cell energy test review
... 13. Where do the Kreb’s cycle and the electron transport system take place? 14 What happens to the H+ produced in the citric acid cycle? 15. In what part of aerobic respiration are the most ATP produced? 16. How are the equations for photosynthesis and aerobic respiration related? ...
... 13. Where do the Kreb’s cycle and the electron transport system take place? 14 What happens to the H+ produced in the citric acid cycle? 15. In what part of aerobic respiration are the most ATP produced? 16. How are the equations for photosynthesis and aerobic respiration related? ...
Biochemistry 3020 1. The consumption of
... 1. The consumption of alcohol (ethanol), especially after periods of strenuous activity or after not eating for several hours, result in a deficiency of glucose in the blood, a condition known as hypoglycemia The first step in the metabolism of ethanol by the liver is oxidation to acetaldehyde, cata ...
... 1. The consumption of alcohol (ethanol), especially after periods of strenuous activity or after not eating for several hours, result in a deficiency of glucose in the blood, a condition known as hypoglycemia The first step in the metabolism of ethanol by the liver is oxidation to acetaldehyde, cata ...
Carbohydrate Storage and Synthesis in Liver and Muscle: Glycogen
... Normally, blood [glucose] range is between 4 – 6.5 mM = glycemia (about 80 – 120 mg/dL) ...
... Normally, blood [glucose] range is between 4 – 6.5 mM = glycemia (about 80 – 120 mg/dL) ...
Unit Two “Energy Acquisition”
... 2. The “Phosphorylated” Glucose is split in two, forming 2 three-carbon sugar phosphates 3. In a series of reactions, both three-carbon sugars phosphate groups are converted to “Pyruvate” 4. The above Pyruvate forming process liberates Hydrogen so it can bond with NAD+ to form NADH, and 2 ATP’s are ...
... 2. The “Phosphorylated” Glucose is split in two, forming 2 three-carbon sugar phosphates 3. In a series of reactions, both three-carbon sugars phosphate groups are converted to “Pyruvate” 4. The above Pyruvate forming process liberates Hydrogen so it can bond with NAD+ to form NADH, and 2 ATP’s are ...
Rest to Exercise Transition
... Inadequate oxygen consumption during exercise – Resulted in oxygen deficit – Body borrowed on its energy reserves – Extra oxygen consumed (above rest) during recovery-oxygen debt Oxygen debt was then used as a measure of anaerobic metabolism during exercise – Inadequate for estimating anaerobic meta ...
... Inadequate oxygen consumption during exercise – Resulted in oxygen deficit – Body borrowed on its energy reserves – Extra oxygen consumed (above rest) during recovery-oxygen debt Oxygen debt was then used as a measure of anaerobic metabolism during exercise – Inadequate for estimating anaerobic meta ...
cellular respiration
... Made in muscles during strenuous exercise B/c the body can’t supply enough O2 to the tissues ...
... Made in muscles during strenuous exercise B/c the body can’t supply enough O2 to the tissues ...
Wheatgrass Chlorophyllcdmcoct022012
... membranes. Too much of Vitamin A from animals (retin) may be toxic, your body stores any amount of vitamin from plants (beta carotene) until it is neede. ...
... membranes. Too much of Vitamin A from animals (retin) may be toxic, your body stores any amount of vitamin from plants (beta carotene) until it is neede. ...
24.8 Fates of the Carbon Atoms from Amino Acids
... Match each of the following citric acid intermediates with the amino acid that provides its carbon skeleton: 1) pyruvate 2) fumarate 3) α-ketoglutarate A. cysteine B. glutamine C. aspartate ...
... Match each of the following citric acid intermediates with the amino acid that provides its carbon skeleton: 1) pyruvate 2) fumarate 3) α-ketoglutarate A. cysteine B. glutamine C. aspartate ...
Hemoglobin as the main protein of erythrocytes. Its structure and
... atoms. Fatty acids activation and transport into mitochondria. The role of carnitine. Fatty acids beta-oxidation: reaction sequence. The relationship between fatty acids beta-oxidation and TCA cycle. The regulation of fatty acids beta-oxidation. Ketone bodies: biosynthesis and acetoacetate utilizati ...
... atoms. Fatty acids activation and transport into mitochondria. The role of carnitine. Fatty acids beta-oxidation: reaction sequence. The relationship between fatty acids beta-oxidation and TCA cycle. The regulation of fatty acids beta-oxidation. Ketone bodies: biosynthesis and acetoacetate utilizati ...
citric acid cycle
... Electrons removed from fatty acids during oxidation pass into the mitochondrial respiratory chain and eventually to O2. The structures I through IV are enzyme complexes that catalyze portions of the electron transfer to oxygen. Fatty acyl-CoA dehydrogenase feeds electrons into an electrontransfer ...
... Electrons removed from fatty acids during oxidation pass into the mitochondrial respiratory chain and eventually to O2. The structures I through IV are enzyme complexes that catalyze portions of the electron transfer to oxygen. Fatty acyl-CoA dehydrogenase feeds electrons into an electrontransfer ...
Class: X Subject: Biology Topic: Life processes No. of
... Energy is stored in the form of ATP Energy is released and stored in the form of ATP Energy is used up Energy is not released at all ...
... Energy is stored in the form of ATP Energy is released and stored in the form of ATP Energy is used up Energy is not released at all ...
EPA/DHA Vegetarian - Pure Encapsulations
... Joint Health: Essential fatty acids promote healthy arachidonic acid metabolism to support joint function and comfort. Research suggests that they modulate immune mediator activity as well as provide support for joint flexibility.* Emotional Well-being: Omega-3 fatty acids have demonstrated the pote ...
... Joint Health: Essential fatty acids promote healthy arachidonic acid metabolism to support joint function and comfort. Research suggests that they modulate immune mediator activity as well as provide support for joint flexibility.* Emotional Well-being: Omega-3 fatty acids have demonstrated the pote ...
Control Mechanisms: Hormones
... which induce many important signal-transduction cascades. Also included are a summary table of structures and functions, as well as descriptions of hormone receptors, second-messenger molecules, & related diseases. Medical Biochemistry Page, Terre Haute Cntr for Medical Education ...
... which induce many important signal-transduction cascades. Also included are a summary table of structures and functions, as well as descriptions of hormone receptors, second-messenger molecules, & related diseases. Medical Biochemistry Page, Terre Haute Cntr for Medical Education ...
Biochemistry - Austin Community College
... • Enzymes are proteins that carry out most catalysis in living organisms. • Unlike heat, enzymes are highly specific. Each enzyme typically speeds up only one or a few chemical reactions. • Unique three-dimensional shape enables an enzyme to stabilize a temporary association between substrates. • Be ...
... • Enzymes are proteins that carry out most catalysis in living organisms. • Unlike heat, enzymes are highly specific. Each enzyme typically speeds up only one or a few chemical reactions. • Unique three-dimensional shape enables an enzyme to stabilize a temporary association between substrates. • Be ...
topic 2 powerpoint
... • Cholesterol and fats: non-polar, low solubility, transported in plasma by blood proteins that have a polar area and a non-polar area. • Oxygen: non-polar, low solubility. Carried in plasma by hemoglobin of red blood cells. • Salt: polar, very soluble in plasma ...
... • Cholesterol and fats: non-polar, low solubility, transported in plasma by blood proteins that have a polar area and a non-polar area. • Oxygen: non-polar, low solubility. Carried in plasma by hemoglobin of red blood cells. • Salt: polar, very soluble in plasma ...
Chapter 8 Lecture Notes - Science Learning Center
... All the NADH and FADH2 from glycolysis and the Krebs cycle must go through electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation to convert the stored energy into ATP. O2 is the final electron acceptor for the electron transport chain, if no O2 then the no electron transport. (Since all the NADH and FADH ...
... All the NADH and FADH2 from glycolysis and the Krebs cycle must go through electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation to convert the stored energy into ATP. O2 is the final electron acceptor for the electron transport chain, if no O2 then the no electron transport. (Since all the NADH and FADH ...
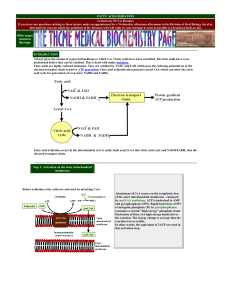
Lipid Synthesis 1. Fatty acid synthesis
... Ultimately, the principal enzyme fatty acid synthase was isolated and characterized. From eucaryotes it was found to be a single large protein with several activites whereas in bacteria, it was a complex of several proteins each with a different activity. Ultimately, the individual activities in the ...
... Ultimately, the principal enzyme fatty acid synthase was isolated and characterized. From eucaryotes it was found to be a single large protein with several activites whereas in bacteria, it was a complex of several proteins each with a different activity. Ultimately, the individual activities in the ...
(a) Name the monosaccharides of which the
... The diagram shows one method by which amino acids are absorbed from the small intestine into the blood. They are co-transported into the epithelial cell with sodium ions (Na+) at point X on the diagram. Normally, the concentration of sodium ions inside the epithelial cell is ...
... The diagram shows one method by which amino acids are absorbed from the small intestine into the blood. They are co-transported into the epithelial cell with sodium ions (Na+) at point X on the diagram. Normally, the concentration of sodium ions inside the epithelial cell is ...
sheet#11
... levels(hyperglycemia) " i. e. while digesting a meal" to store glucose in the form of glycogen, or convert it into fatty acids for storage purposes to normalize glucose level in the circulation. Remember that Km = [S]at 0.5 Vmax. Induction: means the activation of enzyme synthesis. GK is induced b ...
... levels(hyperglycemia) " i. e. while digesting a meal" to store glucose in the form of glycogen, or convert it into fatty acids for storage purposes to normalize glucose level in the circulation. Remember that Km = [S]at 0.5 Vmax. Induction: means the activation of enzyme synthesis. GK is induced b ...
new04CH4E28.62W
... 2. Acetyl CoA enters the Krebs cycle and forms 2 ATP, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen. 3. Hydrogen in the cell combines with two coenzymes that carry it to the electron transport chain. 4. Electron transport chain recombines hydrogen atoms to produce ATP and water. 5. One molecule of glycogen can gener ...
... 2. Acetyl CoA enters the Krebs cycle and forms 2 ATP, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen. 3. Hydrogen in the cell combines with two coenzymes that carry it to the electron transport chain. 4. Electron transport chain recombines hydrogen atoms to produce ATP and water. 5. One molecule of glycogen can gener ...
File - Mr. Shanks` Class
... c) Fructose - 1 ,6 biphosphate d) Glucose 3. Which one of the following is a reduced electron carrier that carries electrons to the ETC? a) GDP b) NADH+H+ c) NAD d) ADP 4. What are the names of both 3 carbon molecules that result when glucose is broken down? a) Glyceraldehyde – 3 – phosphate, 1,3 – ...
... c) Fructose - 1 ,6 biphosphate d) Glucose 3. Which one of the following is a reduced electron carrier that carries electrons to the ETC? a) GDP b) NADH+H+ c) NAD d) ADP 4. What are the names of both 3 carbon molecules that result when glucose is broken down? a) Glyceraldehyde – 3 – phosphate, 1,3 – ...
PDF - MD Body and Med spa
... bodies are produced by liver mitochondria. This is because the large amount of acetyl CoA produced by beta oxidation overloads the citric acid cycle (limited carbohydrate means that citric acid intermediates will be depleted not enough oxaloacetate to condense with all that acetyl CoA). Instead, ace ...
... bodies are produced by liver mitochondria. This is because the large amount of acetyl CoA produced by beta oxidation overloads the citric acid cycle (limited carbohydrate means that citric acid intermediates will be depleted not enough oxaloacetate to condense with all that acetyl CoA). Instead, ace ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.