5.1 Notes
... atom is mathematical...all about probability There is no exact path of e around nucleus ...
... atom is mathematical...all about probability There is no exact path of e around nucleus ...
7.4 The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom
... (x, y, z) in space is proportional to the square of the wave function, Ψ2, in this point • Electron density diagrams – three-dimensional plots of the probability to find the electron (Ψ2) around the nucleus → electron clouds • Contour diagrams – surround the densest regions of the electron cloud – u ...
... (x, y, z) in space is proportional to the square of the wave function, Ψ2, in this point • Electron density diagrams – three-dimensional plots of the probability to find the electron (Ψ2) around the nucleus → electron clouds • Contour diagrams – surround the densest regions of the electron cloud – u ...
The Atom
... Dalton’s atoms. Rutherford’s model for the atom was appealing. It was simple. It was based on the well known electric force. It was consistent with all known experimental evidence. It had one flaw however that led to its demise but opened up a grand new era in physics. We know from Maxwell’s equatio ...
... Dalton’s atoms. Rutherford’s model for the atom was appealing. It was simple. It was based on the well known electric force. It was consistent with all known experimental evidence. It had one flaw however that led to its demise but opened up a grand new era in physics. We know from Maxwell’s equatio ...
Lecture 19, Hydrogen Atom
... orbitals available on the web (http://www.falstad.com/qmatom/). This viewer allows you to plot orbitals for various values of n,l,m, and rotate, zoom, change colors…. Feel free to visit this site and toy around with some orbitals The one thing that falls out from this analysis is that the p orbitals ...
... orbitals available on the web (http://www.falstad.com/qmatom/). This viewer allows you to plot orbitals for various values of n,l,m, and rotate, zoom, change colors…. Feel free to visit this site and toy around with some orbitals The one thing that falls out from this analysis is that the p orbitals ...
Discovery of the Electron, Models & Theories
... Heisenberg also went off of Bohr’s model and elaborated more into quantum mechanics to explain the wave motion of electrons instead of a circular orbit ...
... Heisenberg also went off of Bohr’s model and elaborated more into quantum mechanics to explain the wave motion of electrons instead of a circular orbit ...
Chapter 4
... e- may have a wave-particle nature Would explain why e- only had certain orbits ...
... e- may have a wave-particle nature Would explain why e- only had certain orbits ...
Document
... The meaning of wave function:it’s related to the probability of finding the particle in various regions Character: single value, consecutive limited, be one in whole space ...
... The meaning of wave function:it’s related to the probability of finding the particle in various regions Character: single value, consecutive limited, be one in whole space ...
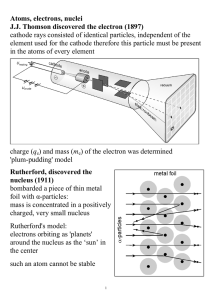
Atoms, electrons, nuclei J.J. Thomson discovered the electron (1897
... Davisson and Germer (1927) used electron beams to induce diffraction through a thin metal foil: interference interference phenomena have been shown with various other particles: duality is a general characteristic of matter Bohr's model (incorrect, but useful) electrons in an atom can only occupy ce ...
... Davisson and Germer (1927) used electron beams to induce diffraction through a thin metal foil: interference interference phenomena have been shown with various other particles: duality is a general characteristic of matter Bohr's model (incorrect, but useful) electrons in an atom can only occupy ce ...
Atomic Theory
... weight, and all atoms of different elements have different weights* 4. Atoms in reactions combine in simple, wholenumber ratios (Law of Definite Proportions) 5. Sometimes atoms combine in more than one ...
... weight, and all atoms of different elements have different weights* 4. Atoms in reactions combine in simple, wholenumber ratios (Law of Definite Proportions) 5. Sometimes atoms combine in more than one ...
Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding
... Azimuthal or orbital or angular or subsidary quantum number: It denotes the sub level to which an electron belongs and also tells about its shape. It is denoted by 'l'. The permitted values of 'l' are 0, 1, 2, etc., upto n-1. 'l' can have zero value unlike 'n'. The maximum value of 'l' is equal to n ...
... Azimuthal or orbital or angular or subsidary quantum number: It denotes the sub level to which an electron belongs and also tells about its shape. It is denoted by 'l'. The permitted values of 'l' are 0, 1, 2, etc., upto n-1. 'l' can have zero value unlike 'n'. The maximum value of 'l' is equal to n ...
l - Gordon State College
... What is the energy of one photon from a yellow light whose wavelength is 589 nm? 5.09 x 1014 Hz ...
... What is the energy of one photon from a yellow light whose wavelength is 589 nm? 5.09 x 1014 Hz ...
Atomic Orbitals and quantum numbers
... •Therefore, on any given energy level, there can be up to 1s orbital, 3p orbitals, 5d orbitals, and 7f orbitals. ...
... •Therefore, on any given energy level, there can be up to 1s orbital, 3p orbitals, 5d orbitals, and 7f orbitals. ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).