Quantum Mechanics
... measure either the energy of anything at the same instant as time or the momentum at the same instant of position This means that if something is moving, there is a real possibility that you do not know where it actually is This is typically a very small number (10-30) for ordinary objects, but ...
... measure either the energy of anything at the same instant as time or the momentum at the same instant of position This means that if something is moving, there is a real possibility that you do not know where it actually is This is typically a very small number (10-30) for ordinary objects, but ...
(n=1).
... • Bohr’s Model gives accurate values for electron energy levels... • But Quantum Mechanics is needed to describe electrons in atom. • Electrons jump between states by emitting or absorbing photons of the appropriate energy. • Each state has specific energy and is labeled by 4 quantum numbers (next t ...
... • Bohr’s Model gives accurate values for electron energy levels... • But Quantum Mechanics is needed to describe electrons in atom. • Electrons jump between states by emitting or absorbing photons of the appropriate energy. • Each state has specific energy and is labeled by 4 quantum numbers (next t ...
WAVE MECHANICS (Schrödinger, 1926)
... WAVE MECHANICS * The energy depends only on the principal quantum number, as in the Bohr model: En = -2.179 X 10-18J /n2 * The orbitals are named by giving the n value followed by a letter symbol for l: l= 0,1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ... s p d f g h ... * All orbitals with the same n are called a “shell”. All ...
... WAVE MECHANICS * The energy depends only on the principal quantum number, as in the Bohr model: En = -2.179 X 10-18J /n2 * The orbitals are named by giving the n value followed by a letter symbol for l: l= 0,1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ... s p d f g h ... * All orbitals with the same n are called a “shell”. All ...
Particles and waves
... possible information about electron motion in an atom In each orbital electron has precise energy, magnitude for angular momentum All other dynamical variables (position, velocity etc.) do not have sharply defined values The square of the wave function directly gives the position probability distrib ...
... possible information about electron motion in an atom In each orbital electron has precise energy, magnitude for angular momentum All other dynamical variables (position, velocity etc.) do not have sharply defined values The square of the wave function directly gives the position probability distrib ...
PHYS 481/681 Quantum Mechanics Stephen Lepp August 29, 2016
... Introduction to Quantum Mechanics nd the interpretation of its solutions, the uncertainty principles, one-dimensional problems, harmonic oscillator, angular momentum, the hydrogen atom. 3 credits. • Class MW 11:30-12:45 BPB 249. • Office Hours TTh 12:45-1:30 or by arrangement. • Textbook “Quantum Me ...
... Introduction to Quantum Mechanics nd the interpretation of its solutions, the uncertainty principles, one-dimensional problems, harmonic oscillator, angular momentum, the hydrogen atom. 3 credits. • Class MW 11:30-12:45 BPB 249. • Office Hours TTh 12:45-1:30 or by arrangement. • Textbook “Quantum Me ...
Bohr`s equation for the hydrogen atom Bohr derived an equation to
... Bohr derived an equation to give the values of the energy levels in the hydrogen atom. Bohr showed that the energy levels were proportional to 1/n2, where n is an integer. When an electron falls from one energy level E2 to another level E1 radiation of frequency f will be emitted. Bohr showed that t ...
... Bohr derived an equation to give the values of the energy levels in the hydrogen atom. Bohr showed that the energy levels were proportional to 1/n2, where n is an integer. When an electron falls from one energy level E2 to another level E1 radiation of frequency f will be emitted. Bohr showed that t ...
L - Purdue Physics
... The atom of modern physics can be symbolized only through a partial differential equation in an abstract space of many dimensions. All its qualities are inferential; no material properties can be directly attributed to it. An understanding of the atomic world in that primary sensuous fashion…is impo ...
... The atom of modern physics can be symbolized only through a partial differential equation in an abstract space of many dimensions. All its qualities are inferential; no material properties can be directly attributed to it. An understanding of the atomic world in that primary sensuous fashion…is impo ...
Corso di Fisica Moderna
... Thus L is not only conserved, but constrained to discrete values by the quantum number n. This quanAzaAon of angular momentum is a crucial result and can be used in determining the Bohr orbit radi ...
... Thus L is not only conserved, but constrained to discrete values by the quantum number n. This quanAzaAon of angular momentum is a crucial result and can be used in determining the Bohr orbit radi ...
Chemistry 1 Concept 5 “Electrons in Atoms” Study Guide
... 4. Give the number of orbitals for each sublevel: s _____, p ______, d ______, f ______ 5. What is the wavelength of microwaves of 4.0 x 109 Hz frequency? _______________ 6. An electron for which n = 4 has more _______ than an electron for which n = 2. 7. What is the frequency of a photon with an en ...
... 4. Give the number of orbitals for each sublevel: s _____, p ______, d ______, f ______ 5. What is the wavelength of microwaves of 4.0 x 109 Hz frequency? _______________ 6. An electron for which n = 4 has more _______ than an electron for which n = 2. 7. What is the frequency of a photon with an en ...
Document
... Solutions of the Schrödinger equation are 'exact' in the mathematical sense. They are not quite 'correct', however. The errors are very small for the hydrogen atom, but become more significant for heavier atoms. Partly, this is due to the assumption that only the electron moves, the nucleus being st ...
... Solutions of the Schrödinger equation are 'exact' in the mathematical sense. They are not quite 'correct', however. The errors are very small for the hydrogen atom, but become more significant for heavier atoms. Partly, this is due to the assumption that only the electron moves, the nucleus being st ...
WAVE MECHANICS AND QUANTUM NUMBERS
... equation describing the location and energy of an electron in a hydrogen atom. 2. Modern day quantum mechanical model comes from the math solutions to Schrödinger’s equations. It extended de Broglie’s work by considering the movement of a particle in an electromagnetic field. 3. Defined quantum numb ...
... equation describing the location and energy of an electron in a hydrogen atom. 2. Modern day quantum mechanical model comes from the math solutions to Schrödinger’s equations. It extended de Broglie’s work by considering the movement of a particle in an electromagnetic field. 3. Defined quantum numb ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI-600034 M.Sc. Part-A NOVEMBER 2015
... Why is a molecular plane always identified to form a class by itself? Mention the significance of Secular determinant. Write down the Hamiltonian for Hydrogen molecular ion. ...
... Why is a molecular plane always identified to form a class by itself? Mention the significance of Secular determinant. Write down the Hamiltonian for Hydrogen molecular ion. ...
L - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... angular momentum magnitude l =0,1,2… orbital angular momentum quantum number l=0: “s” orbital in chemistry l=1: “p” orbital in chemistry l=2: “d” orbital in chemistry ...
... angular momentum magnitude l =0,1,2… orbital angular momentum quantum number l=0: “s” orbital in chemistry l=1: “p” orbital in chemistry l=2: “d” orbital in chemistry ...
HWU4-21 QUESTION: The principal quantum number, n, describes
... The principal quantum number, n, describes the energy level of a particular orbital as a function of the distance from the center of the nucleus. Additional quantum numbers exist to quantify the other characteristics of the electron. The angular momentum quantum number (ℓ), the magnetic quantum numb ...
... The principal quantum number, n, describes the energy level of a particular orbital as a function of the distance from the center of the nucleus. Additional quantum numbers exist to quantify the other characteristics of the electron. The angular momentum quantum number (ℓ), the magnetic quantum numb ...
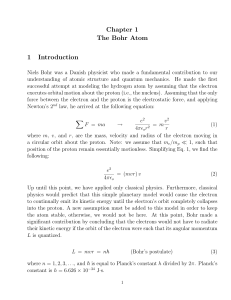
Chapter 1 The Bohr Atom 1 Introduction
... into the proton. A new assumption must be added to this model in order to keep the atom stable, otherwise, we would not be here. At this point, Bohr made a significant contribution by concluding that the electrons would not have to radiate their kinetic energy if the orbit of the electron were such ...
... into the proton. A new assumption must be added to this model in order to keep the atom stable, otherwise, we would not be here. At this point, Bohr made a significant contribution by concluding that the electrons would not have to radiate their kinetic energy if the orbit of the electron were such ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).