TAP538-0: Electron scattering
... (The virtue of the approach is not that students should be able to reproduce the mathematics, but that they should be able to see that a systematic application of the mathematics related to diffraction and the wave nature of the electron can give the size of the nucleus.) Electron beam energy = 100 ...
... (The virtue of the approach is not that students should be able to reproduce the mathematics, but that they should be able to see that a systematic application of the mathematics related to diffraction and the wave nature of the electron can give the size of the nucleus.) Electron beam energy = 100 ...
Document
... Since particles move aside the reduction of potential then as time goes by they gather in units. In each point gradient force has a cross-section and longitudinal component. But the longitudinal component in the sum gives zero. Hence the gradient force operates only with a cross-section direction an ...
... Since particles move aside the reduction of potential then as time goes by they gather in units. In each point gradient force has a cross-section and longitudinal component. But the longitudinal component in the sum gives zero. Hence the gradient force operates only with a cross-section direction an ...
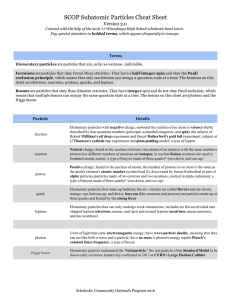
SCOP Subatomic Particles Cheat Sheet
... sheet are electrons, neutrons, protons, quarks, and leptons. Bosons are particles that obey BoseEinstein statistics. They have integer spin and do not obey Pauli exclusion, which means that multiple bosons can occupy the same quantum ...
... sheet are electrons, neutrons, protons, quarks, and leptons. Bosons are particles that obey BoseEinstein statistics. They have integer spin and do not obey Pauli exclusion, which means that multiple bosons can occupy the same quantum ...
Energy_and_Momentum_Units_in_Particle_Physics
... Particle physicists measure energies in GeV, where 1 GeV = 109 eV = energy gained by an electron or proton accelerated through 109 volts. How does one use E2 = p2c2 + m2c4 to measure mass using particle physicists’ units? For the units in each term of E2 = p2c2 +m2c4 to be the same, p must be in Ge ...
... Particle physicists measure energies in GeV, where 1 GeV = 109 eV = energy gained by an electron or proton accelerated through 109 volts. How does one use E2 = p2c2 + m2c4 to measure mass using particle physicists’ units? For the units in each term of E2 = p2c2 +m2c4 to be the same, p must be in Ge ...
History of The Atom2014 (1)
... • Since the mere act of observing an echanges it’s direction or momentum, we can only measure the PROBABILITY of finding an electron in a specific location. • Quantum tells us the statistical probability of finding an electron at a given location derived from wave equations and used to determine the ...
... • Since the mere act of observing an echanges it’s direction or momentum, we can only measure the PROBABILITY of finding an electron in a specific location. • Quantum tells us the statistical probability of finding an electron at a given location derived from wave equations and used to determine the ...
The Modern Nuclear Atom
... • Isotopes = atoms with the same number of electrons and protons but different numbers of neutrons. • Atomic number = number of protons • Mass number = the sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus ...
... • Isotopes = atoms with the same number of electrons and protons but different numbers of neutrons. • Atomic number = number of protons • Mass number = the sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus ...
Document
... Fermions versus Bosons Quantum theory tells us that angular momentum (amount of spin) = n (h/2) Experimental fact: Fermions have n = 1, 3, 5, … Bosons have n = 0, 2, 4, … ...
... Fermions versus Bosons Quantum theory tells us that angular momentum (amount of spin) = n (h/2) Experimental fact: Fermions have n = 1, 3, 5, … Bosons have n = 0, 2, 4, … ...
Glossary - Angelfire
... cross. Although black holes are strictly speaking still a theory, there is strong evidence to support their existence. It is thought that black holes exist at the centre of some galaxies, and inside "QUASARS" Blue-shift - When an object is moving towards us very quickly, the light waves coming from ...
... cross. Although black holes are strictly speaking still a theory, there is strong evidence to support their existence. It is thought that black holes exist at the centre of some galaxies, and inside "QUASARS" Blue-shift - When an object is moving towards us very quickly, the light waves coming from ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 18. Discuss the Born approximation method to obtain an expression for the scattering amplitude 19. Discuss the time evolution of quantum mechanical problem in the case of constant perturbation and obtain the Fermi’s Golden rule. 20. Obtain the plane wave solutions and the energy spectrum of the Dira ...
... 18. Discuss the Born approximation method to obtain an expression for the scattering amplitude 19. Discuss the time evolution of quantum mechanical problem in the case of constant perturbation and obtain the Fermi’s Golden rule. 20. Obtain the plane wave solutions and the energy spectrum of the Dira ...
Atomic Emission Spectra and Quantum mechanical Model
... cars, baseball, marbles • In quantum mechanics, matter moves like waves and it ...
... cars, baseball, marbles • In quantum mechanics, matter moves like waves and it ...
What is a Force?
... This particle would be holding not only protons to protons but protons to neutrons and neutrons to neutrons He predicted the properties the new particle should have. The neutral pion (π0) was discovered in 1947 and it was thought to be totally responsible for the strong force. We now know this is no ...
... This particle would be holding not only protons to protons but protons to neutrons and neutrons to neutrons He predicted the properties the new particle should have. The neutral pion (π0) was discovered in 1947 and it was thought to be totally responsible for the strong force. We now know this is no ...
Evolution of the Atomic Theory
... • 1. a large majority of alpha particles passed directly through the foil. • 2. few particles were deflected when shot at the foil. • 3. rarely, one particle would come back almost directly at the alpha source ...
... • 1. a large majority of alpha particles passed directly through the foil. • 2. few particles were deflected when shot at the foil. • 3. rarely, one particle would come back almost directly at the alpha source ...
There is a theory which states that if ever for... Universe is for and why it is here it will...
... ________________________________________________________________________ ...
... ________________________________________________________________________ ...
Chapter 5: Electrons In Atoms
... levels, and these electron lose energy by emitting light when they return to lower energy levels. Ordinary light is a mixture of all wavelengths, but light emitted by ...
... levels, and these electron lose energy by emitting light when they return to lower energy levels. Ordinary light is a mixture of all wavelengths, but light emitted by ...
Electron scattering

Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors.The application of electron scattering is such that it can be used as a high resolution microscope for hadronic systems, that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks.Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways:Not at all: no electron scattering occurs at all and the beam passes straight through.Single scattering: when an electron is scattered just once.Plural scattering: when electron(s) scatter several times.Multiple scattering: when electron(s) scatter very many times over.The likelihood of an electron scattering and the proliferance of the scattering is a probability function of the specimen thickness to the mean free path.