Topic 7_1_Ext C__The Bohr theory of the hydrogen atom
... accelerating charges. Since the hydrogen atom only radiates when its electron "drops" from one excited state to a less energetic state, Bohr postulated that "the hydrogen electron does NOT radiate energy when it is in one of its bound states (allowed by n). It only does so when "dropping" from a hig ...
... accelerating charges. Since the hydrogen atom only radiates when its electron "drops" from one excited state to a less energetic state, Bohr postulated that "the hydrogen electron does NOT radiate energy when it is in one of its bound states (allowed by n). It only does so when "dropping" from a hig ...
CHAPTER 7: The Hydrogen Atom
... The atom of modern physics can be symbolized only through a partial differential equation in an abstract space of many dimensions. All its qualities are inferential; no material properties can be directly attributed to it. An understanding of the atomic world in that primary sensuous fashion…is impo ...
... The atom of modern physics can be symbolized only through a partial differential equation in an abstract space of many dimensions. All its qualities are inferential; no material properties can be directly attributed to it. An understanding of the atomic world in that primary sensuous fashion…is impo ...
atoms
... In the following pictures, there is a target hidden by a cloud. To figure out the shape of the target, we shot some beams into the cloud and recorded where the beams came out. Can you figure out the shape of the target? ...
... In the following pictures, there is a target hidden by a cloud. To figure out the shape of the target, we shot some beams into the cloud and recorded where the beams came out. Can you figure out the shape of the target? ...
Some Quantum Considerations II
... Which of the following statements is false? a. Longer wavelength radiation carries higher energies. b. Light can be considered to be made up of particles called photons. c. All material objects have some wave characteristics. d. Electrons can be viewed as standing waves in an atom. e. Bohr’s model o ...
... Which of the following statements is false? a. Longer wavelength radiation carries higher energies. b. Light can be considered to be made up of particles called photons. c. All material objects have some wave characteristics. d. Electrons can be viewed as standing waves in an atom. e. Bohr’s model o ...
Quantum Mechanical Model
... • Heisenberg showed it is impossible to take any measurement of an object without disturbing it. • The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is fundamentally impossible to know precisely both the velocity and position of a particle at the same time. • The only quantity that can be known is ...
... • Heisenberg showed it is impossible to take any measurement of an object without disturbing it. • The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is fundamentally impossible to know precisely both the velocity and position of a particle at the same time. • The only quantity that can be known is ...
Quantum review
... Assigning the Numbers The three quantum numbers (n, l, and m) are integers. The principal quantum number (n) cannot be zero. n must be 1, 2, 3, etc. The angular momentum quantum number (l) can be any integer between 0 and n - 1. Ex. For n = 3, l can be either 0, 1, or 2. The magnetic quantu ...
... Assigning the Numbers The three quantum numbers (n, l, and m) are integers. The principal quantum number (n) cannot be zero. n must be 1, 2, 3, etc. The angular momentum quantum number (l) can be any integer between 0 and n - 1. Ex. For n = 3, l can be either 0, 1, or 2. The magnetic quantu ...
Text Questions from Corwin - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
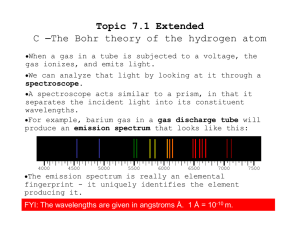
... 37. An __________ spectrum is emitted when a gas is excited by an electrical ________. The gas, which is sealed in a ____________ tube, emits light that can be separated into a ________ of narrow _____ when passed through a ________. 38. Bohr realized that the emission spectrum of hydrogen was exper ...
... 37. An __________ spectrum is emitted when a gas is excited by an electrical ________. The gas, which is sealed in a ____________ tube, emits light that can be separated into a ________ of narrow _____ when passed through a ________. 38. Bohr realized that the emission spectrum of hydrogen was exper ...
Chapter 5 Worksheet 1
... The double – slit experiment. 5. What equation was able to calculate an electron behaving as both a particle and a wave? The Schrödinger equation (also known as the wave – mechanical equation). 6. Describe the quantum mechanical (electron cloud) model of the atom. The electron cloud is the three dim ...
... The double – slit experiment. 5. What equation was able to calculate an electron behaving as both a particle and a wave? The Schrödinger equation (also known as the wave – mechanical equation). 6. Describe the quantum mechanical (electron cloud) model of the atom. The electron cloud is the three dim ...
L20
... This means that the energy of an electron in any excited orbital depends purely on the energy level in which it resides. From your knowledge of chemistry, you will know that each energy level can contain more than one electron. These electrons must therefore have the same energy. We say that there e ...
... This means that the energy of an electron in any excited orbital depends purely on the energy level in which it resides. From your knowledge of chemistry, you will know that each energy level can contain more than one electron. These electrons must therefore have the same energy. We say that there e ...
Atomic Theory - WaylandHighSchoolChemistry
... • Planetary model • Proposed electrons have a set amount of energy putting them in different energy levels, or orbits around the nucleus. • Electrons can change energy levels; higher energy levels are further from the nucleus. electron ...
... • Planetary model • Proposed electrons have a set amount of energy putting them in different energy levels, or orbits around the nucleus. • Electrons can change energy levels; higher energy levels are further from the nucleus. electron ...
Physics IV - Exam - Winter 2007/08 Please note:
... Work out the probability, immediately after this change takes place, of measuring the system in (i) its new ground state and (ii) its new first excited state. ...
... Work out the probability, immediately after this change takes place, of measuring the system in (i) its new ground state and (ii) its new first excited state. ...
Document
... which is close to, but not exactly equal to, the electron mass. The origin of our coordinate system is now at the center of mass between the electron and proton, which of course will stay quite close to the proton. The key to solving the hydrogen atom is to take advantage of the spherical symmetry, ...
... which is close to, but not exactly equal to, the electron mass. The origin of our coordinate system is now at the center of mass between the electron and proton, which of course will stay quite close to the proton. The key to solving the hydrogen atom is to take advantage of the spherical symmetry, ...
Chapter 7: Electrons in Atoms Electromagnetic Radiation
... But, for circular orbits, electrons would possess angular momentum (acceleration) and therefore radiate energy! So, using Planck’s quantum hypothesis, 1) Electrons move in fixed orbits around the nucleus 2) Fixed orbits (stationary states) mean properties of individual electrons will have unique v ...
... But, for circular orbits, electrons would possess angular momentum (acceleration) and therefore radiate energy! So, using Planck’s quantum hypothesis, 1) Electrons move in fixed orbits around the nucleus 2) Fixed orbits (stationary states) mean properties of individual electrons will have unique v ...
Problem set 7
... 2. Is a linear combination of density matrices an allowed density matrix in general? Why? 3. An SG apparatus with inhomogeneous magnetic field in the z direction is fed an unpolarized beam of atoms with l = 1. Find the density matrix (for angular momentum degrees of freedom) for an atom in a beam th ...
... 2. Is a linear combination of density matrices an allowed density matrix in general? Why? 3. An SG apparatus with inhomogeneous magnetic field in the z direction is fed an unpolarized beam of atoms with l = 1. Find the density matrix (for angular momentum degrees of freedom) for an atom in a beam th ...
Chapter 2 (Lecture 2-3) Old Quantum Theory The Postulates of Bohr
... where pr is the radial momentum canonically conjugate to the coordinate q which is the radial position and T is one full orbital period. The Bohr-Sommerfeld model was fundamentally inconsistent and led to many paradoxes. The Sommerfeld quantization can be performed in different canonical coordinates ...
... where pr is the radial momentum canonically conjugate to the coordinate q which is the radial position and T is one full orbital period. The Bohr-Sommerfeld model was fundamentally inconsistent and led to many paradoxes. The Sommerfeld quantization can be performed in different canonical coordinates ...
Solid State Electronic Devices
... Finding the wave functions for the hydrogen atom requires a solution of the Schrodinger equation in three dimensions for a coulombic potential field. Since the problem is spherically symmetric, the spherical coordinate system is used in the calculation. The term V (x, y, z) in Eq. (2-24) must be rep ...
... Finding the wave functions for the hydrogen atom requires a solution of the Schrodinger equation in three dimensions for a coulombic potential field. Since the problem is spherically symmetric, the spherical coordinate system is used in the calculation. The term V (x, y, z) in Eq. (2-24) must be rep ...
Chapter 28 Atoms
... Schroedinger used de Brogli’s wave model to create a quantum theory of atom based on waves. The theory does not provide a simple planetary picture of an atom as in the Bohr model. In particular, the radius of the electron orbit is not like the radius of the orbit of a planet about the sun. In wave p ...
... Schroedinger used de Brogli’s wave model to create a quantum theory of atom based on waves. The theory does not provide a simple planetary picture of an atom as in the Bohr model. In particular, the radius of the electron orbit is not like the radius of the orbit of a planet about the sun. In wave p ...
The Second Law of Thermodynamics
... The physical and chemical properties of elements is determined by the atomic structure. The atomic structure is, in turn, determined by the electrons and which shells, subshells and orbitals they reside in. The rules of placing electrons within shells is known as the Aufbau principle. As protons are ...
... The physical and chemical properties of elements is determined by the atomic structure. The atomic structure is, in turn, determined by the electrons and which shells, subshells and orbitals they reside in. The rules of placing electrons within shells is known as the Aufbau principle. As protons are ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034 M.Sc. DEGREE EXAMINATION - PHYSICS SECOND SEMESTER – APRIL 2008 PH 2808 - QUANTUM MECHANICS Date : 22/04/2008 Time : 1:00 - 4:00 ...
... LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034 M.Sc. DEGREE EXAMINATION - PHYSICS SECOND SEMESTER – APRIL 2008 PH 2808 - QUANTUM MECHANICS Date : 22/04/2008 Time : 1:00 - 4:00 ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).