Document
... All states with the same principle quantum number are said to form a shell The states with given values of n and ℓ are said to form a subshell ...
... All states with the same principle quantum number are said to form a shell The states with given values of n and ℓ are said to form a subshell ...
Modern Physics Guide
... Modern Physics Guide Relativity: What will all observers agree on? Speed of light What events take place (collisions, emission and absorption, and so forth) What events cause others. The mass of an object. What measurements change from one observer to another? Simultaneity of events separated in spa ...
... Modern Physics Guide Relativity: What will all observers agree on? Speed of light What events take place (collisions, emission and absorption, and so forth) What events cause others. The mass of an object. What measurements change from one observer to another? Simultaneity of events separated in spa ...
Chapter 6 review
... work for atoms larger than hydrogen. • Electrons are not behaving in a manner that agrees with the circular orbit model. ...
... work for atoms larger than hydrogen. • Electrons are not behaving in a manner that agrees with the circular orbit model. ...
Torres: Copenhagen Quantum Mechanics
... Probable positions of electrons are not exactly set Based on energy levels ...
... Probable positions of electrons are not exactly set Based on energy levels ...
CHM1045 - Michael Blaber
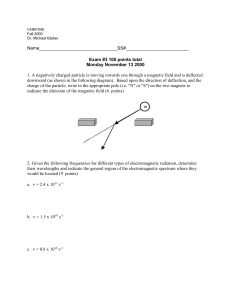
... * = c (the relationship between wavelength, frequency and speed of light for electromagnetic radiation) E = h * (the relationship between energy and frequency for electromagnetic radiation En = -RH / n2 or En = -B / n2 (the relationship between the energy of an electron in Bohr's model of the ...
... * = c (the relationship between wavelength, frequency and speed of light for electromagnetic radiation) E = h * (the relationship between energy and frequency for electromagnetic radiation En = -RH / n2 or En = -B / n2 (the relationship between the energy of an electron in Bohr's model of the ...
CHAPTER 7: The Hydrogen Atom
... And there is another type of uncertainty: we often simply don’t know which state an atom is in. For example, suppose we have a batch of, say, 100 atoms, which we excite with just one photon. Only one atom is excited, but which one? We might say that each atom has a 1% chance of being in an excited s ...
... And there is another type of uncertainty: we often simply don’t know which state an atom is in. For example, suppose we have a batch of, say, 100 atoms, which we excite with just one photon. Only one atom is excited, but which one? We might say that each atom has a 1% chance of being in an excited s ...
PHY215: Study Guide for Introductory Quantum Mechanics Explain 1. Cathode Ray tubes, Cathode rays, and the generation of X‐rays.
... 1. Cathode Ray tubes, Cathode rays, and the generation of X‐rays. 2. The photoelectric effect, Compton Scattering, Planck’s constant: explain how light behaves as though it is made of particles. 3. The de Broglie wavelength, the Davisson‐Germer experiment: explain how electrons (an ...
... 1. Cathode Ray tubes, Cathode rays, and the generation of X‐rays. 2. The photoelectric effect, Compton Scattering, Planck’s constant: explain how light behaves as though it is made of particles. 3. The de Broglie wavelength, the Davisson‐Germer experiment: explain how electrons (an ...
2·QUIZLET VOCABULARY: Quantum Numbers Study online at
... 4. Hunds rule: orbitals of equal energy are each occupied by one electron before any orbital is occupied by a second electron, and all electrons in singly occupied orbitals must have the same spin 5. Magnetic (orbital) quantum Number: ml Indicates orientation of orbital in space S- 1 orbital P- 3 or ...
... 4. Hunds rule: orbitals of equal energy are each occupied by one electron before any orbital is occupied by a second electron, and all electrons in singly occupied orbitals must have the same spin 5. Magnetic (orbital) quantum Number: ml Indicates orientation of orbital in space S- 1 orbital P- 3 or ...
ch 11 - THE QUANTUM DEFECT - probs
... 11.2 A spherically symmetric singly charged positive ion (the "ionic core") is situated at the origin of coordinates. An electron is assumed to be at a fixed distance z along the z-axis. This electron induces in the ion a dipole moment, the magnitude of which is determined by the ion's polarizabilit ...
... 11.2 A spherically symmetric singly charged positive ion (the "ionic core") is situated at the origin of coordinates. An electron is assumed to be at a fixed distance z along the z-axis. This electron induces in the ion a dipole moment, the magnitude of which is determined by the ion's polarizabilit ...
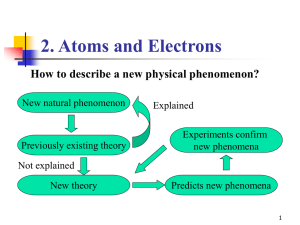
Development of the Model of the Atom
... around an atomic nucleus. Experiments demonstrated that electrons, like light waves, can be bent or diffracted (bending as it passes through a small opening). Also, some experiments showed that electron beams interfere with each other. ...
... around an atomic nucleus. Experiments demonstrated that electrons, like light waves, can be bent or diffracted (bending as it passes through a small opening). Also, some experiments showed that electron beams interfere with each other. ...
from last time:
... The big problem with most models was number 4 – how to account for discrete energy changes. We’re going to start with Bohr’s model because it was the first to really explain this. Sort of. ...
... The big problem with most models was number 4 – how to account for discrete energy changes. We’re going to start with Bohr’s model because it was the first to really explain this. Sort of. ...
Word Format
... These rules can be used to extrapolate QM results to classical physics, but were usually used to determine QM selection rules from classical physics. ...
... These rules can be used to extrapolate QM results to classical physics, but were usually used to determine QM selection rules from classical physics. ...
Chemistry Science Notebook
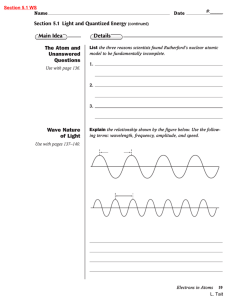
... List the three reasons scientists found Rutherford’s nuclear atomic model to be fundamentally incomplete. ...
... List the three reasons scientists found Rutherford’s nuclear atomic model to be fundamentally incomplete. ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).