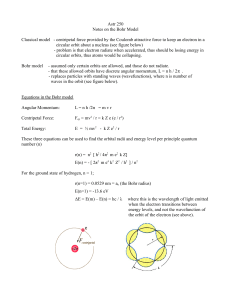
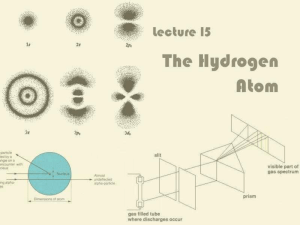
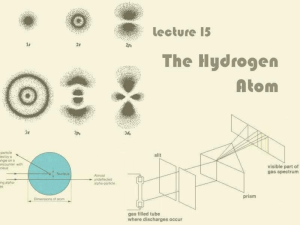
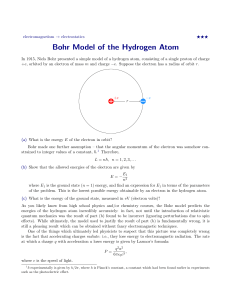
1. Low pressure gas (hydrogen,neon, mercury, argon, etc.) is
... 2. A diffraction grating or prism is used to determine what frequencies pass through the gas and which are absorbed. ...
... 2. A diffraction grating or prism is used to determine what frequencies pass through the gas and which are absorbed. ...
Lecture 15: The Hydrogen Atom
... One of the transitions in the Balmer series corresponds to the emission of red light ...
... One of the transitions in the Balmer series corresponds to the emission of red light ...
Chapters 3
... How It All Fits Together Developing a model of the atom in order to explain, predict and perform chemical reactions and chemical properties. ...
... How It All Fits Together Developing a model of the atom in order to explain, predict and perform chemical reactions and chemical properties. ...
PHYSICS 215 - Thermodynamics and Modern Physics Name:
... What is the energy difference between adjacent levels? ...
... What is the energy difference between adjacent levels? ...
Tutorial - Brock physics
... orbital quantum number `. This rule is called a selection rule and states that ∆` = ±1. In other words, when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, the value of ` can only increase or decrease by one. The value of ` may not remain the same or increase or decrease by more than one. Acc ...
... orbital quantum number `. This rule is called a selection rule and states that ∆` = ±1. In other words, when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, the value of ` can only increase or decrease by one. The value of ` may not remain the same or increase or decrease by more than one. Acc ...
Name: Date: Blk:____
... Name:_______________________________________ Date:______________________________ Blk:____ ...
... Name:_______________________________________ Date:______________________________ Blk:____ ...
Lecture 5
... Chapter 4. Atomic Spectroscopy Hartree Approximation (mean field approximation) - electronelectron repulsion is replaced with average mean field potential. Many electron system is described in terms of hydrogen-like single electron states. n : principal quantum number (shell) l, m, s : angular momen ...
... Chapter 4. Atomic Spectroscopy Hartree Approximation (mean field approximation) - electronelectron repulsion is replaced with average mean field potential. Many electron system is described in terms of hydrogen-like single electron states. n : principal quantum number (shell) l, m, s : angular momen ...
(Bohr Model And X-Rays) Part-1
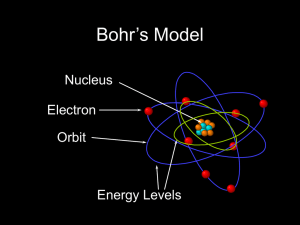
... Bohr gave following postulates for electron in hydrogen atom :• An electron in an atom could resolve in certain stable orbits without the emission of radiant energy. • An electron resolves around the nucleus only in those orbits for which the angular momentum is some integral multiple of L= ...
... Bohr gave following postulates for electron in hydrogen atom :• An electron in an atom could resolve in certain stable orbits without the emission of radiant energy. • An electron resolves around the nucleus only in those orbits for which the angular momentum is some integral multiple of L= ...
Problem Set 05
... c) An accelerating charge will lose energy due to radiation. Show that this will lead to a decrease in the electron orbital radius described by dr 2r 2 dE ...
... c) An accelerating charge will lose energy due to radiation. Show that this will lead to a decrease in the electron orbital radius described by dr 2r 2 dE ...
Powerpoint handout
... Bohr derived a more general formula to predict the observed energies of light: Each electron’s energy is determined by which level it is in. The levels are designated by whole numbers, n. ...
... Bohr derived a more general formula to predict the observed energies of light: Each electron’s energy is determined by which level it is in. The levels are designated by whole numbers, n. ...
Physics 43 Ch 42 HW# Key
... 54. Review problem. (a) How much energy is required to cause an electron in hydrogen to move from the n = 1 state to the n = 2 state? (b) Suppose the electron gains this energy through collisions among hydrogen atoms at a high temperature. At what temperature would the average atomic kinetic energy ...
... 54. Review problem. (a) How much energy is required to cause an electron in hydrogen to move from the n = 1 state to the n = 2 state? (b) Suppose the electron gains this energy through collisions among hydrogen atoms at a high temperature. At what temperature would the average atomic kinetic energy ...
Introduction to Chemistry
... To describe how diffraction experiments were used to demonstrate the dual nature of all matter. To show that the line spectrum of hydrogen demonstrates the quanitzed nature of the energy of its electron. To describe the development of the Bohr model for the hydrogen atom. To show how standing waves ...
... To describe how diffraction experiments were used to demonstrate the dual nature of all matter. To show that the line spectrum of hydrogen demonstrates the quanitzed nature of the energy of its electron. To describe the development of the Bohr model for the hydrogen atom. To show how standing waves ...
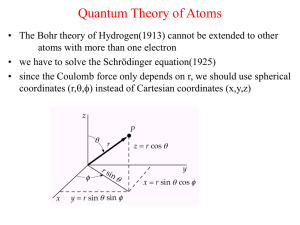
Quantum Theory of Atoms
... distance r of an electron from the nucleus • l is the orbital quantum number and the angular momentum of the electron is given by L=[l(l+1)]1/2 ħ • m is the magnetic quantum number and the component of the angular momentum along the z-axis is Lz = m ħ ...
... distance r of an electron from the nucleus • l is the orbital quantum number and the angular momentum of the electron is given by L=[l(l+1)]1/2 ħ • m is the magnetic quantum number and the component of the angular momentum along the z-axis is Lz = m ħ ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).