
Activity 17 Follow-up
... neutrons, but always has the same number of protons •The atomic weight is the average weight of all the known isotopes of the element •The element which appears on the periodic table is the isotope which is most abundant ...
... neutrons, but always has the same number of protons •The atomic weight is the average weight of all the known isotopes of the element •The element which appears on the periodic table is the isotope which is most abundant ...
in-class worksheet
... A maximum of ____ e– fit in each orbital! PAULI EXCLUSION PRINCIPLE In a given atom, no two electrons can have four identical quantum numbers. ...
... A maximum of ____ e– fit in each orbital! PAULI EXCLUSION PRINCIPLE In a given atom, no two electrons can have four identical quantum numbers. ...
THE ATOM - A COMPUTER GUIDED LESSON
... 3. What is Indirect Evidence? 4. What is a model? 5. Scientists have been making models of atoms for a long time. Can a model ever be changed? Explain why or why not. 6. The word atom comes from the Greek word, atomos. What is the meaning of this word? 7. Who was Democritus and what did he do? 8. Wh ...
... 3. What is Indirect Evidence? 4. What is a model? 5. Scientists have been making models of atoms for a long time. Can a model ever be changed? Explain why or why not. 6. The word atom comes from the Greek word, atomos. What is the meaning of this word? 7. Who was Democritus and what did he do? 8. Wh ...
Ch4 notes - Midway ISD
... • Unique to each element, used for identification • Continuous spectrum ...
... • Unique to each element, used for identification • Continuous spectrum ...
PH469 Fall 2002
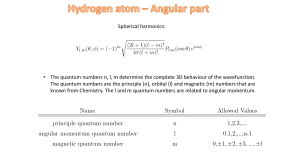
... momentum and magnetic quantum numbers (n, l, ml ) when the energy level E = 0.25E0, L2 = 2 ħ2, Lz= ħ, where E0 is the ground state energy, L is the magnitude of the angular momentum and Lz the z component of the angular momentum. ...
... momentum and magnetic quantum numbers (n, l, ml ) when the energy level E = 0.25E0, L2 = 2 ħ2, Lz= ħ, where E0 is the ground state energy, L is the magnitude of the angular momentum and Lz the z component of the angular momentum. ...
Transcript - the Cassiopeia Project
... Amazingly, the radius where the probability reaches a maximum is precisely equal to the radius of the first allowed orbit of Niels Bohr ‘s model of the hydrogen atom. And it’s energy is exactly equal to the energy of an electron in this orbit in the Bohr atom. So this is a VERY good picture of a hyd ...
... Amazingly, the radius where the probability reaches a maximum is precisely equal to the radius of the first allowed orbit of Niels Bohr ‘s model of the hydrogen atom. And it’s energy is exactly equal to the energy of an electron in this orbit in the Bohr atom. So this is a VERY good picture of a hyd ...
Atoms, electrons, nuclei J.J. Thomson discovered the electron (1897
... no energy loss and anode current (I) will increase; if Ugrid = U*, collisions might become inelastic: electrons may transfer their energy to a Mercury atom and anode current will decrease Coclusion: energy of Mercury atom cannot change continuously, but only by certain discrete values, so-called qua ...
... no energy loss and anode current (I) will increase; if Ugrid = U*, collisions might become inelastic: electrons may transfer their energy to a Mercury atom and anode current will decrease Coclusion: energy of Mercury atom cannot change continuously, but only by certain discrete values, so-called qua ...
Lecture 24: Quantum mechanics
... following Planck’s hypothesis is said to be quantized, the allowed energy states are called quantum states, and the integer n is called the quantum number. ...
... following Planck’s hypothesis is said to be quantized, the allowed energy states are called quantum states, and the integer n is called the quantum number. ...
The end
... attack the cathode of a photocell. The maximum value of the photoelectrons are v1 and v2 v1 respectively. Find the numerical threshold wavelength for the photoelectric effect of the cathode. b/ One milliwatt of light of wavelength 4,560A is incident on a caesium surface. Calculate the electron cur ...
... attack the cathode of a photocell. The maximum value of the photoelectrons are v1 and v2 v1 respectively. Find the numerical threshold wavelength for the photoelectric effect of the cathode. b/ One milliwatt of light of wavelength 4,560A is incident on a caesium surface. Calculate the electron cur ...
Periodic boundary physics etc
... In physics, specifically quantum mechanics, the Schrödinger equation is an equation that describes how the quantum state of a physical system changes in time. It is as central to quantum mechanics as Newton's laws are to classical mechanics. In the standard interpretation of quantum mechanics, the q ...
... In physics, specifically quantum mechanics, the Schrödinger equation is an equation that describes how the quantum state of a physical system changes in time. It is as central to quantum mechanics as Newton's laws are to classical mechanics. In the standard interpretation of quantum mechanics, the q ...
J.E. Strong, Jr. 1/21/2012 How big is a Hydrogen Atom? It is very
... reference. Let’s look at how large a simple hydrogen atom is by comparing it to something more familiar. What is hydrogen (and why do we care)? Hydrogen is the simplest chemical element, with an atomic number of 1, meaning its nucleus consists of a single proton. In its normal state (a gas), a hydro ...
... reference. Let’s look at how large a simple hydrogen atom is by comparing it to something more familiar. What is hydrogen (and why do we care)? Hydrogen is the simplest chemical element, with an atomic number of 1, meaning its nucleus consists of a single proton. In its normal state (a gas), a hydro ...
Unit 2 Intro Worksheet - Coral Gables Senior High
... ____ 7. discrete bundle of electromagnetic energy ____ 8. energy needed to move an electron from one energy level to another ____ 9. number of wave cycles passing a point per unit of time ____ 10. distance between wave crests ____ 11. separation of light into different wavelengths ____ 12. frequenci ...
... ____ 7. discrete bundle of electromagnetic energy ____ 8. energy needed to move an electron from one energy level to another ____ 9. number of wave cycles passing a point per unit of time ____ 10. distance between wave crests ____ 11. separation of light into different wavelengths ____ 12. frequenci ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).









![Chapter7_1 - Department of Chemistry [FSU]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016128835_1-aea3c1aec04363d6cbf538e8faf80e45-300x300.png)











