* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NAME: AP Biology/ Ms. Gaynor (Unit #10: Animal Physiology
Survey
Document related concepts
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Patch clamp wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Threshold potential wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
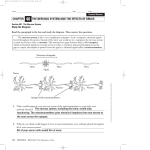
NAME: _______________________________________________ AP Biology/ Ms. Gaynor (Unit #10: Animal Physiology) CHAPTER 48: Nervous System PART 6 1. Draw and label the parts of a neuron including: cell body, dendrites, nucleus, axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cells, and Nodes of Ranvier. Then add arrows to your drawing to show the direction of impulse. 2. Fill in the table below: Type of Neuron Description Sensory Neuron Motor Neuron Interneuron 3. What is polarization? 4. When a cell is POLARIZED, how are ions (cations and anions) distributed in a nerve cell? 5. When a cell is DEPOLARIZED, how are ions (cations and anions) distributed in a nerve cell? 6. What does membrane potential mean? 7. What does resting potential mean? 8. Is an unstimulated nerve cell polarized or depolarized? __________________________________ 9. How is polarization maintained across a neuron’s membrane? 10. Fill in the table below: Steps in How a Nerve Impulse Travels Description #1: #2: #3: 11. Why does a nerve impulse only travel in one direction? 12. How does a nerve reset itself after an impulse? 13. Label the diagram below demonstrating the conduction of the action potential. 14. Label the graph below: 15. What is the refractory period? 16. Why is the myelin sheath important in conducting nerve impulses? 17. What is a synapse? 18. What is the function of neurotransmitters? 19. Give 3 examples of neurotransmitters, a. b. c. 20. Fill in the table below: Type of Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Description 21. Fill in the table below: Part of Motor Nervous System Description Somatic Nervous System Automatic Nervous System 22. Draw a outline of a brain and label the following parts: forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain, cerecellum, cerebum, pons, and Medulla oblongata. 23. Fill in the table below: Part of Brain Pons/Medulla Oblongata Midbrain 24. What is a reflex arc? Function