* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
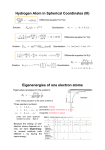
Download Spherical harmonics: • The quantum numbers n, l, m determine the
Path integral formulation wikipedia , lookup
Spin (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Coherent states wikipedia , lookup
Quantum machine learning wikipedia , lookup
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Copenhagen interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum key distribution wikipedia , lookup
Quantum group wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Many-worlds interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum teleportation wikipedia , lookup
Measurement in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Identical particles wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Probability amplitude wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Spherical harmonics: • The quantum numbers n, l, m determine the complete 3D behaviour of the wavefunction. The quantum numbers are the principle (n), orbital (l) and magnetic (m) numbers that are known from Chemistry. The l and m quantum numbers are related to angular momentum. s-type orbital l=0 p-type orbital l=1 d-type orbital l=2 f-type orbital l=3 Spherical harmonics – normal plots l=4 m=0 m=1 m=2 m=3 m=4 • The probability densities in r and 𝜃 have zeros for several values. These result in nodal surfaces where the probability of finding the electron vanishes. This is because bound particles are standing waves! • All eigenstates (except for the ground state) are degenerate in energy since the energy only depends on n. Now let’s investigate the spherical harmonics using polar plots. In these plots, the distance from origin to curve in direction 𝜃 is given by Yl,m(𝜃,𝜙). 3D dependence from rotating around z-axis (ie, through all 𝜙). Spherical harmonics – polar plots l=0, m=0 l=1, m=-1,0,1 l=2, m=-2,-1,0,1,2 l=3, m=-3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3 The Hydrogen atom wavefunction: Born’s rule: Probability of finding the particle within some volume: