Chapter 4
... Development of a New Atomic Model • There were some problems with the Rutherford model…It did not answer: – Where the e- were located in the space outside the nucleus – Why the e- did not crash into the nucleus – Why atoms produce spectra (colors) at specific wavelengths when energy is added ...
... Development of a New Atomic Model • There were some problems with the Rutherford model…It did not answer: – Where the e- were located in the space outside the nucleus – Why the e- did not crash into the nucleus – Why atoms produce spectra (colors) at specific wavelengths when energy is added ...
Electrons in Atoms
... Apply the Rydberg equation to predict the positions of spectral lines for hydrogenic atoms. Define and classify atomic orbitals in terms of the quantum numbers (n, l , ml) and the nomenclature s, p, d, f etc Relate properties of atomic orbitals (e.g. energy, shape, directional) to the quantum ...
... Apply the Rydberg equation to predict the positions of spectral lines for hydrogenic atoms. Define and classify atomic orbitals in terms of the quantum numbers (n, l , ml) and the nomenclature s, p, d, f etc Relate properties of atomic orbitals (e.g. energy, shape, directional) to the quantum ...
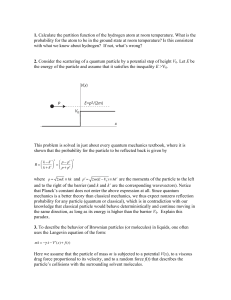
A Helium atom has a nuclear charge of Ze, where Z=2. One of the
... A Helium atom has a nuclear charge of Ze, where Z=2. One of the electrons is removed leaving an atom that resembles a Hydrogen atom but with twice the nuclear charge. What are the energy levels in this atom? a) En= - mZe4 / ( e028n2h2) b) En= - mZ2e4 / ( e028n2h2) c) En= - mZ4e4 / ( e028n2h2) d) En= ...
... A Helium atom has a nuclear charge of Ze, where Z=2. One of the electrons is removed leaving an atom that resembles a Hydrogen atom but with twice the nuclear charge. What are the energy levels in this atom? a) En= - mZe4 / ( e028n2h2) b) En= - mZ2e4 / ( e028n2h2) c) En= - mZ4e4 / ( e028n2h2) d) En= ...
Teaching the Atomic Theory: A Visual
... 1. Spectral lines are produced by atoms one at a time 2. A single electron is responsible for each line 3. The Rutherford nuclear atom is the correct model 4. The quantum laws apply to jumps between different states characterized by discrete values of angular momentum and energy ...
... 1. Spectral lines are produced by atoms one at a time 2. A single electron is responsible for each line 3. The Rutherford nuclear atom is the correct model 4. The quantum laws apply to jumps between different states characterized by discrete values of angular momentum and energy ...
De Broglie waves
... of nucleus. The electron is free to move in three dimensions. • Since the electrical potential is a function of r rather than of x,y,z, Schrődinger’s equation is expressed in terms of spherical polar coordinates r,θ,φ. – r: the length of radius vector from origin O to point P; – θ: zenith angle, ang ...
... of nucleus. The electron is free to move in three dimensions. • Since the electrical potential is a function of r rather than of x,y,z, Schrődinger’s equation is expressed in terms of spherical polar coordinates r,θ,φ. – r: the length of radius vector from origin O to point P; – θ: zenith angle, ang ...
Dr.Eman Zakaria Hegazy Quantum Mechanics and Statistical
... - The Schrödinger equation cannot be solved exactly for this system because of the term involving r12 . - Equation (1) can be written in the form ...
... - The Schrödinger equation cannot be solved exactly for this system because of the term involving r12 . - Equation (1) can be written in the form ...
quantum mechanical model of the atom
... hydrogen’s spectral lines, but failed to explain any other element’s lines. • For this and other reasons, the Bohr model was replaced with a more sophisticated model called the quantum-mechanical or wavemechanical model. ...
... hydrogen’s spectral lines, but failed to explain any other element’s lines. • For this and other reasons, the Bohr model was replaced with a more sophisticated model called the quantum-mechanical or wavemechanical model. ...
Chapter 4 Test Question Topics
... 1- Know the definitions of the ground state and the excited states of an atom. 2- What must occur for an atom to move from the ground to the excited state or from the excited to the ground state? 3- Know the definitions of an electron cloud and an atomic nucleus. 4- What determines the size and shap ...
... 1- Know the definitions of the ground state and the excited states of an atom. 2- What must occur for an atom to move from the ground to the excited state or from the excited to the ground state? 3- Know the definitions of an electron cloud and an atomic nucleus. 4- What determines the size and shap ...
DOC - 嘉義大學
... 1. The total energy of a neutron is five times its rest energy. Answer the following questions: (20%) (a) Find the neutron’s rest energy in electron volts. (Hint: mn = 1.681027 kg) (b) Determine the kinetic energy of the neutron in electron volts. (c) What speed (in units of c) is the neutron movi ...
... 1. The total energy of a neutron is five times its rest energy. Answer the following questions: (20%) (a) Find the neutron’s rest energy in electron volts. (Hint: mn = 1.681027 kg) (b) Determine the kinetic energy of the neutron in electron volts. (c) What speed (in units of c) is the neutron movi ...
FINAL REVIEW 1st SEMESTER 2014-2015
... electron configurations (to include orbitals, quantum numbers, order of filling, relation to position of element in periodic table to its configuration) relate atomic number and atomic mass to position in the periodic table, isotopes, numbers of subatomic particles (protons, neutrons, electrons) com ...
... electron configurations (to include orbitals, quantum numbers, order of filling, relation to position of element in periodic table to its configuration) relate atomic number and atomic mass to position in the periodic table, isotopes, numbers of subatomic particles (protons, neutrons, electrons) com ...
Lecture 12
... • How to initialize the qubits - how to cool and trap atoms? • How to manipulate atomic states (i.e. qubits)? • How to perform two-qubits gates - which physical processes can we use? • How to read out the result? • What are the error sources? • How large are the errors? • How can we minimize errors? ...
... • How to initialize the qubits - how to cool and trap atoms? • How to manipulate atomic states (i.e. qubits)? • How to perform two-qubits gates - which physical processes can we use? • How to read out the result? • What are the error sources? • How large are the errors? • How can we minimize errors? ...
Ideas of Modern Physics
... 4. A quantum particle in a box is in the lowest energy (ground) state. If the size of the box is decreased, momentum uncertainty of the particle? a. becomes larger b. becomes smaller c. is unchanged d. becomes negative e. cannot be measured 5. A photon is found to have 100 eV of energy. Which answer ...
... 4. A quantum particle in a box is in the lowest energy (ground) state. If the size of the box is decreased, momentum uncertainty of the particle? a. becomes larger b. becomes smaller c. is unchanged d. becomes negative e. cannot be measured 5. A photon is found to have 100 eV of energy. Which answer ...
3.4 Quantum Numbers
... The Magnetic Quantum Number (ml) • Gives the exact orbital • Describes the orientation of an atomic orbital in space (how it lines up on the xyz plane) • ml can have integer values from –l to +l including 0 • The Zeemen effect showed that if a gas discharge tube was placed near a strong magnet some ...
... The Magnetic Quantum Number (ml) • Gives the exact orbital • Describes the orientation of an atomic orbital in space (how it lines up on the xyz plane) • ml can have integer values from –l to +l including 0 • The Zeemen effect showed that if a gas discharge tube was placed near a strong magnet some ...
Physics 228, Lecture 11 Monday, February 28, 2005 Bohr Model
... The same issue came up with spectial relativity, where we “threw out” the fundamental understanding of how coordinate systems were related, challenging Newtonian mechanics. But in that case it was pretty clear what was happening — the relativistic expressions, for example for momentum, reduced to th ...
... The same issue came up with spectial relativity, where we “threw out” the fundamental understanding of how coordinate systems were related, challenging Newtonian mechanics. But in that case it was pretty clear what was happening — the relativistic expressions, for example for momentum, reduced to th ...
(Quantum Mechanics) 1. State basic concepts (or postulates) of
... Estimate the ground state energy using the uncertainty principle. 4. One of the uncertainty relations is expressed as = , where ∆ is the uncertainty in the position and ∆ , that in the momentum . (a) Using the uncertainty relation, estimate the ground state energy and radius of the hydr ...
... Estimate the ground state energy using the uncertainty principle. 4. One of the uncertainty relations is expressed as = , where ∆ is the uncertainty in the position and ∆ , that in the momentum . (a) Using the uncertainty relation, estimate the ground state energy and radius of the hydr ...
CHEM 532 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Chemistry) Fall 2013
... approximation, Møller-Plesset perturbation theory, configuration interaction, the Aufbau Principle, spin eigenfunctions for many electron wave functions, angular momentum eigenfunctions and term symbols, Hund's Rules X. Molecular wavefunctions the molecular Schrödinger equation, the Born-Oppenheimer ...
... approximation, Møller-Plesset perturbation theory, configuration interaction, the Aufbau Principle, spin eigenfunctions for many electron wave functions, angular momentum eigenfunctions and term symbols, Hund's Rules X. Molecular wavefunctions the molecular Schrödinger equation, the Born-Oppenheimer ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).