Chapter 1: Matter and Measurement
... Principle Shells and Subshells • Principle electronic shell, n = 1, 2, 3… • Angular momentum quantum number, l = 0, 1, 2…(n-1) l = 0, s l = 1, p l = 2, d l = 3, f ...
... Principle Shells and Subshells • Principle electronic shell, n = 1, 2, 3… • Angular momentum quantum number, l = 0, 1, 2…(n-1) l = 0, s l = 1, p l = 2, d l = 3, f ...
Balmer Series
... The spectrum of hydrogen is particularly important in astronomy because most of the Universe is made of hydrogen. Emission or absorption processes in hydrogen give rise to series, which are sequences of lines corresponding to atomic transitions, each ending or beginning with the same atomic state in ...
... The spectrum of hydrogen is particularly important in astronomy because most of the Universe is made of hydrogen. Emission or absorption processes in hydrogen give rise to series, which are sequences of lines corresponding to atomic transitions, each ending or beginning with the same atomic state in ...
Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
... Distinguishes the shape of the orbitals • Magnetic Quantum Number (ml) distinguishes orientation in space • Spin Quantum Number (ms) gives the 2 possible locations of the spin ...
... Distinguishes the shape of the orbitals • Magnetic Quantum Number (ml) distinguishes orientation in space • Spin Quantum Number (ms) gives the 2 possible locations of the spin ...
Spectra of Atoms
... emitted by atoms of a given element is absolutely the same for every atom of that element, no matter how hot or cold it is. Mystery #4. What is the dynamics that causes line spectra? ...
... emitted by atoms of a given element is absolutely the same for every atom of that element, no matter how hot or cold it is. Mystery #4. What is the dynamics that causes line spectra? ...
Bohr Model of the Atom
... The Danish physicist Niels Bohr, who first presented this model of the atom, based it on 3 fundamental postulates. (1) Electrons move around the nucleus in circular non-radiating orbits - called “stationary states”. However, they are not at rest! (2) An atom only emits or absorbs electromagnetic rad ...
... The Danish physicist Niels Bohr, who first presented this model of the atom, based it on 3 fundamental postulates. (1) Electrons move around the nucleus in circular non-radiating orbits - called “stationary states”. However, they are not at rest! (2) An atom only emits or absorbs electromagnetic rad ...
107 chem Assement Q
... c. Avogadro’s number d. 4.184 2. The energy of a photon of electromagnetic energy divided by its frequency equals: a. c, the speed of light b. h, Planck’s constant c. Avogadro’s number d. 4.184 3. Light that contains colors of all wavelengths is called: a. b. c. d. ...
... c. Avogadro’s number d. 4.184 2. The energy of a photon of electromagnetic energy divided by its frequency equals: a. c, the speed of light b. h, Planck’s constant c. Avogadro’s number d. 4.184 3. Light that contains colors of all wavelengths is called: a. b. c. d. ...
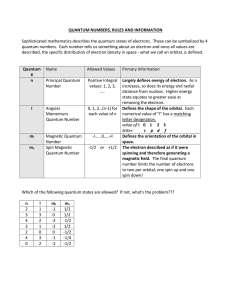
Quantum Number Table
... Largely defines energy of electron. As n increases, so does its energy and radial distance from nucleus. Higher energy state equates to greater ease at removing the electron. Defines the shape of the orbital. Each numerical value of "l" has a matching letter designation. value of l: 0 1 2 3 letter: ...
... Largely defines energy of electron. As n increases, so does its energy and radial distance from nucleus. Higher energy state equates to greater ease at removing the electron. Defines the shape of the orbital. Each numerical value of "l" has a matching letter designation. value of l: 0 1 2 3 letter: ...
03-02BohrAtom
... eV to -13.6 eV, so it releases 10.2 eV of energy. A photon with this energy has this wavelength: ...
... eV to -13.6 eV, so it releases 10.2 eV of energy. A photon with this energy has this wavelength: ...
Chapter 2: Data Analysis
... or being absorbed by atoms indicate that there are very specific energy changes within the atomic entities (atoms and ions). No nuclear changes have ever been observed ...
... or being absorbed by atoms indicate that there are very specific energy changes within the atomic entities (atoms and ions). No nuclear changes have ever been observed ...
Transparancies for Atomic Structure Section
... Angular momentum has made small contribution to energy (order 10,000th ) ...
... Angular momentum has made small contribution to energy (order 10,000th ) ...
The Zeeman Effect
... The same expressions, but with ml and ms replaced by ML and MS, apply to the combined magnetic moments of several coupled electrons. When an atom has L≠0 and S≠0, these net magnetic moments are simply additive. Spin-orbit coupling (itself a magnetic effect) is usually large enough that the total ele ...
... The same expressions, but with ml and ms replaced by ML and MS, apply to the combined magnetic moments of several coupled electrons. When an atom has L≠0 and S≠0, these net magnetic moments are simply additive. Spin-orbit coupling (itself a magnetic effect) is usually large enough that the total ele ...
Semiclassical calculation of electron spectra in atoms through two
... The features of the one-electron spectra in the spherically symmetric self-consistent attraction potentials have been under study in the paper [1] (also, reviews [2, 3]). Specifically, the potentials with the Coulomb singularity have been there considered. As is well known, the screening of the Coul ...
... The features of the one-electron spectra in the spherically symmetric self-consistent attraction potentials have been under study in the paper [1] (also, reviews [2, 3]). Specifically, the potentials with the Coulomb singularity have been there considered. As is well known, the screening of the Coul ...
- Physics
... Lyman series (UV) Paschen series (infrared) What does classical physics predict for the future of an electron orbiting a proton? What are the two postulates of Bohr's theory for the Hydrogen atom? hf = Eupper - Elower What is true about the angular momentum of the electron in an atom? What is the pr ...
... Lyman series (UV) Paschen series (infrared) What does classical physics predict for the future of an electron orbiting a proton? What are the two postulates of Bohr's theory for the Hydrogen atom? hf = Eupper - Elower What is true about the angular momentum of the electron in an atom? What is the pr ...
$doc.title
... knocked out. For high Z atoms, these are very tightly bound states (K shells), so require high energies (many keV) to eject them Spectrum shows sharp peaks, due to emission of photons by outer electrons falling to vacated core states. Energy (frequency) is characteristic of element. N.B. Lower ene ...
... knocked out. For high Z atoms, these are very tightly bound states (K shells), so require high energies (many keV) to eject them Spectrum shows sharp peaks, due to emission of photons by outer electrons falling to vacated core states. Energy (frequency) is characteristic of element. N.B. Lower ene ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).