* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Many-worlds interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum fiction wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Quantum dot wikipedia , lookup
Orchestrated objective reduction wikipedia , lookup
Quantum computing wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Quantum machine learning wikipedia , lookup
Quantum key distribution wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Quantum group wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Quantum teleportation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
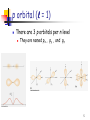
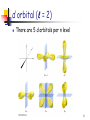
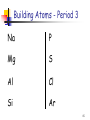
The Quantum Mechanical Picture of the Atom The allowed energy states of atoms and molecules can be described by sets of numbers called quantum numbers n m ms 1 Quantum Numbers n - the principal quantum number n = 1, 2, 3, 4, ...... “shells” - the angular momentum quantum number = 0, 1, 2, 3, … , n – 1 “subshells” = s, p, d, f, ...... m - the magnetic quantum number m = –, – + 1, … , – 1, ms - the spin quantum number ms = –½, +½ 2 Quantum Numbers and Orbitals n + Define the energy of the electron Defines the shape of the orbital Orbital The volume around the nucleus where the electron appears 90-95% of the time The Pauli principle No two electrons in an atom may have identical sets of four quantum numbers 3 s orbital ( = 0) There is only one s orbital per n level 4 p orbital ( = 1) There are 3 p orbitals per n level They are named px , py , and pz 5 d orbital ( = 2) There are 5 d orbitals per n level 6 f orbital ( = 3) There are 7 f orbitals per n level 7 Order of Orbital Energy 8 Building Atoms 1) Build the nucleus by adding the required # of protons and neutrons according to the atomic # and mass # of the atom 2) Fill energy levels (orbitals) with the required # of electrons starting from the lowest available energy level and following Pauli and Hund rules (this is called Aufbau principle) 9 Building Atoms - Period 1 n m ms H He 10 Building Atoms - Period 2 n m ms Li Be 11 Building Atoms - Period 2 n m ms B C 12 Hund’s Rule Electrons occupy all the orbitals of a given subshell (with the same ) singly before pairing begins. These unpaired electrons have parallel spins (the same sign of ms). n m ms C 13 Building Atoms - Period 2 N O F Ne 14 Building Atoms - Period 3 Na P Mg S Al Cl Si Ar 15 Building Atoms - Period 4 K Ca Sc – 4p or 3d ? 16