Development of Quantum Mechanics Waves
... If light is a wave with particle properties, are electrons particles with wave properties? C. J. Davisson and L. H. Germier at Bell labs proved that electrons produce diffraction patterns and verified deBroglies hypothesis ...
... If light is a wave with particle properties, are electrons particles with wave properties? C. J. Davisson and L. H. Germier at Bell labs proved that electrons produce diffraction patterns and verified deBroglies hypothesis ...
NAME PERIOD ______ DATE Chapter 5 Sec. 2
... NAME _______________________________________________ ...
... NAME _______________________________________________ ...
28-2 Models of the Atom
... The next major advance in our understanding of the atom came from the Danish physicist, Niels Bohr, who incorporating ideas from Rutherford and quantum ideas. In Bohr’s model, electrons traveled in circular orbits around a central nucleus, similar to the way planets travel around the Sun. It is impo ...
... The next major advance in our understanding of the atom came from the Danish physicist, Niels Bohr, who incorporating ideas from Rutherford and quantum ideas. In Bohr’s model, electrons traveled in circular orbits around a central nucleus, similar to the way planets travel around the Sun. It is impo ...
File
... from the nucleus. • When an atom absorbs energy, the electron jumps to a level further from the nucleus • If it radiated energy, that means that the electron is falling to a level closer to the nucleus. ...
... from the nucleus. • When an atom absorbs energy, the electron jumps to a level further from the nucleus • If it radiated energy, that means that the electron is falling to a level closer to the nucleus. ...
Chapter 31 Atomic Physics
... **** The idea that all matter is composed of atoms is fundamental to our modern view of the world. It has given us a firm basis for understanding the properties of solid, liquids, and gases. This understanding has led to a host of useful devices, one of the most famous being the laser. The laser be ...
... **** The idea that all matter is composed of atoms is fundamental to our modern view of the world. It has given us a firm basis for understanding the properties of solid, liquids, and gases. This understanding has led to a host of useful devices, one of the most famous being the laser. The laser be ...
File
... known as quanta, Albert Einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. Einstein’s theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has characteristics of both a wave and a stream of particles. ...
... known as quanta, Albert Einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. Einstein’s theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has characteristics of both a wave and a stream of particles. ...
Matter Vocab Part 4
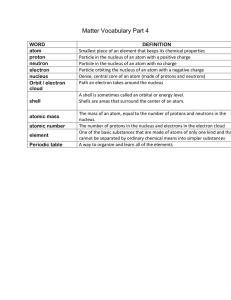
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
Atomic Structure and Atomic Spectra
... mechanical treatment also results in two other quantum numbers in addition to Bohr's principal quantum number n. That is, the energy for a hydrogen atom electron is determined by the principal quantum number, but for each n, there are also other quantum numbers required to fully describe the allowed ...
... mechanical treatment also results in two other quantum numbers in addition to Bohr's principal quantum number n. That is, the energy for a hydrogen atom electron is determined by the principal quantum number, but for each n, there are also other quantum numbers required to fully describe the allowed ...
Atomic Spectra II
... In a previous laboratory experiment on diffraction, you noticed that light from a mercury discharge tube was composed of only three colors, or three distinct wavelengths of light. This feature, that an element emits light of specific colors, is an enormously useful probe of how individual atoms of t ...
... In a previous laboratory experiment on diffraction, you noticed that light from a mercury discharge tube was composed of only three colors, or three distinct wavelengths of light. This feature, that an element emits light of specific colors, is an enormously useful probe of how individual atoms of t ...
Document
... • Quantum physics explains the energy levels of atoms with enormous accuracy. This is possible, since these levels have long lifetime (uncertainty relation for E, t). • Radiation from atoms and molecules enables the most accurate time and length measurements: Atomic clocks • Quantum physics explai ...
... • Quantum physics explains the energy levels of atoms with enormous accuracy. This is possible, since these levels have long lifetime (uncertainty relation for E, t). • Radiation from atoms and molecules enables the most accurate time and length measurements: Atomic clocks • Quantum physics explai ...
The Quantum Mechanical Picture of the Atom
... The allowed energy states of atoms and molecules can be described by sets of numbers called quantum numbers ...
... The allowed energy states of atoms and molecules can be described by sets of numbers called quantum numbers ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE NOTES n hcZ E ℜ
... The zero energy is when electron and nucleus are widely separated. 1/n2 relationship for E indicates that the energy levels converge at high (less negative) energies. Zero energy = ionisation. Electron Spin – 2 more Quantum Numbers are needed to define the state of an electron (spin). s = spin angul ...
... The zero energy is when electron and nucleus are widely separated. 1/n2 relationship for E indicates that the energy levels converge at high (less negative) energies. Zero energy = ionisation. Electron Spin – 2 more Quantum Numbers are needed to define the state of an electron (spin). s = spin angul ...
Chapter 13 – Electrons in Atoms
... Electron Arrangement in Atoms Physics and the Quantum Mechanical Model ...
... Electron Arrangement in Atoms Physics and the Quantum Mechanical Model ...
Atomic Theory Study Guide - Reading Community Schools
... 4. Describe the uses and limitations of the Bohr model, particularly as it related to the quantization of electron energies. 5. Use examples from the history of the development of atomic theory to explain how scientific theories are modified or replaced, and identify two or more barriers to acceptan ...
... 4. Describe the uses and limitations of the Bohr model, particularly as it related to the quantization of electron energies. 5. Use examples from the history of the development of atomic theory to explain how scientific theories are modified or replaced, and identify two or more barriers to acceptan ...
o Lecturer: Dr. Peter Gallagher Email:
... 1. Calculate the bind energy in eV of the Hydrogen atom using Eqn 3? o How does this compare with experiment? 2. Calculate the velocity of the electron in the ground state of Hydrogen. o How does this compare with the speed of light? o Is a non-relativistic model justified? 3. What is a Rydber ...
... 1. Calculate the bind energy in eV of the Hydrogen atom using Eqn 3? o How does this compare with experiment? 2. Calculate the velocity of the electron in the ground state of Hydrogen. o How does this compare with the speed of light? o Is a non-relativistic model justified? 3. What is a Rydber ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).