* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Brain: Your Crowning Glory
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Spinal cord wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
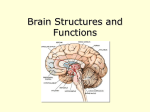
341770_ch_02_058 58 5/28/02 8:35 AM Page 58 mac117 mac117:1252_AS: Chapter 2 Biological Foundations of Behavior when a gust of wind sent particles of debris hurtling toward your eyeballs. By saving the many milliseconds it would take to send a message to your brain, have it interpreted, and have a command sent back along the spinal highway to motor neurons, spinal reflexes can spell the difference between a minor injury and a serious one. The Brain: Your Crowning Glory Concept 2.16 The brain is divided into three major parts: the hindbrain, the midbrain, and the forebrain. We begin our tour of the brain at the lowest level, the hindbrain — the part of the brain where the spinal cord enters the skull and widens. We then work our way upward, first to the midbrain, which lies above the hindbrain, and then to the forebrain, which lies in the highest part of the brain. Concept Chart 2.3 shows these major brain structures. The Hindbrain The lowest part of the brain, the hindbrain, is also the oldest part in evolutionary terms. The hindbrain includes the medulla, pons, and cerebellum. These structures control such basic life-support functions as breathing and heart rate. The medulla and pons contain sensory neurons that transmit information from the spinal cord to the forebrain. The medulla is the section of the hindbrain that lies closest to the spinal cord. It forms the marrow, or core, of the brainstem, CONCEPT CHART 2.3 Major Structures of the Human Brain Forebrain Cerebral Cortex Higher mental functions including thinking, language, learning, memory, emotions, and control of voluntary movement Hindbrain Pons Conveying sensory information from the spinal cord to the forebrain; regulation of states of wakefulness and sleep Corpus Callosum Bundle of nerve fibers that connect the two cerebral hemispheres Thalamus Relay station for sorting and integrating sensory input; regulation of sleep-wake cycles Limbic System Emotional processing, motivated behavior, and learning and memory functioning; consists of amygdala, hippocampus, parts of the hypothalamus and thalamus, and nearby structures Basal Ganglia Regulation of movement and coordination Cerebellum Regulation of balance and coordination Midbrain Reticular Formation Regulation of attentional processes and states of alertness and arousal Spinal cord Medulla Conveying sensory information from the spinal cord to the forebrain; control of basic bodily processes including heart rate and breathing and certain reflexes