyl CoA. • An oxidized gram of fat produces more than twice as much ATP as an oxidized gram of carbohydrate. ...
Platelets
... Factor II(Prothrombin): Inactive precursor of thrombin Factor III(Tissue factor/ Tissue thromboplastin): converts prothrombin to thrombin in presence of factors V, VII, ...
... Factor II(Prothrombin): Inactive precursor of thrombin Factor III(Tissue factor/ Tissue thromboplastin): converts prothrombin to thrombin in presence of factors V, VII, ...
Ketone Body Metabolism Preserves Hepatic Function during
... ketone body metabolism during a classically ketogenic period, the transition to birth, and in a classically ‘non-ketogenic’ state, overnutrition, using novel genetic mouse models, high-resolution measures of dynamic metabolism using ...
... ketone body metabolism during a classically ketogenic period, the transition to birth, and in a classically ‘non-ketogenic’ state, overnutrition, using novel genetic mouse models, high-resolution measures of dynamic metabolism using ...
PREGNANCY AND PKU: The Journey
... help women with PKU gain metabolic control before or during a pregnancy by providing social support and promoting a positive attitude about treatment through home visitation. The Resource Mothers are women who have children with PKU, and thus understand the diet and hardships associated with the dis ...
... help women with PKU gain metabolic control before or during a pregnancy by providing social support and promoting a positive attitude about treatment through home visitation. The Resource Mothers are women who have children with PKU, and thus understand the diet and hardships associated with the dis ...
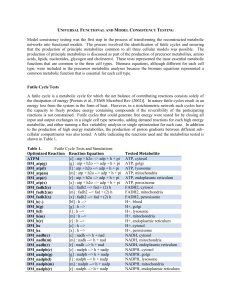
Universal Functional and Model Consistency Testing
... aminotransferase reaction and the mitochondrial alanine transporter ALAtm were both removed, based on the evidence that the mitochondrial alanine transaminase is present only on gluconeogenic tissues [DeRosa and Swick, J Biol Chem (1975)] and that there were no other alanine reactions in mitochondri ...
... aminotransferase reaction and the mitochondrial alanine transporter ALAtm were both removed, based on the evidence that the mitochondrial alanine transaminase is present only on gluconeogenic tissues [DeRosa and Swick, J Biol Chem (1975)] and that there were no other alanine reactions in mitochondri ...
Respiration 2 PPT
... • Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle connect to many other metabolic pathways • Our bodies generally use many sources of energy in respiration (fig 9.19) regulated by feedback inhibition (fig 9.20) • Carbohydrates simple sugars, enter glycolysis • Proteins amino acids (used to build new prot ...
... • Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle connect to many other metabolic pathways • Our bodies generally use many sources of energy in respiration (fig 9.19) regulated by feedback inhibition (fig 9.20) • Carbohydrates simple sugars, enter glycolysis • Proteins amino acids (used to build new prot ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.