e-the-quantum-numberssv-2
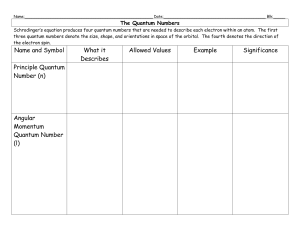
... The Quantum Numbers Schrodinger’s equation produces four quantum numbers that are needed to describe each electron within an atom. The first three quantum numbers denote the size, shape, and orientations in space of the orbital. The fourth denotes the direction of the electron spin. ...
... The Quantum Numbers Schrodinger’s equation produces four quantum numbers that are needed to describe each electron within an atom. The first three quantum numbers denote the size, shape, and orientations in space of the orbital. The fourth denotes the direction of the electron spin. ...
Document
... magnetic quantum number ml are possible? (c) For a given value of n, how many values of ml are possible? ANSWER: (a) n; (b) 2l + 1; (c) n2 8. (a) What is the magnitude of the orbital angular momentum in a state with l = 3? (b) What is the magnitude of its largest projection on an imposed z axis? ANS ...
... magnetic quantum number ml are possible? (c) For a given value of n, how many values of ml are possible? ANSWER: (a) n; (b) 2l + 1; (c) n2 8. (a) What is the magnitude of the orbital angular momentum in a state with l = 3? (b) What is the magnitude of its largest projection on an imposed z axis? ANS ...
Solution - UMD Physics
... 1. Consider an electron bound to a two-dimensional infinite quantum well with sides of length ...
... 1. Consider an electron bound to a two-dimensional infinite quantum well with sides of length ...
Ch.3 lecture
... Rydberg formula (Balmer for nf = 2) : 1 / = R (1/nf2 - 1/ni2) R = Rydberg constant = 1.097 x 107 m-1 ...
... Rydberg formula (Balmer for nf = 2) : 1 / = R (1/nf2 - 1/ni2) R = Rydberg constant = 1.097 x 107 m-1 ...
Atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a nucleus
... (or, to be precise, their electron clouds) can be observed individually using special instruments such as the scanning tunneling microscope. Hydrogen-1 (one proton + one electron) is the simplest form of atoms, and not surprisingly, our quantum mechanical understanding of atoms evolved with the unde ...
... (or, to be precise, their electron clouds) can be observed individually using special instruments such as the scanning tunneling microscope. Hydrogen-1 (one proton + one electron) is the simplest form of atoms, and not surprisingly, our quantum mechanical understanding of atoms evolved with the unde ...
Consider the following solution to the hydrogen atom problem
... a) What is the energy of this state? b) What is the angular momentum quantum number, l associated with this state? c) What is the expectation of the angular momentum projection? In other words, < Lz> = ? d) What is the probability of finding the electron somewhere along the z-axis? e) What is the pr ...
... a) What is the energy of this state? b) What is the angular momentum quantum number, l associated with this state? c) What is the expectation of the angular momentum projection? In other words, < Lz> = ? d) What is the probability of finding the electron somewhere along the z-axis? e) What is the pr ...
Mid Term Examination 2 Text
... c) (5 Points): Consider the angular momentum eigenfunction with eigenvalue 0 (zero). What kind of motion corresponds to this eigenvalue? From the corresponding eigenfunction, write down the probability density to find the rotating particle on the ring at the position given by the azimuthal angle ...
... c) (5 Points): Consider the angular momentum eigenfunction with eigenvalue 0 (zero). What kind of motion corresponds to this eigenvalue? From the corresponding eigenfunction, write down the probability density to find the rotating particle on the ring at the position given by the azimuthal angle ...
CHM 50- Class activity
... The retina of a human eye can detect light when radiant energy incident on it is at least 4.0 x 10-17 J. For light of 5.85 nm wavelength , how many photons does this energy correspond to? ...
... The retina of a human eye can detect light when radiant energy incident on it is at least 4.0 x 10-17 J. For light of 5.85 nm wavelength , how many photons does this energy correspond to? ...
Problem Set 4
... 24. (Quadratic Stark effect) Calculate the shift in energy of the ground state of hydrogen like atom in the presence of an electric field upto second order in Hel given in problem 23 in terms of an infinte sum involving all the eigenstates of the unperturbed hydrogen atom. Estimate the shift using o ...
... 24. (Quadratic Stark effect) Calculate the shift in energy of the ground state of hydrogen like atom in the presence of an electric field upto second order in Hel given in problem 23 in terms of an infinte sum involving all the eigenstates of the unperturbed hydrogen atom. Estimate the shift using o ...
Quantum Numbers Primer The quantum numbers
... ml is the magnetic quantum number (ml = -ℓ, …, –2, -1, 0, +1, +2, …, +ℓ) (note: ℓ is lowercase L... it was used here so it is not confused with the number one). ml determines the number and orientation of the orbital. When n = 1, l must be 0. When l = 0, ml = 0. Because ml has only one value (the va ...
... ml is the magnetic quantum number (ml = -ℓ, …, –2, -1, 0, +1, +2, …, +ℓ) (note: ℓ is lowercase L... it was used here so it is not confused with the number one). ml determines the number and orientation of the orbital. When n = 1, l must be 0. When l = 0, ml = 0. Because ml has only one value (the va ...
Skill Assessment Sheet Modern Atomic Theory (Quantum Mechanics)
... I am approaching proficiency in meeting the standard. ( I could finish with some help) I can consistently demonstrate proficiency in meeting the standard. ( I can do this and will be able to do it later) I can consistently exceed key concepts, processes & skills. Exceeds the standard ( I can do more ...
... I am approaching proficiency in meeting the standard. ( I could finish with some help) I can consistently demonstrate proficiency in meeting the standard. ( I can do this and will be able to do it later) I can consistently exceed key concepts, processes & skills. Exceeds the standard ( I can do more ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).