* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HP Authorized Customer
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
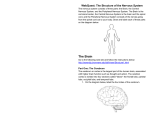
PSY 340 University of Phoenix Material Brain Structures as well as Functions Worksheet Two columns are given below: Brain Structure along with Function(s). Items in the column, “Brain Structure” will explain an area of the brain, whereas items in the column titled “Function(s)” will explain skill, the general behavior, and/or activity of the related brain construction. Fill in the blank for each statement below, either by listing the brain construction responsible for the function explained, or by providing the common function (skill, behavior, and/or activity) of the related brain construction. Brain Structure Meninges Function(s) The three films within the skull that encloses and defends your brain. The meninges are made of the "Pia Mater", the "Arachnoid", and the "Dura Mater". Defensive bone surrounding the central nervous CNS – Skull and Spinal system. Cord Concave areas in the brain crammed with cerebral Ventricles spinal fluid (CSF). The visual dealing out hub of the mammalian brain Occipital Lobe containing nearly the entire anatomical visual cortex area. The lobe involved in orderliness, inhibition, as well Frontal Lobe as planning control. Temporal Lobe Parietal Lobe Lymbic System The lobe involved in reminiscence, hearing, as well as language understanding. This lobe works to combine sensory information to different parts of the body, for object manipulation, calculations, as well as for visuospatial processing. A “system” (also identified as the piriform lobe or 5th lobe) engaged in intricate sentiment conducts. Spinal Cord It controls diffusions of neural inputs between the brain and the outside edge. Optic Chiasm They let the way of information commencing the optic nerves. PSY 340 Cerebral Arteries Corpus Callosum Cranial Nerves Hippocampus Supplies the brain with nourishment (food) and oxygen. The main white substance area of dendrites as well as axons linking both hemispheres of the brain. It adds information from the two dissimilar halves of the cerebral cortex, main sensory as well as motor information. These 12 formations send and receive motor and sensory signs between the brain and body. Involved in damaged by Alzheimer’s disease, spatial memory, short term memory, and learning. Treats sensory information and transmits it to the cerebellum where it is treated more. It connects the nervous system with the endocrine system through the pituitary gland. It is Hypothalamus accountable for certain metabolic treatments as well as other functions pertaining to the Autonomic Nervous System. “System” separated into two major parts: the autonomic nervous system and somatic nervous Autonomic System system. Controls essential functions such as blood Medulla Oblongata pressure, breathing, and heart rate. The specific olfactory receptor neurons related to the olfactory nerve are situated in the olfactory mucosa of the nasal hollow space. Whilst you inhale air molecules connect to the olfactory Olfactory nerve (Cranial mucosa and inspire the olfactory sensors of Nerve I) cranial nerve I as well as electrical activity is transuded to olfactory bulb. Olfactory bulb cells convey electrical action to other components of the central nervous system through the olfactory region. Latin for “little brain” this arrangement is involved in movement, balance, and posture. Cerebellum Thalamus Medulla Anterior Hypothalamus and Posterior Hypothalamus Engages exchanges Accountable for sustaining crucial body functions, for instance heart rate and inhalation. Involved in imaginings and sleep. PSY 340 between the Cortex and the Thalamus. Cerebrospinal Fluid Cerebral cortex Neurons Dendrite Axon Neurotransmitters Soma Terminal Liquid which provides cushion, and cheerfulness to the brain, feeds the brain, emits waste. It is accountable for the treatments of memory, thought, and perception and serves like the seat of problem solving, language, social capabilities, and advanced motor function. Cells of the nervous system that transmit messages via electrochemical signs. It is a slim, normally branched projection of a neuron or nerve cell, which steers the electrical stimulation obtained from new cells to as well as from the soma, or cell body, of the neuron from which it throws. It steers electrical impulses farther away from the neuron's cell body. Chemical messenger liberated from the neuron that are engaged in all kinds of activity/behavior. It is the cell body of the neuron. It helps to control related organelles and the nucleus. They liberate transmitters to convey information to the subsequent neuron. They create the transmitters (excluding peptide transmitters) too, and receive the liberated transmitters back up after liberating them.