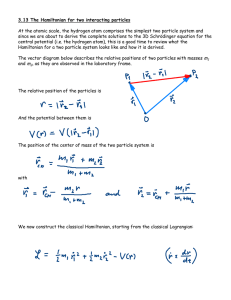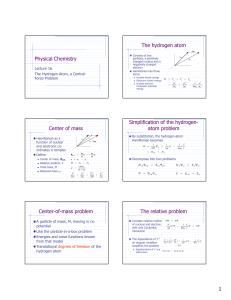
Bohr Model and Principal Quantum Number
... developed his model Bohr postulated: 1. Electrons exist in circular orbits 2. Electrons exist only in allowed orbits 3. Electrons do not radiate energy within an orbit 4. Electrons can jump between orbits ...
... developed his model Bohr postulated: 1. Electrons exist in circular orbits 2. Electrons exist only in allowed orbits 3. Electrons do not radiate energy within an orbit 4. Electrons can jump between orbits ...
Transparancies for Revision Lecture - University of Manchester
... For multi-electron atoms Energy splitting depends on l even in absence of magnetic field. ...
... For multi-electron atoms Energy splitting depends on l even in absence of magnetic field. ...
Lecture 14
... The energy depends only on n: En = -R/n2, with E0 = ħ2/2ma02 = 13.6 eV The example we gave in Lecture 13 corresponds to n=2, l=1, m=0. The energy level diagram starts at -13.6 eV, which is the binding energy of the ground state n = 1, and continues with -3.4 eV, which is the binding energy of the fi ...
... The energy depends only on n: En = -R/n2, with E0 = ħ2/2ma02 = 13.6 eV The example we gave in Lecture 13 corresponds to n=2, l=1, m=0. The energy level diagram starts at -13.6 eV, which is the binding energy of the ground state n = 1, and continues with -3.4 eV, which is the binding energy of the fi ...
Answer
... values from 0 to n − 1. In this case n = 2, so the allowed values of the angular momentum quantum number are 0 and 1. Each allowed value of the angular momentum quantum number labels a subshell. Within a given subshell (label l) there are 2l + 1 allowed energy states (orbitals) each labeled by a dif ...
... values from 0 to n − 1. In this case n = 2, so the allowed values of the angular momentum quantum number are 0 and 1. Each allowed value of the angular momentum quantum number labels a subshell. Within a given subshell (label l) there are 2l + 1 allowed energy states (orbitals) each labeled by a dif ...
Quantum Numbers and Electron Configurations Worksheet
... (# 78 from text) The energy required to ionize sodium is 496 kJ / mol. What minimum frequency of light is required to ionize sodium? ...
... (# 78 from text) The energy required to ionize sodium is 496 kJ / mol. What minimum frequency of light is required to ionize sodium? ...
Spectroscopy
... The principle quantum number is n = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, . . . En is the energy of the nth energy level. The constant R is called the Rydberg constant. Planck’s constant is h; the speed of light is c. In the Bohr Model, the Rydberg constant is predicted to be R 1.0975 x10 7 m 1 . We shall determine R e ...
... The principle quantum number is n = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, . . . En is the energy of the nth energy level. The constant R is called the Rydberg constant. Planck’s constant is h; the speed of light is c. In the Bohr Model, the Rydberg constant is predicted to be R 1.0975 x10 7 m 1 . We shall determine R e ...
Atomic Spectra
... make a transition to an s orbital (l = 0) because one photon cannot carry away enough ...
... make a transition to an s orbital (l = 0) because one photon cannot carry away enough ...
Problem Set 1
... ~ J~ and Jz where J~ is the total angular momentum operator must be eigenfunctions of J. and Jz is its z-component. ( You have a total of six wave functions) 5. Assuming the spin-orbit interaction hamiltonian is given by Hsl = ...
... ~ J~ and Jz where J~ is the total angular momentum operator must be eigenfunctions of J. and Jz is its z-component. ( You have a total of six wave functions) 5. Assuming the spin-orbit interaction hamiltonian is given by Hsl = ...
Particle on a Sphere
... Designated by letters: s, p, d, f, … Specifies the shape of an orbital Magnetic quantum number = ml Determines the z component of orbital angular momentum Z component = ml restricted to values: Specifies orientation of orbital in space ...
... Designated by letters: s, p, d, f, … Specifies the shape of an orbital Magnetic quantum number = ml Determines the z component of orbital angular momentum Z component = ml restricted to values: Specifies orientation of orbital in space ...
lecture 7
... • We want to obtain the energy of the hydrogen atom system. We will do this the same way as we got it for the particle-in-a-box: by performing the “energy operation” on the wavefunction which describes the H atom system. ...
... • We want to obtain the energy of the hydrogen atom system. We will do this the same way as we got it for the particle-in-a-box: by performing the “energy operation” on the wavefunction which describes the H atom system. ...
Notes
... There are various selection rules pertaining to how elections change orbits and produce spectral lines. For instance, if Δ 1 the transition is forbidden and occurs with very low probability. The photon carries away the angular momentum lost in the allowed transition as spin. For complex atoms, ...
... There are various selection rules pertaining to how elections change orbits and produce spectral lines. For instance, if Δ 1 the transition is forbidden and occurs with very low probability. The photon carries away the angular momentum lost in the allowed transition as spin. For complex atoms, ...
3.4oquantum.4u
... Problems with Bohr’s Model: Bohr visualised the e- as a particle by which its exact location and momentum could be determined. Actually, the e- is so small that it has both particle and wave properties so we cannot specify exact orbits. Another problem is when an electron changes energy levels durin ...
... Problems with Bohr’s Model: Bohr visualised the e- as a particle by which its exact location and momentum could be determined. Actually, the e- is so small that it has both particle and wave properties so we cannot specify exact orbits. Another problem is when an electron changes energy levels durin ...
The Modern Nuclear Atom
... and protons but different numbers of neutrons. • Atomic number = number of protons • Mass number = the sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus ...
... and protons but different numbers of neutrons. • Atomic number = number of protons • Mass number = the sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus ...
3.3 Review Name________________________________ Period_______Date_____________________
... contribution to the quantum theory listed below. Each name may be used more than once. Planck ...
... contribution to the quantum theory listed below. Each name may be used more than once. Planck ...
x 100 QUANTUM NUMBERS AND SYMBOLS
... 5. What type of orbital in an atom is designated by quantum numbers n=4, l =3, and ml =0? 6. A subshell in an atom has the values, n = 3, l =2. How many orbitals are there in this ...
... 5. What type of orbital in an atom is designated by quantum numbers n=4, l =3, and ml =0? 6. A subshell in an atom has the values, n = 3, l =2. How many orbitals are there in this ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).